Encrypting object storage buckets with customer-managed keys is a cornerstone of modern cloud security architecture—a best practice that transforms data protection from mere compliance into a genuine defense. Yet in the real world of enterprise infrastructure, legacy Infrastructure as Code scripts often pose an immutable challenge: sweeping architectural changes aren’t just complex—they’re temporarily impossible.
For organizations caught in this transitional space, I’ve engineered an elegant solution: an OCI Function that serves as an intelligent security guardian, automatically triggered by OCI Events whenever a new bucket is created in your environment. This function performs real-time encryption validation, examining each bucket’s configuration against security standards. When it detects a bucket lacking customer-managed key encryption, it doesn’t simply alert—it acts, seamlessly reconfiguring the bucket to meet enterprise security requirements without human intervention.
This approach bridges the gap between security ideals and operational reality, ensuring that even as legacy code continues to provision infrastructure, your encryption standards remain uncompromised. This is just one example of security automation using OCI server-less function. There are ample number of other use cases that we can support using server-less functions.
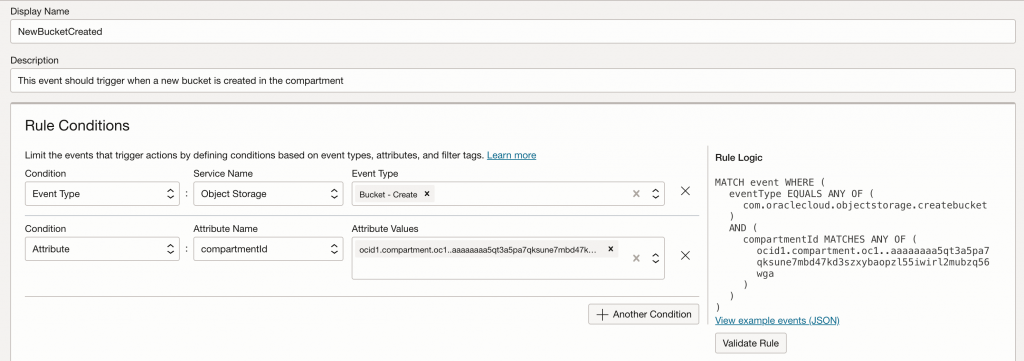
OCI Events Configuration
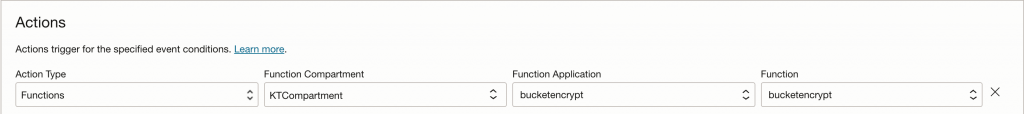
Deploy OCI Function
To create and deploy an OCI function, refer to the steps in the OCI documentation. https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/developer/functions/func-setup-cli/01-summary.htm
Once you finish setting up fn cli, choose to create a Python function. Once the function is created, download the function code (func.py and requirements.txt) from my GitHub handle to the encryption bucket.
https://github.com/kiranthakkar/ocifunctions/tree/main/bucketencrypt
OCI IAM Policies
For the function to work, you need to create IAM policies and allow the function instance to manage buckets and use keys.
- Create a dynamic group as defined in the screenshot below. Make sure the compartment OCID is correct.
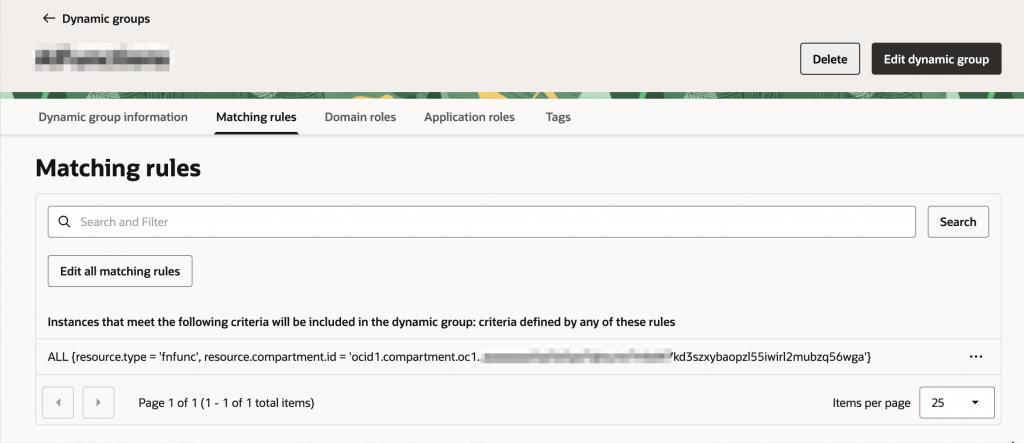
- For the dynamic group created, write IAM policies. Make sure to replace <target_compartment_name> with the compartment where target buckets are created. You need to create an event rule in the same compartment. Keys and key-delegate permissions need to be granted in the compartment where the OCI Vault is created. Please note that the policies below are just samples. You can and should write more granular policies for the specific use case.
Allow dynamic-group encryptbucketfunction to manage object-family in compartment <target_compartment_name>
Allow dynamic-group encryptbucketfunction to use keys in compartment <target_compartment_name>
Allow dynamic-group encryptbucketfunction to use key-delegate in compartment <target_compartment_name>
OCI Function Configuration
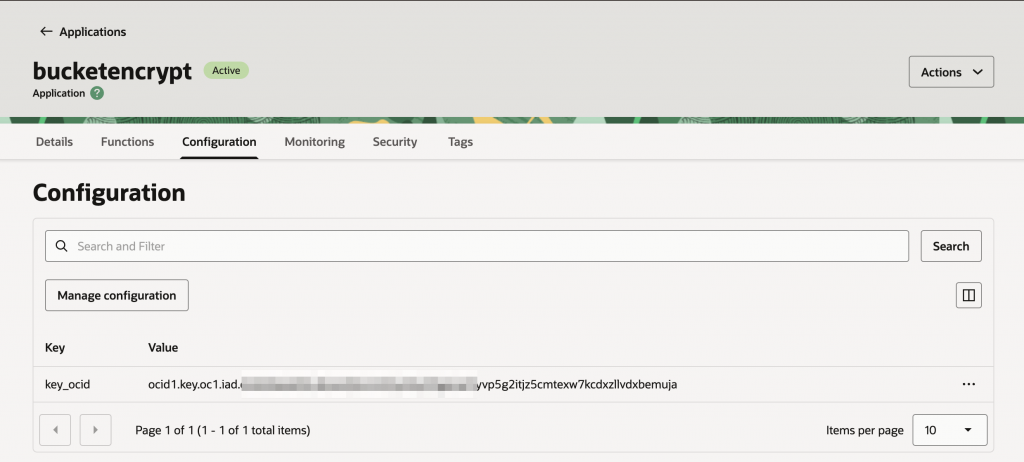
The OCI Function requires a key OCID to encrypt buckets. We can add that configuration to the OCI function.
Summary
This blog demonstrates how to automatically enforce customer-managed key encryption on OCI object storage buckets using serverless automation. Implementation involves setting up the OCI Functions CLI, deploying Python code from GitHub, and configuring IAM policies through dynamic groups that grant the function permissions to manage buckets and encryption keys. By adding the target key OCID as a function configuration parameter, organizations can ensure every new bucket meets encryption standards automatically. This event-driven approach maintains security compliance even as existing provisioning scripts continue to operate.
