When developing a Component Service (i.e., Custom Component or Entity Event Handler) using the bots-node-sdk (https://github.com/oracle/bots-node-sdk), you will most likely find yourself wanting to do some unit testing and debugging before pushing to ODA. In the GitHub repository, you will see a section on testing that leverages Jasmine (https://jasmine.github.io/). However, if you are old-school and a visual person like myself, having the ability to run a test locally with logging statements goes a long way. This blog post will focus on the testing section of bots-node-sdk but use plain-ole-javascript for the unit tester instead of Jasmine assertions.
Anatomy of the Testing Script
The tester script that we will be looking at contains the following sections:
- Pull in the bots-node-sdk testing module and the custom component we are testing
- Create a MockRequest for the custom component
- Setup the JSON parameters for the MockRequest function
- Create the MockRequest using the JSON parameters
- Create a component context from the MockRequest object
- Set the various loggers in the component context
- Invoke the custom component and review the results
The require(...) Function
For our simple tester, we will have the following two lines to get the appropriate module/code into our script:
const Testing = require('@oracle/bots-node-sdk/testing');
const Component = require('../components/cc_translate2pirate.js');
These two constants will provide access to the necessary testing objects and the custom component.
The MockRequest
Setting up the MockRequest is an essential part of the unit tester code. It is here that we define all the pieces of data that the custom component will need. The MockRequest function takes four parameters: messagePayload, properties, variables, and type. Of these four parameters, you will most likely only need properties and variables. However, in our example, we specify all four of them in the first MockRequest so we can see how they surface in the component context:
// Example use for ODA variables
// system.config.PIRATEURL - Custom Parameter defined in ODA skill Settings > Configuration
// exampleNumber - Basic ODA variable defined in the YAML under variables:
let odaVariables = {
'system.config.PIRATEURL': {
'type': 'STRING',
'entity': false,
'value': 'https://api.funtranslations.com/translate/pirate.json?text={PHRASE}'
},
'exampleNumber': {
'type': 'NUMBER',
'entity': false,
'value': 8
}
};
// function MockRequest(messagePayload = {}, properties = {}, variables = {}, type = 'test')
let getPirateTranslation = Testing.MockRequest(
// messagePayload
{
'docsDetails': 'Can take a string payload, an object payload or a MessageModel payload. A string or object payload will be parsed into a MessageModel payload. If the MessageModel payload has a valid common message format, then reply will use it as messagePayload, else it will use the payload to create a rawConversationMessage (see MessageModel) as messagePayload.'
},
// properties
{
'phrase': 'Hey there! Where do you think you are going?'
},
// variables
odaVariables,
// type ... channel type and if not specified it defaults to 'test'
'websdk'
);
let getPirateTranslation2 = Testing.MockRequest({}, {
'phrase': 'Hello, this is a different translator than the default one!',
'pirateURL': 'https://api.fungenerators.com/pirate/translate?text={PHRASE}'
},
odaVariables);
Notice that the second MockRequest only provides the properties and variables.
Invoking the Custom Component
At this point, we only have a few housekeeping items before we can invoke the custom component. The first item we need is the context object that we pass in the custom component invoke method. To get the context, we will use the Testing.MockConversation.fromRequest(...) function:
const mockContext = Testing.MockConversation.fromRequest(mockRequest);
The context is the primary object used for reading and changing variables and sending back results to ODA. It also provides access to things like logging, which is what we will set up next. It’s important to understand that various loggers are available for debug, error, fatal, info, trace, and warn levels/scenarios. For our tester, we will use the same logger (i.e., the console):
// Setup the Logging Levels // Comment/Uncomment the various logger levels to control the amount of logging details to the console // NOTE: The debug logger will produce various SDK log messages var logger = mockContext.logger(); logger.debug = console.log; logger.error = console.log; logger.fatal = console.log; logger.info = console.log; logger.trace = console.log; logger.warn = console.log;
We are now ready to call the custom component invoke function:
await Component.invoke(mockContext);
Once the invoke method returns, we can access things in the context that the custom component updated or set. In our example, we print out the entire context so we can see the big picture:
logger.info(JSON.stringify(mockContext, null, 2));
The tester script now can be run via the command-line using Node.js (i.e., the node command), If you need to debug, you can set breakpoints in your code and run the above command in a JavaScript Debug Terminal window. Here is the output in the terminal window for our example:
$ node unit-testers/cc_translate2pirate_tester.js
invoke.context ...
{
"_request": {
"botId": "mockbot",
"platformVersion": "1.1",
"state": "someState",
"context": {
"variables": {
"system.config.PIRATEURL": {
"type": "STRING",
"entity": false,
"value": "https://api.funtranslations.com/translate/pirate.json?text={PHRASE}"
},
"exampleNumber": {
"type": "NUMBER",
"entity": false,
"value": 8
}
}
},
"properties": {
"phrase": "Hey there! Where do you think you are going?"
},
"message": {
"payload": {},
"messagePayload": {
"docsDetails": "Can take a string payload, an object payload or a MessageModel payload. A string or object payload will be parsed into a MessageModel payload. If the MessageModel payload has a valid common message format, then reply will use it as messagePayload, else it will use the payload to create a rawConversationMessage (see MessageModel) as messagePayload."
},
"retryCount": 0,
"channelConversation": {
"botId": "mockbot",
"sessionId": "1234",
"type": "websdk",
"userId": "1234",
"channelId": "mockchannel"
},
"componentResponse": {},
"executionContext": "any",
"tenantId": "1234",
"createdOn": "2021-11-01T18:40:37.086Z",
"id": "1234"
}
},
"_response": {
"platformVersion": "1.1",
"context": {
"variables": {
"system.config.PIRATEURL": {
"type": "STRING",
"entity": false,
"value": "https://api.funtranslations.com/translate/pirate.json?text={PHRASE}"
},
"exampleNumber": {
"type": "NUMBER",
"entity": false,
"value": 8
}
}
},
"keepTurn": true,
"transition": false,
"error": false,
"modifyContext": false
},
"_logger": {}
}
fetchResult.status: 200
translation:
{
"success": {
"total": 1
},
"contents": {
"translated": "Avast there! whar do ye think ye be goin'?",
"text": "Hey there! Where do you think you are going?",
"translation": "pirate"
}
}
SDK: About to set variable fetchResult
SDK: Creating new variable fetchResult
SDK: Setting variable {"type":"string","entity":false,"value":{"success":{"total":1},"contents":{"translated":"Avast there! whar do ye think ye be goin'?","text":"Hey there! Where do you think you are going?","translation":"pirate"}}}
creating messageModel with payload
valid messageModel
{
"_request": {
"botId": "mockbot",
"platformVersion": "1.1",
"state": "someState",
"context": {
"variables": {
"system.config.PIRATEURL": {
"type": "STRING",
"entity": false,
"value": "https://api.funtranslations.com/translate/pirate.json?text={PHRASE}"
},
"exampleNumber": {
"type": "NUMBER",
"entity": false,
"value": 8
},
"fetchResult": {
"type": "string",
"entity": false,
"value": {
"success": {
"total": 1
},
"contents": {
"translated": "Avast there! whar do ye think ye be goin'?",
"text": "Hey there! Where do you think you are going?",
"translation": "pirate"
}
}
}
}
},
"properties": {
"phrase": "Hey there! Where do you think you are going?"
},
"message": {
"payload": {},
"messagePayload": {
"docsDetails": "Can take a string payload, an object payload or a MessageModel payload. A string or object payload will be parsed into a MessageModel payload. If the MessageModel payload has a valid common message format, then reply will use it as messagePayload, else it will use the payload to create a rawConversationMessage (see MessageModel) as messagePayload."
},
"retryCount": 0,
"channelConversation": {
"botId": "mockbot",
"sessionId": "1234",
"type": "websdk",
"userId": "1234",
"channelId": "mockchannel"
},
"componentResponse": {},
"executionContext": "any",
"tenantId": "1234",
"createdOn": "2021-11-01T18:40:37.086Z",
"id": "1234"
}
},
"_response": {
"platformVersion": "1.1",
"context": {
"variables": {
"system.config.PIRATEURL": {
"type": "STRING",
"entity": false,
"value": "https://api.funtranslations.com/translate/pirate.json?text={PHRASE}"
},
"exampleNumber": {
"type": "NUMBER",
"entity": false,
"value": 8
},
"fetchResult": {
"type": "string",
"entity": false,
"value": {
"success": {
"total": 1
},
"contents": {
"translated": "Avast there! whar do ye think ye be goin'?",
"text": "Hey there! Where do you think you are going?",
"translation": "pirate"
}
}
}
}
},
"action": "success",
"keepTurn": false,
"transition": true,
"error": false,
"modifyContext": true,
"messages": [
{
"tenantId": "1234",
"channelConversation": {
"botId": "mockbot",
"sessionId": "1234",
"type": "websdk",
"userId": "1234",
"channelId": "mockchannel"
},
"messagePayload": {
"type": "text",
"text": "Avast there! whar do ye think ye be goin'?"
}
}
]
},
"_logger": {}
}
Source Screenshots
Unfortunately, it is not possible to provide the code but the following are what the source files look like for your reference:
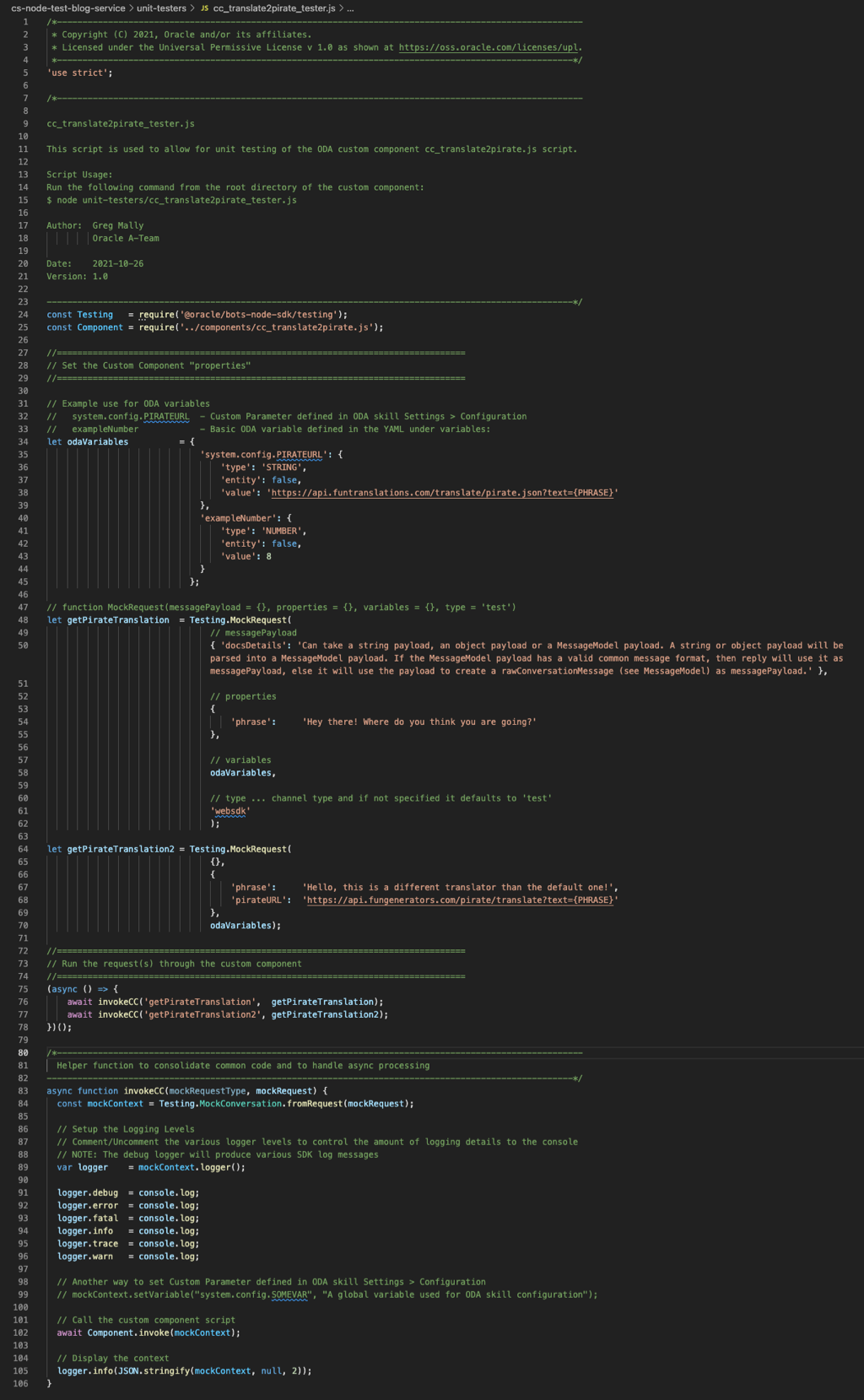
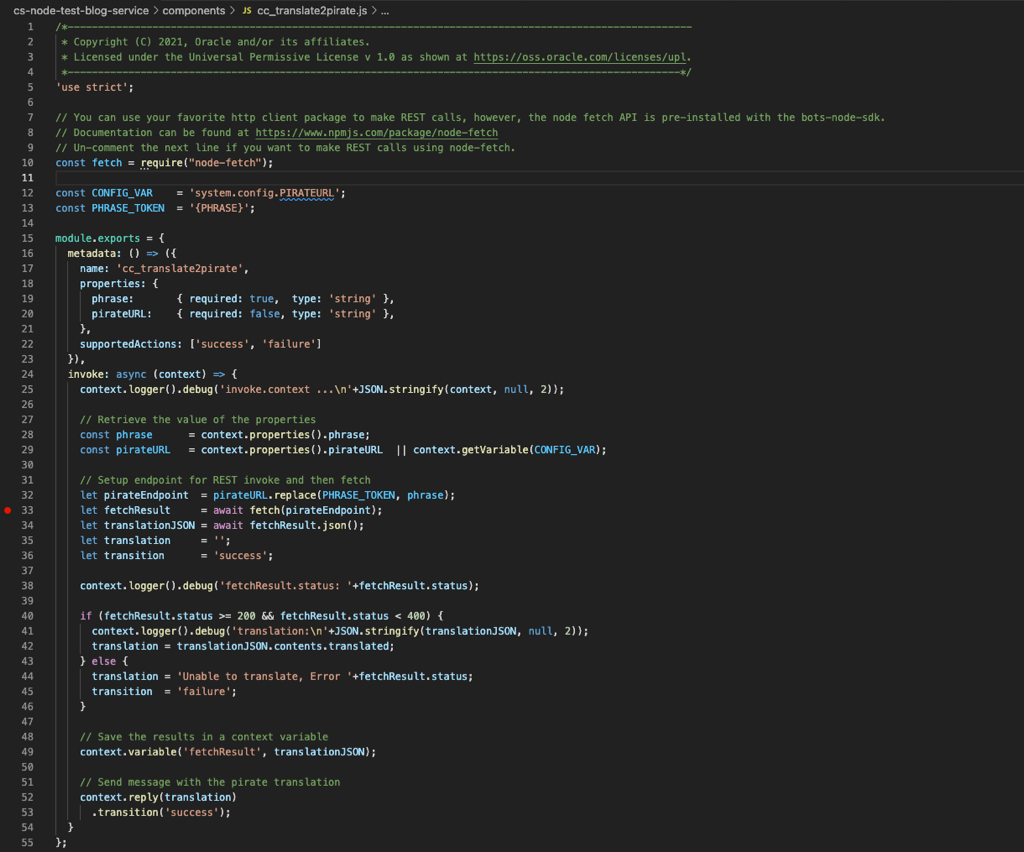
I hope you find this helpful and if you need something similar for Entity Event Handlers, see my complimentary blog Oracle Digital Assistant (ODA) Entity Event Handler Testing via Node.js.
