Introduction
Multicloud strategies are becoming essential for enterprises that want flexibility, performance, and resilience across cloud providers. Oracle Database@GCP brings this vision to life by allowing organizations to run OCI-managed databases directly within GCP regions, combining the strengths of both cloud providers.
This approach lets teams leverage Exadata and Autonomous Database services while seamlessly integrating with GCP tools, simplifying operations, improving connectivity, and enabling powerful Multicloud solutions.
Agenda
- What is Oracle Database@GCP?
- Networking Fundamentals – The ODB Network
- Benefits for customers
- Availability
- DNS Configuration
- Routing and Security
- Conclusion
What is Oracle Database@GCP?
Oracle Database@GCP is a service that brings OCI-managed Oracle Database infrastructure into GCP data centers. Unlike running Oracle workloads on GCP Compute Engine, this offering is built on Exadata systems operated by Oracle, giving you the same high-performance platform you’d expect on OCI, but accessible through GCP tools.
The service is fully integrated into the GCP experience. You can purchase, provision, and manage your Oracle database through the GCP Console, CLI, or APIs. While Oracle ensures the database stack runs on optimized Exadata hardware within GCP.
Key Features
Oracle Database@GCP combines best-of-breed Oracle technology with GCP-native services:
- Exadata Database Service and Autonomous Database- enterprise grade performance with fully managed automation.
- GCP Integration – works seamlessly with Cloud Monitoring, Eventarc, Cloud Audit Logs, and Terraform.
- Durable Back Ups – backup Oracle databases using OCI Autonomous Recovery Service or Object Storage with high durability and easy recovery.
- Private Networking – use the ODB Network to connect Oracle DBs with GCP workloads through peering, ensuring secure, low-latency communication.
Networking Fundamentals – The ODB Network
Before proceeding, please ensure you’ve completed the onboarding tasks, which are not covered in this blog. Refer to the link below for more details.
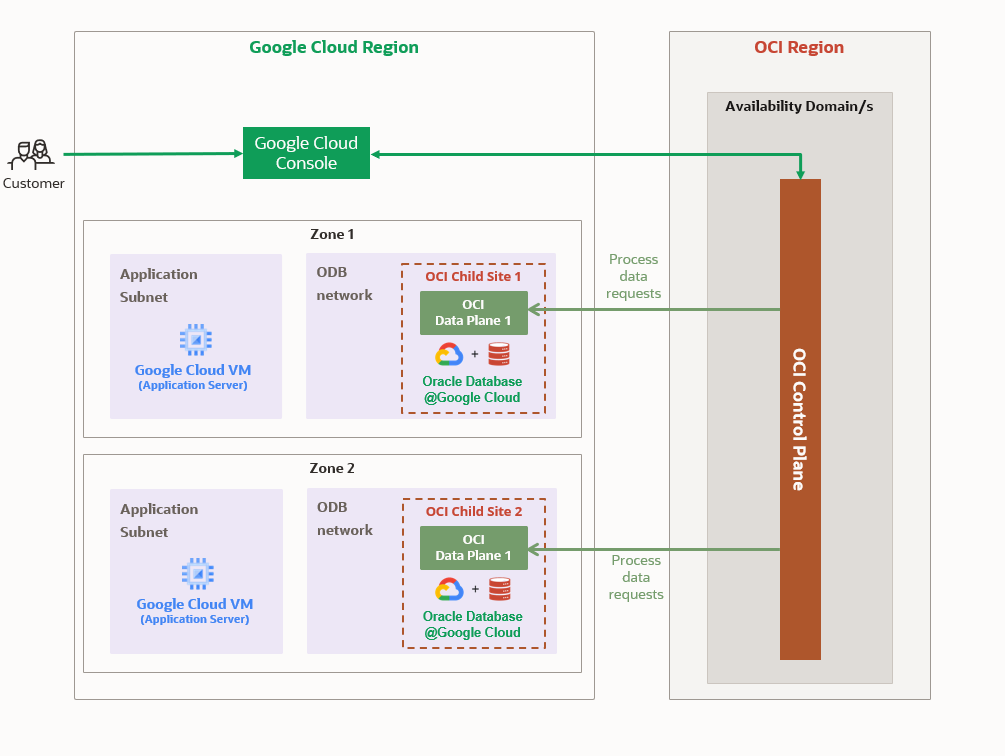
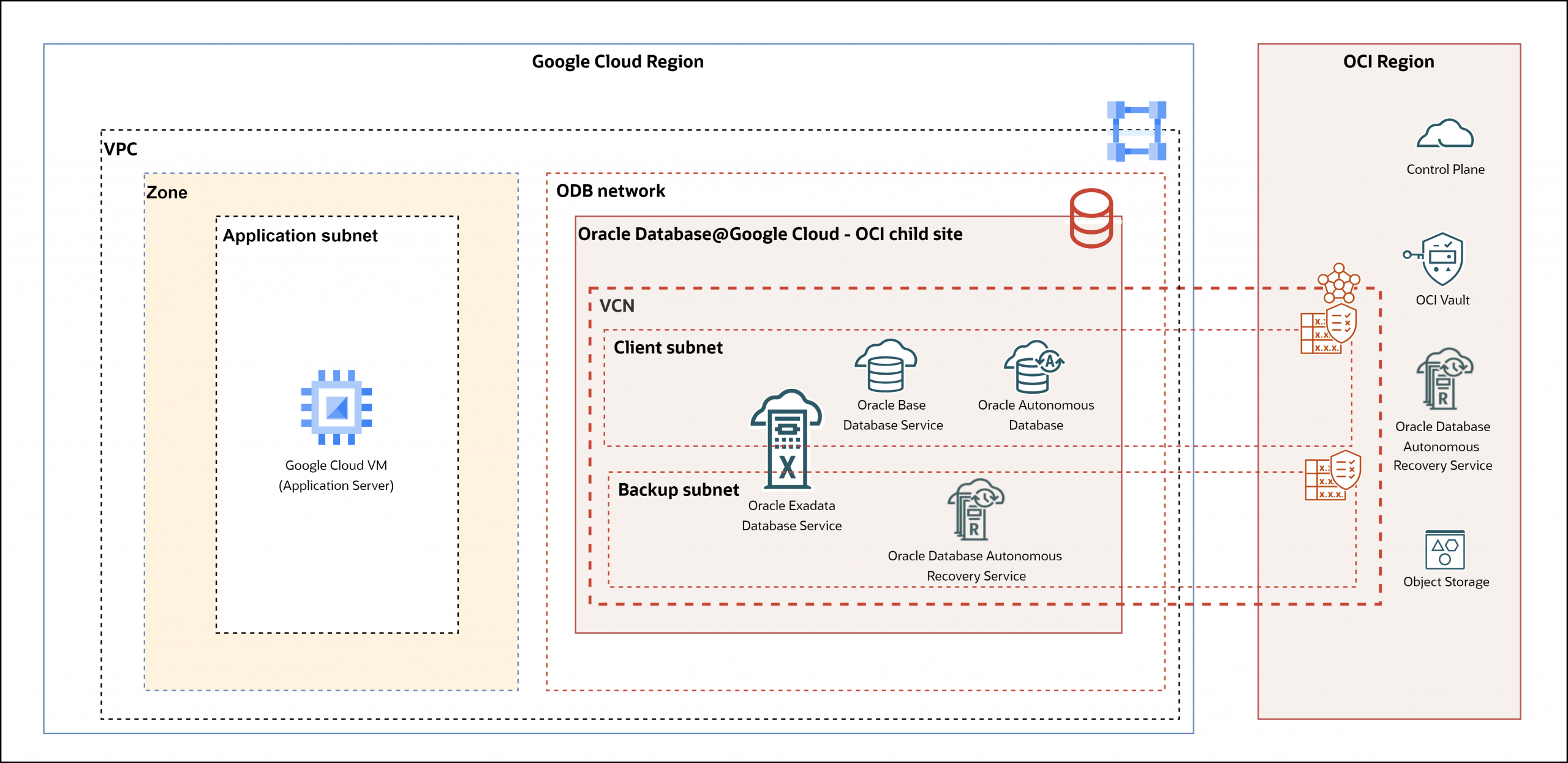
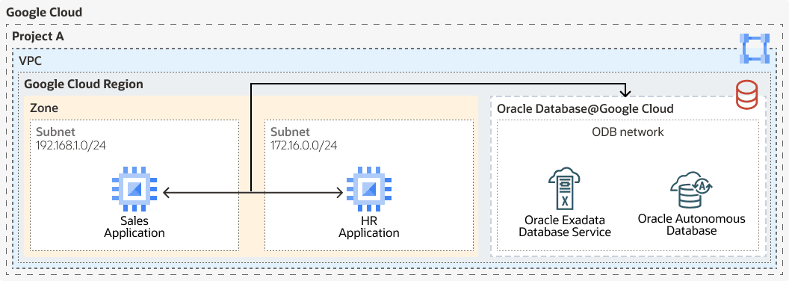
One of the most unique aspects of Oracle Database@GCP is the dedicated Oracle Database (ODB) Network created inside GCP. This is a private, isolated network that Oracle manages (Child Site) for database connectivity. To link your applications running on GCP Compute or other GCP services, you’ll provision the ODB network in an existing Standalone or Shared VPC.
The ODB network is basically a representation of an OCI VCN within the GCP VPC. Each ODB network can support up to five ODB subnets. Underlying connectivity between the ODB network and the associated VPC is established via an underlying Cloud Router and Partner Interconnect.
This approach eliminates the need for complex third-party direct connect or VPN. Instead, your applications communicate with the database over a private, secure channel with minimal latency, as if both were running inside the same environment.
Why this matters:
- Reduced network hops and lower latency.
- No exposure to the public internet.
- Simple setup via GCP networking constructs.
For customers with latency sensitive workloads like financial systems or e-commerce platform, this design ensures database calls remain fast and predictable while keeping traffic private.
Benefits for Customers
Deploying Oracle Database@GCP offers several practical advantages:
- Performance – Exadata infrastructure provides unmatched throughput and scalability.
- Flexibility – Keep workloads close to GCP-native applications while leveraging Oracle’s database strengths.
- Multicloud Strategy – No longer an either-or decision combine Oracle + GCP to get the best of both worlds.
- Simplify management and operation – With Oracle DB@GCP, you will utilize a unified experience for collaborative support, purchasing, management, and operations.
- Pricing – Purchase Oracle DB@GCP through GCP as a Private or Public offer via the Google Cloud Marketplace.
Availability
Oracle Database@GCP is available in many GCP regions worldwide, currently supported GCP regions and zones are located here.
Note: An OCI region is paired to each Google region where DB@GCP is present, this OCI region is known as a Parent Site.
GCP regions are independent geographic areas that also consist of zones. Zones represent a specific, isolated infrastructure location for hosting resources. Resources deployed within a zone are referred to as a zonal resource. While regional resources can be used by any resource in that region, regardless of zone. Oracle Database@GCP zones are known as GCP Oracle Zones.
Oracle Database@GCP resources are either regional or zonal in scope. The scope of the resource determines where it is provisioned. Zonal resources can be placed together in the same location while regional resources can run in any zone. Autonomous Databases are regional resources while the following DB@GCP constructs are considered zonal resources:
- Exadata Infrastructure
- Exadata VM Clusters
- Exadata VM Clusters and Exascale Storage Vaults
- ODB Networks and ODB Subnets
- DB Systems
DNS configuration
Oracle DB@Google Cloud utilizes the GCP private DNS Zone and Cloud DNS forwarding service to allow GCP workloads to resolve fully qualified domain names (FQDNs) of the databases hosted in the ODB network and its associated DNS Zone.
The ODB Network includes a GCP Cloud private DNS Zone that’s set to use either oraclevcn.com (for Exadata and BaseDB), or oraclecloud.com / oraclecloudapps.com (for Autonomous DB) for the DNS zone name. Along with a DNS listener endpoint IP that handles FQDN resolution within the private DNS Zone.
For example a DB@GCP Exadata VM cluster with the hostname db1 would have the FQDN of db1.subnet1.oraclevcn.com
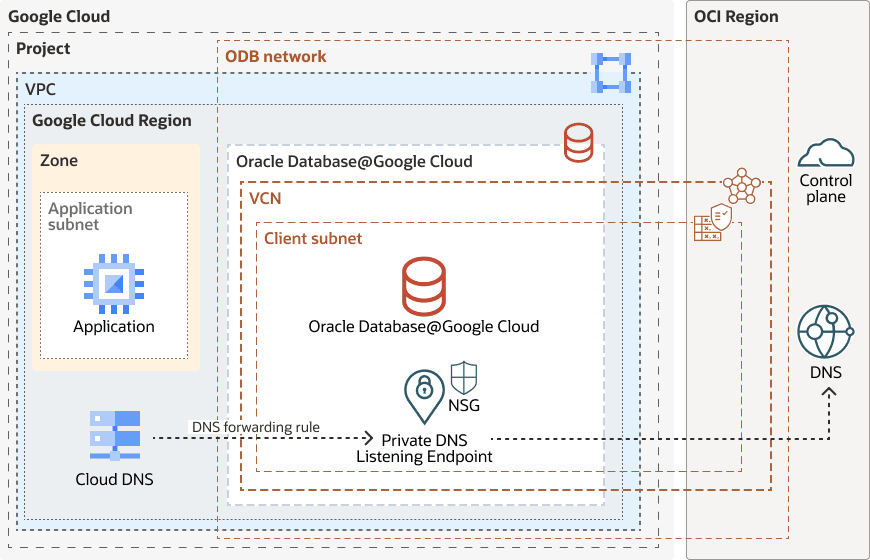
Forwarding rules are configured within GCP Cloud DNS to send DNS queries to the DNS Listener IP provisioned in the ODB network. The listener is governed by a Network Security Group (NSG) rule, that provides precise control over ingress IPs and ports allowed to communicate with the endpoint. This allows for secure and proper DNS resolution of DB@GCP database FQDNs when queries are originated from the GCP VPC to the ODB network.
Routing and Security
When provisioning a new ODB network, automation links the ODB to a Cloud Router in the VPC (with Partner Interconnect). No additional routing configuration is needed to allow communication between the VPC subnets and the ODB network within the same VPC. Inherently, even if the VPC has subnets in different GCP regions, these subnets will have network reachability to the ODB network by default.
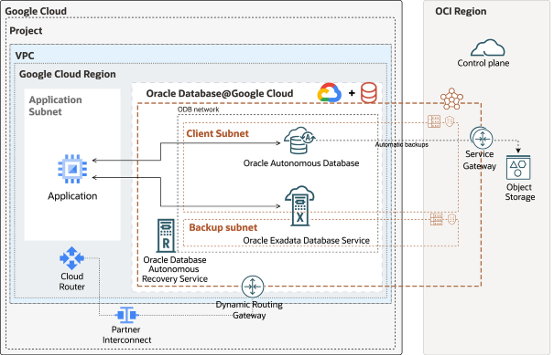
There are two types of ODB subnets, Client subnets for the databases and Backup subnets to back up the databases. Client subnets are used by both Autonomous DBs and Exadata VM Clusters. While backup subnets are used only for Exadata VM Clusters. As mentioned, each ODB network can support up to five subnets.
Details on specific CIDR size requirements for each ODB subnet type can be found here. But in summary note that the minimum CIDR size for both Client and Backup subnets is /27 while the maximum size is /22. The CIDR for Client and Backup subnets must be part of the RFC 1918 range – 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12 or 192.168.0.0/16.
Client Subnet Consumed IPs:
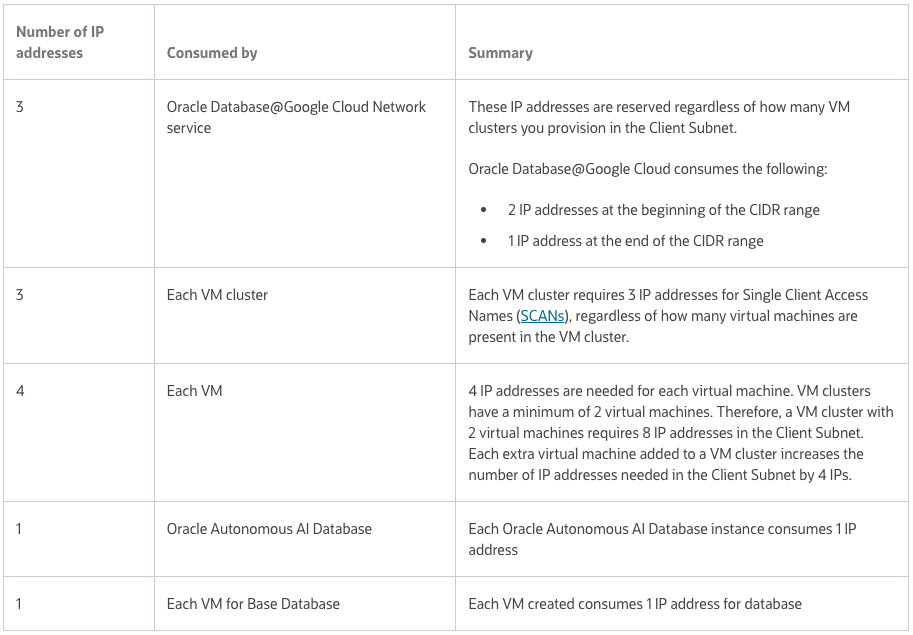
Backup Subnet Consumed IPs:

ODB Network security is handled by an OCI construct called a Network Security Group (NSG). The NSG acts as a virtual firewall for a set of cloud resources that share the same security posture. Each NSG can consist of ingress and egress security rules based on IP address(or another NSG), Protocol, & Port. The NSG is applied to the VNIC of the resource, in our case it would be the ADB, Exadata VM Cluster, or Base DB instance. The default TCP ports 22 and 1521 are used for accessing the databases.
While out of scope for this blog, it’s important to note there are many ways to design your DB@GCP network topology to support needs such as scalability, management, or segmentation. Such validated designs include support for the following:
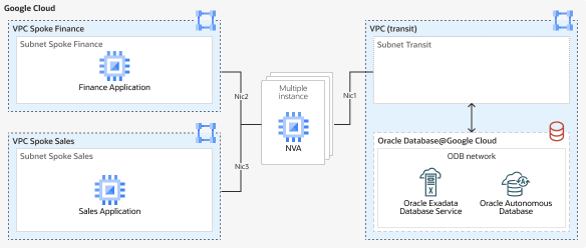
Multiple VPCs
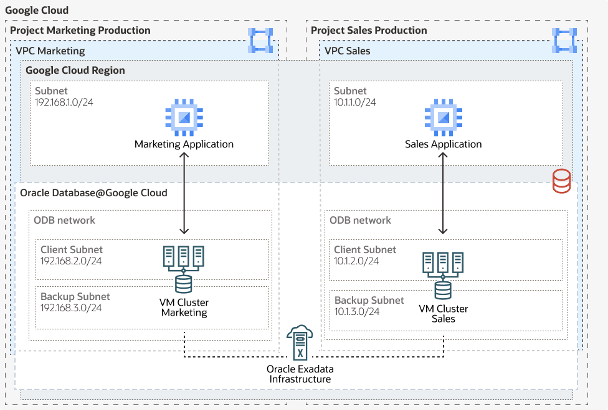
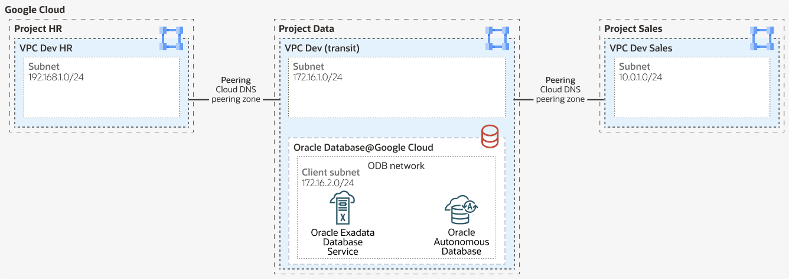
VPC peering
NVA Hub & Spoke
Conclusion
Oracle Database@GCP delivers a powerful combination, the reliability and performance of Oracle Exadata and Autonomous Database in GCP regions, with seamless integration into the GCP environment. This unique approach to multicloud design allows organizations to run mission critical applications closer to their GCP workloads while relying on Oracle’s proven database and cloud technology.
For enterprise balancing between performance, simplicity, and flexibility, Oracle Database@GCP represents not just another cloud service, but a milestone in multicloud strategy.
