As you scale workloads in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) over time, there is a proliferation of cloud resources and sensitive data—bringing increased complexity and risk. As a result, discovering and managing user access to critical resources becomes a top priority. Understanding who has access to what, and ensuring those permissions are appropriate, is essential to maintaining security, achieving compliance, and optimizing operational efficiency.
This makes the role of security leadership (especially for CISOs) more critical than ever. To effectively safeguard critical cloud resources and meet compliance obligations, CISOs must ask themselves a few fundamental questions:
- Who has access to what in my cloud environment?
- How was that access granted?
- Is that access still required?
- Are adequate security controls in place to enforce the principle of least privilege?
By addressing these questions proactively, organizations can reduce risk, improve governance, and build a more secure and resilient cloud environment.
This is where Oracle Access Governance service becomes a strategic asset for security leadership—providing clear, actionable answers to the questions above. Oracle Access Governance, a native cloud service, is purpose-built to help organizations gain visibility into and manage access across a wide range of IT systems, including OCI, enforce the principle of least privilege, and streamline compliance with confidence.
In this blog, we’ll walk through the high-level process explaining how Oracle Access Governance helps unlock access visibility in your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy—supporting your journey from access discovery to compliance.
First, let’s understand how to connect Oracle Access Governance with your OCI tenancy before diving into the use cases. This involves below steps.
- Setup Oracle Access Governance instance
- Onboard your OCI tenancy in Access Governance
Setup Oracle Access Governance instance
If you’ve already created an Oracle Access Governance instance, you can skip this step. Otherwise, you can create one directly from the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console as shown below.
- Log in to OCI Console.
- Navigate to Identity & Security > Access Governance
- Click on “Create service instance“
- Fill in all details and set license type to “Access Governance for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure” and click on “Create Service instance“
The following is a view of the Access Governance dashboard.
Onboard OCI tenancy in Access Governance
Before you onboard your OCI tenancy into Access Governance, you need to complete certain prerequisites in your OCI tenancy. These include creating a dedicated IAM user and group for this integration, generating an API key for the user, and setting up the necessary IAM policies. You can perform these steps either manually or use the terraform script provided by Oracle. See the product documentation for complete details.
If you’re wondering which policies are required in OCI for this integration, here they are:
allow group agcs_group to inspect all-resources in tenancy
allow group agcs_group to manage policies in tenancy where all {request.permission in ('POLICY_UPDATE', 'POLICY_DELETE'), target.policy.name !='Tenant Admin Policy'
allow group agcs_group to manage domains in tenancy
allow group agcs_group to read audit-events in tenancy
allow group agcs_group to read objectstorage-namespace in tenancy
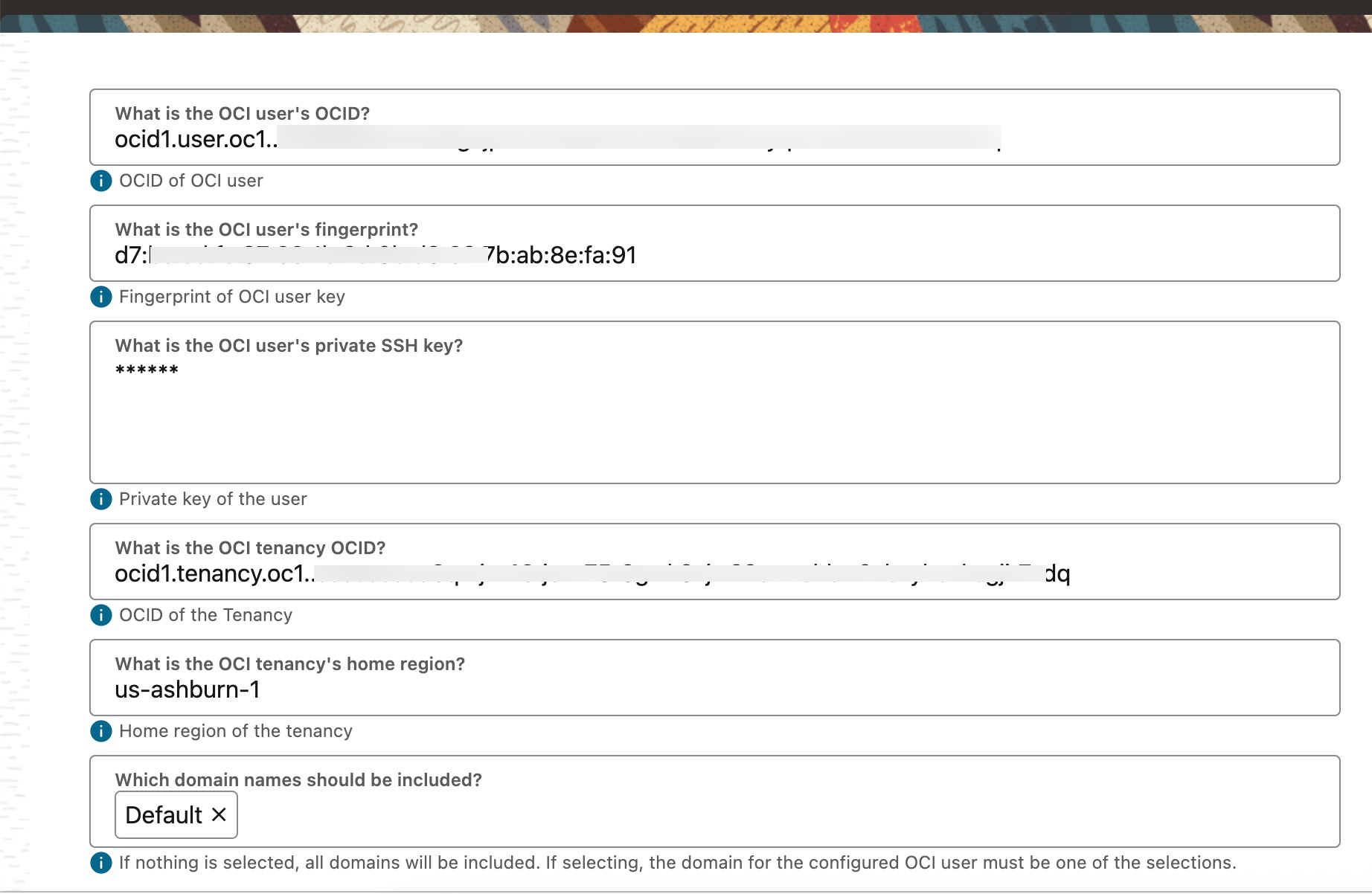
After completing the prerequisites in your OCI tenancy, gather the following details required for Oracle Access Governance to establish a connection with your tenancy.
- User’s OCID
- User’s fingerprint (Fingerprint of the public key of the API Signing Key)
- User’s private SSH key (Private key (.pem file) of the API Signing Key)
- OCI tenancy OCID
- OCI tenancy’s home region
- IAM Domains to be included (Optional)
Now proceed to the Oracle Access Governance console to onboard your OCI tenancy as a connected system.
From the Access Governance console, navigate to Service Administration -> Orchestrated System -> Add an orchestrated system, select “Oracle Cloud Infrastructure” from the list, and enter the required details as shown below.
Once the connection to your OCI tenancy is validated, Access goverance service begins loading the tenancy data. The data retrieved by Access Governance includes IAM users, groups, policies, and cloud resources. The duration of the data loading process depends on the size of your tenancy.
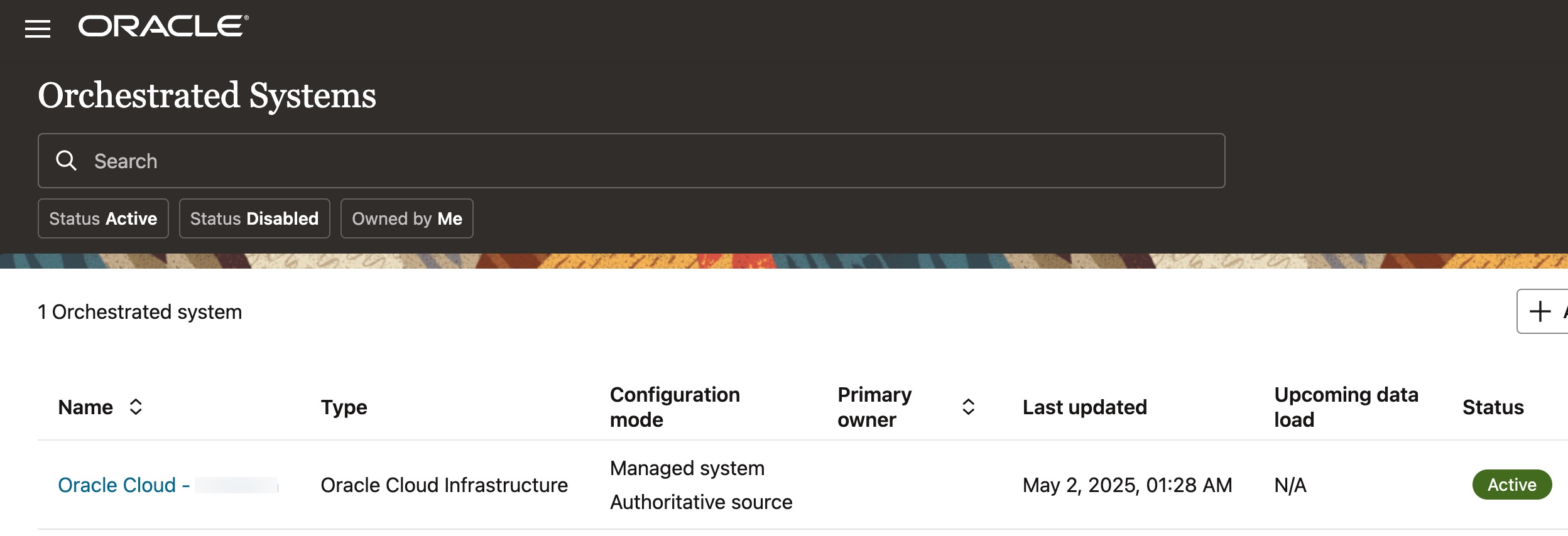
Once the data is loaded, Access Governance automatically establishes relationships within the data and can immediately help address key use cases—ranging from access discovery to compliance—right away, with no further configuration needed.
Let’s take a closer look at few important use cases.
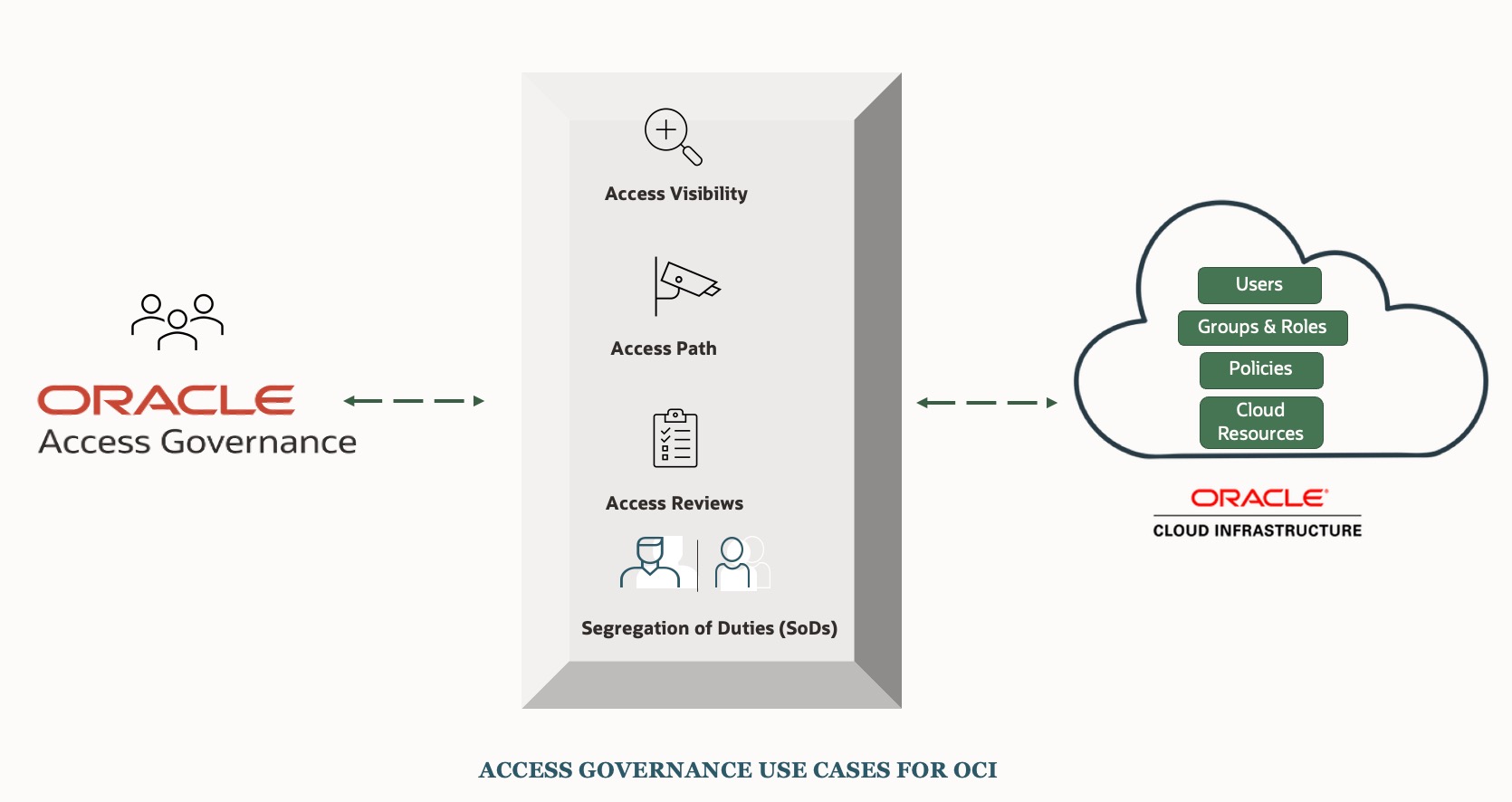
Use Case # 1: Identifying Who has Access to What (Access Visibility)
To gain visibility into access across OCI resources, from the Access Governance dashboard, navigate to ‘Who Has Access to What‘ -> ‘Enterprise-Wide Browser‘ .
Enterprise-Wide Browser provides a clear and centralized view of access-related information. It shows the relationships between OCI IAM users, their group memberships, the policies applied to them, and the cloud resources they have access to—all in one place. This makes it much easier to monitor and track who has access to what, understand the specific permissions on each resource, and identify any over-privileged access—supporting more effective access governance.
You can gain access insights both from a user-centric perspective and from the viewpoint of cloud resources.
From a user-centric perspective
The view below display the list of users currently present in the OCI tenancy. Let’s see what access the user ‘Cara Anderson‘ has in the OCI tenancy. Click on the ‘View Details’ link for this user, as shown below.
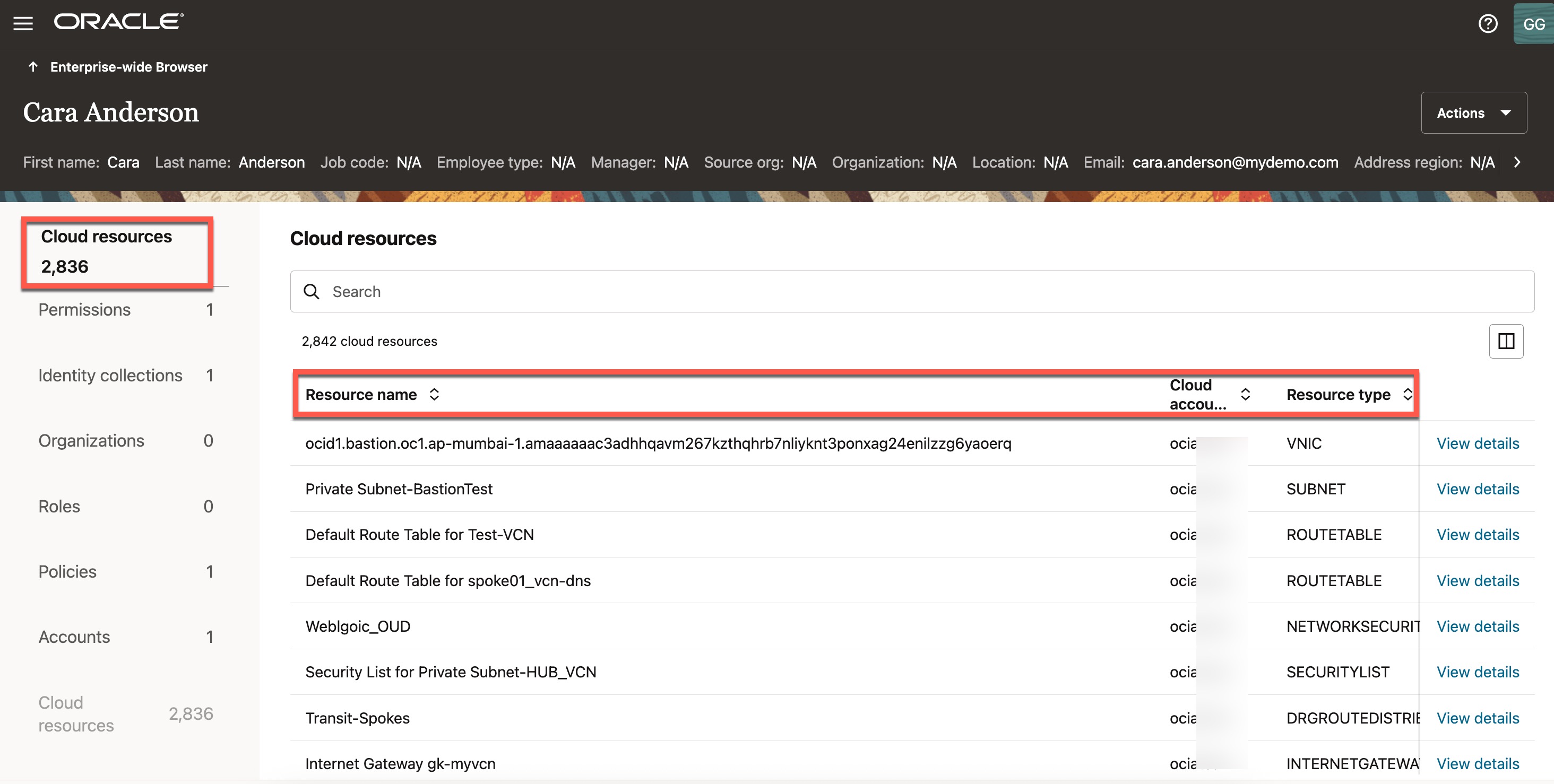
It will display the access profile for this user, you can see that user has access to 2,836 OCI cloud resources, along with details such as the resource name, resource type, compartment name, corresponding poicy name, the tenancy name (cloud account), and the other details.
Use Case # 2: Understanding How Access Was Granted (Access Path)
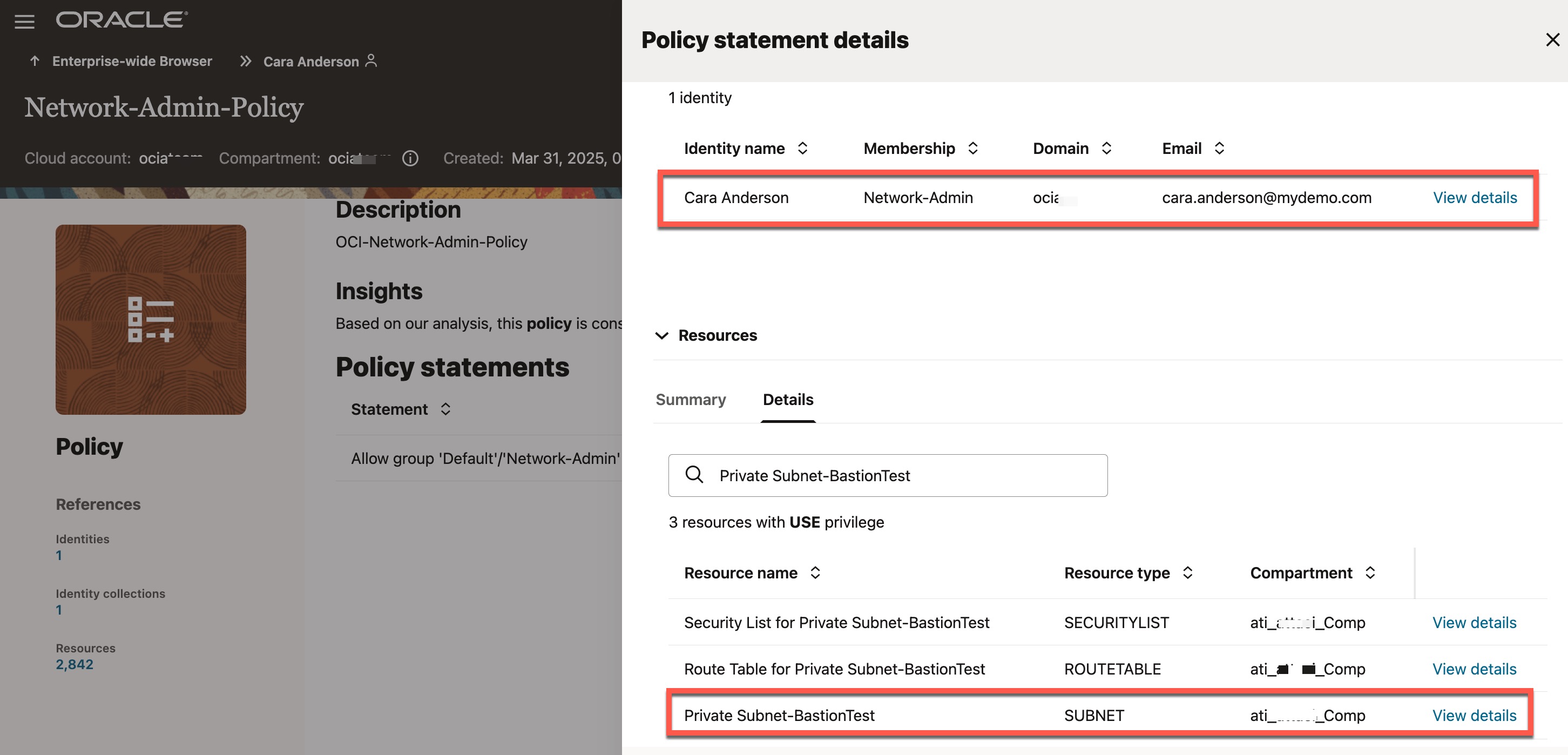
Now let’s explore how this access was granted to the user “Cara Anderson“. In other words, what caused this user to have access to 2836 resources. For example, let’s see how the user has got access to a subnet called “Private Subnet-BastionTest“
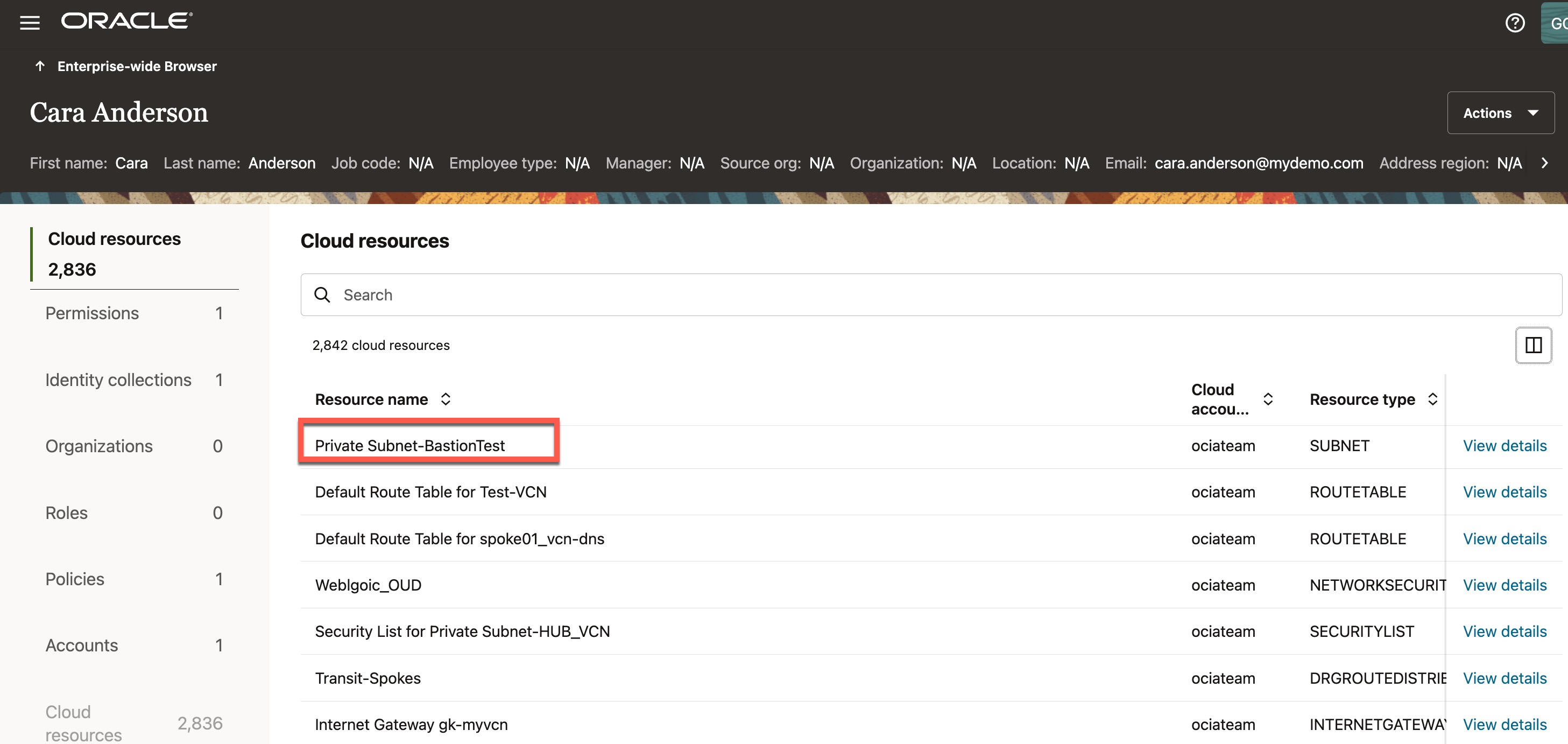
Scroll to the right to view additional columns under “Cloud Resources.” Locate the “Policy Name” column for the subnet resource “Private Subnet-BastionTest.” The user gained access to this subnet through the “Network Admin Policy”. Next, click on “Policies” on the left side to view the list of policies associated with this user..
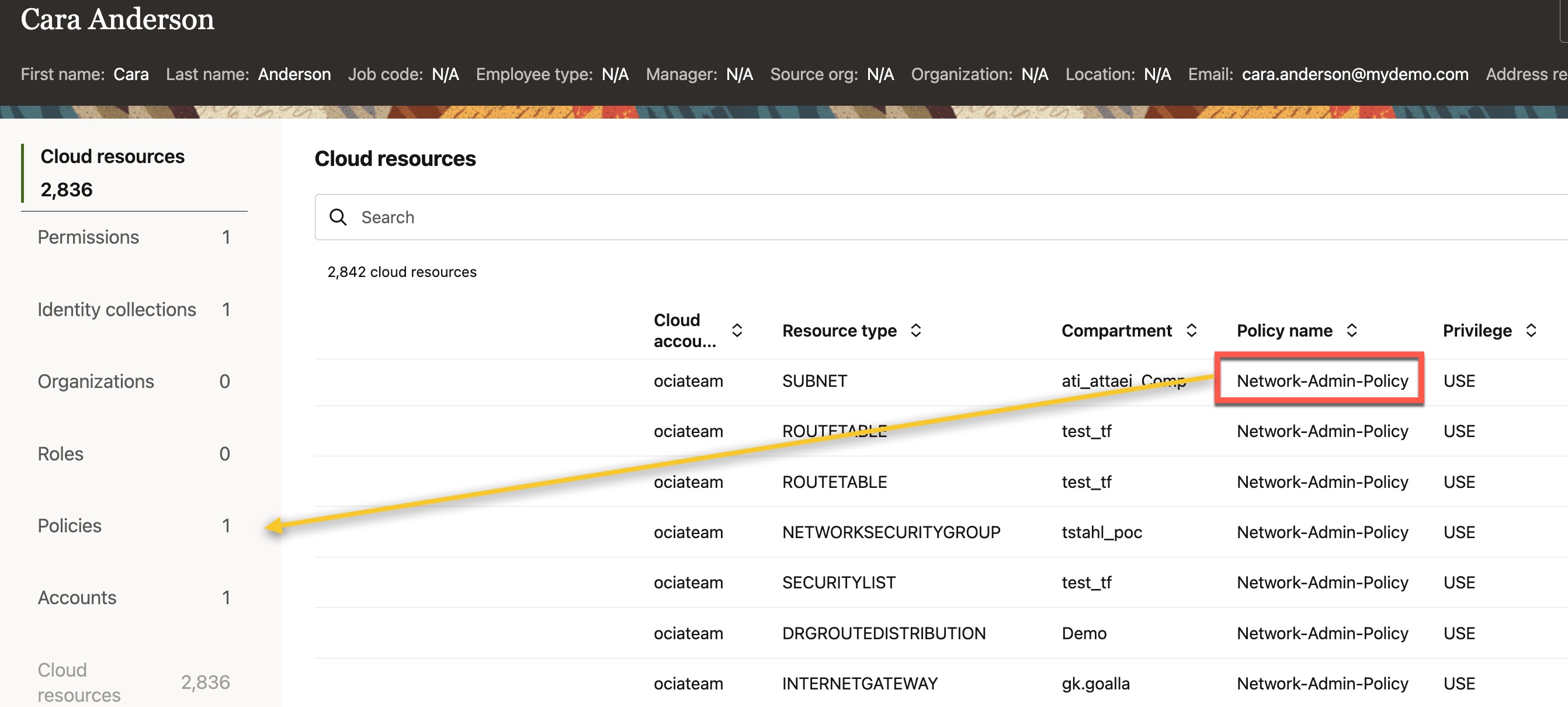
You can see that there is only one policy (i.e., ‘Network-Admin-Policy‘) associated with this user. Click on ‘View Details’ next to the policy
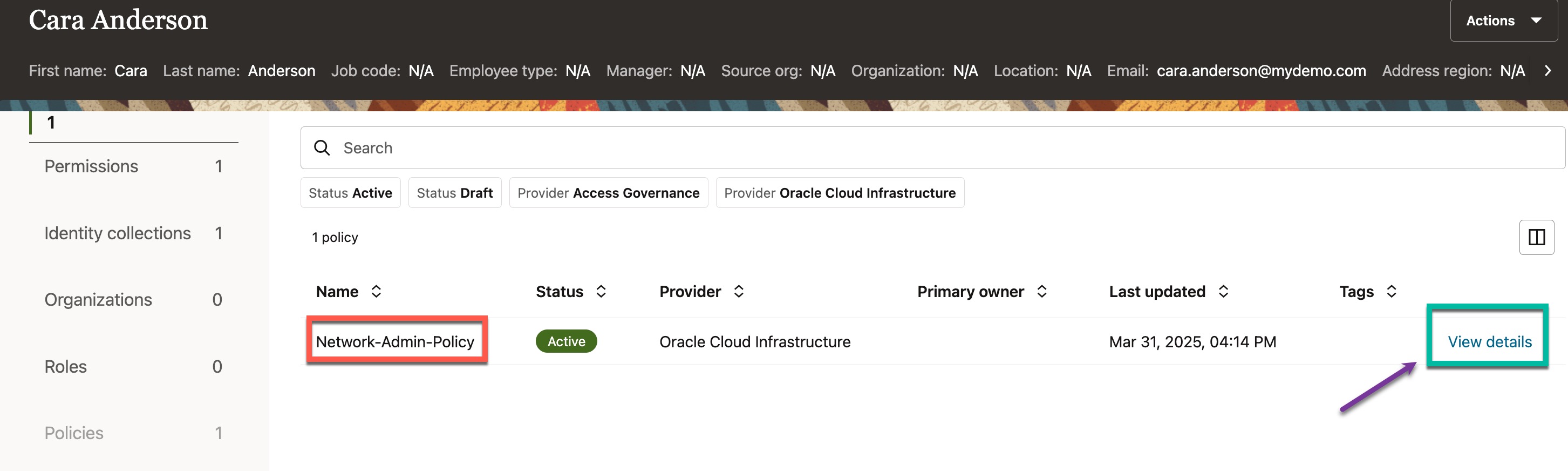
This policy has a statement that grants access to all resources belonging to the virtual network family, provided the user is a member of the “Network-Admin” group. To view more details, click “View” next to the policy statement.
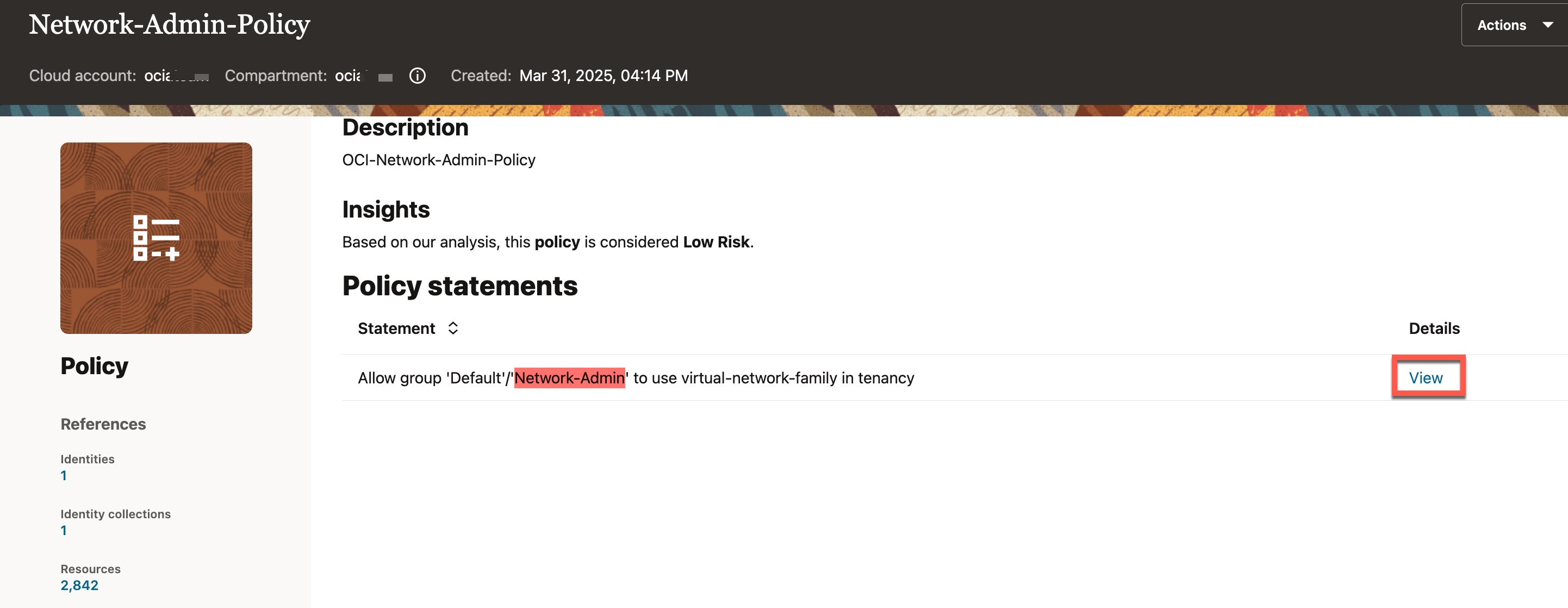
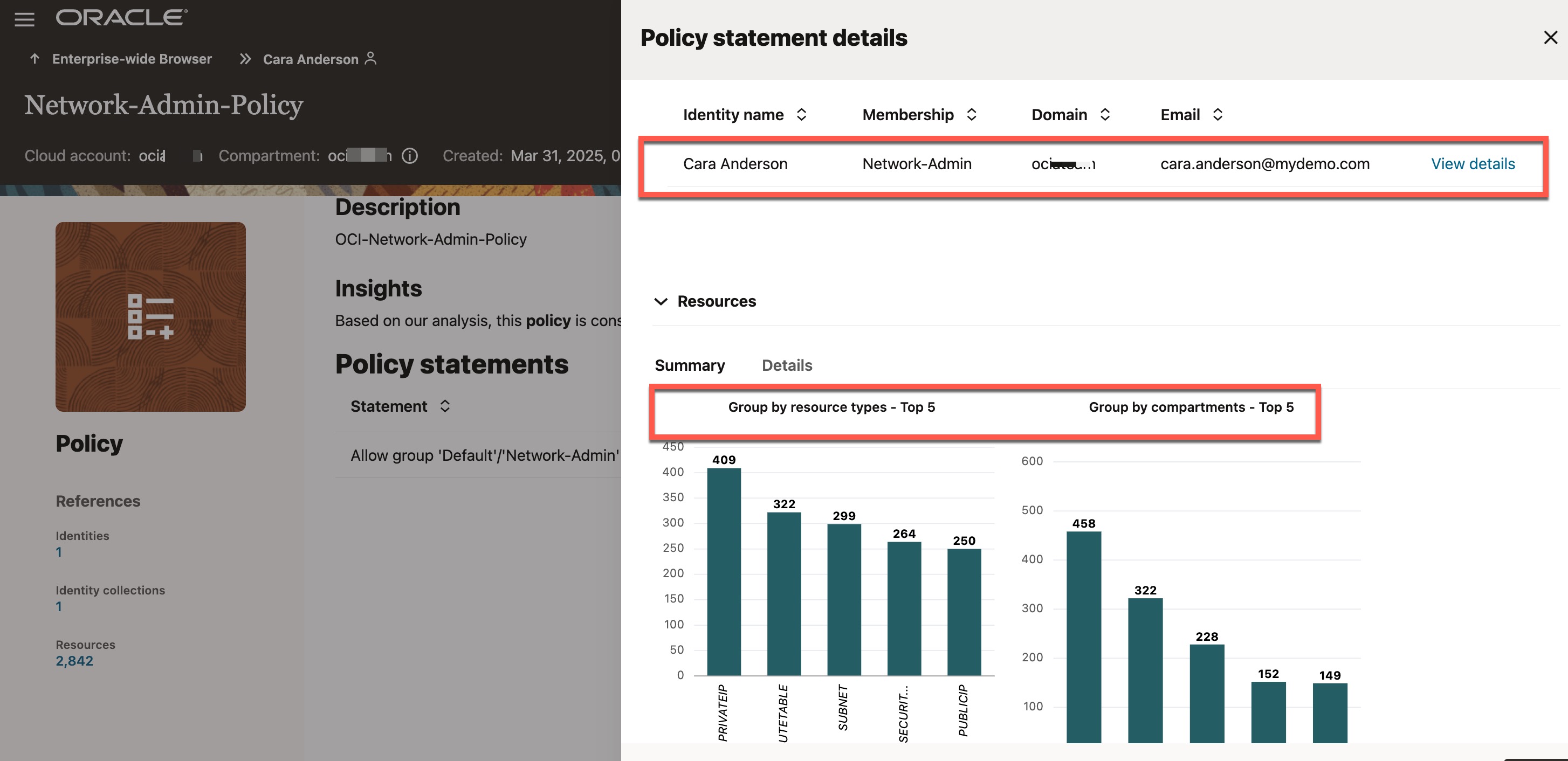
You can now see that the user is associated with a policy, and as a result, the user has access to several network resources, which are listed under “Resources” section. One of the resources granted to “Cara Anderson” through this policy is the “Private Subnet-BastionTest.”
Use Case # 3: Determining If Access Is Still Needed (Access Reviews)
In the last two use cases, we saw how Access Governance makes it easy to explore what cloud access users have and how that access was granted. The next crucial step is determining whether users still need access to those cloud resources. A common best practice for this is conducting access reviews—also known as access attestation or access certification. Access review is the process of evaluating and certifying whether an identity’s access privileges are still necessary and aligned with their current role.
Oracle Access Governance supports different types of access reviews based on the connected system. For Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, you can conduct access review campaigns such as:
- Identity Access Reviews – refers to evaluating access privileges for identities in your OCI tenancy.
- Policy Reviews – refers to review of OCI IAM policies to evaluate its effectiveness and compliance.
- Identity Collection Reviews – refers to review of a group to verify if only eligible set of members are assigned to a group. This is commonly known as “Group membership reviews.”
These access review campaigns can be conducted either on a scheduled basis or as ad-hoc reviews. The images below illustrate access reviews for OCI in two different scenarios.
- Access review of OCI Tenancy Admin Policy
- Access review of OCI “Administrator” Group Membership
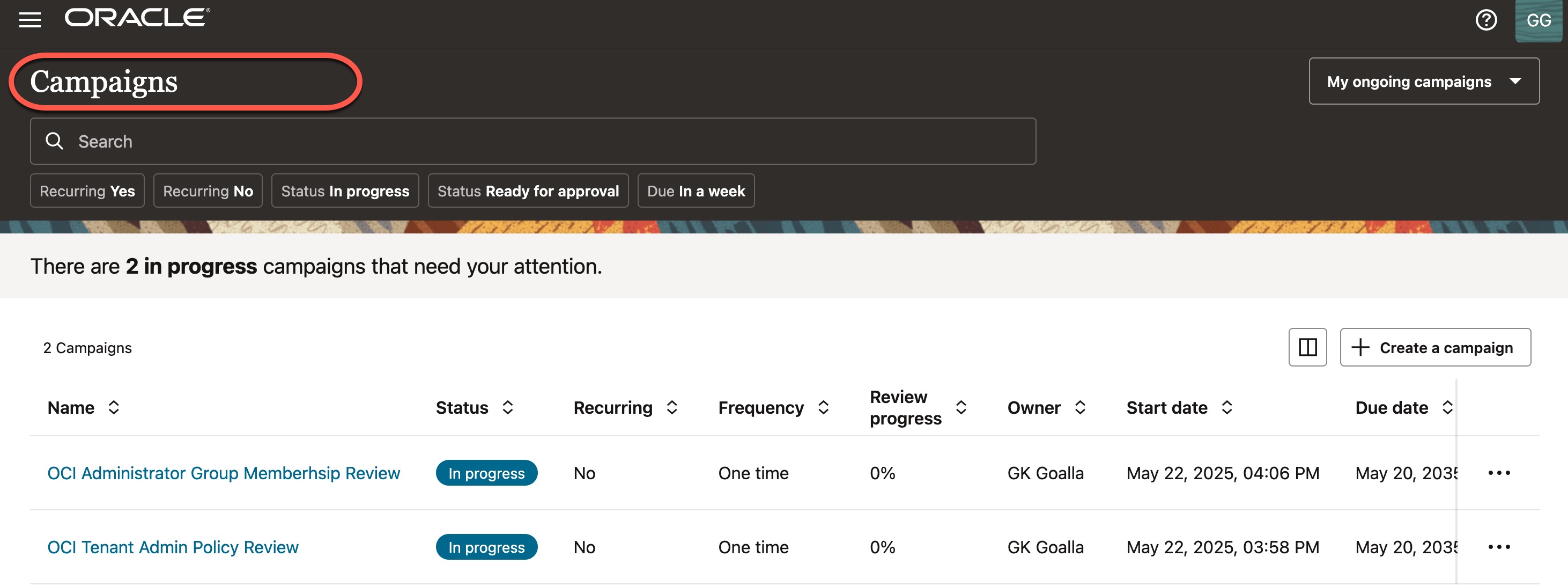
After an access review campaign is created, a notification is sent to the designated access reviewers, who should evaluate the assigned access reviews and decide whether to Accept or Revoke access. In this example, both access review campaigns are assigned to the same reviewer, GK Goalla, as shown below.
Now, let’s take a look at how this review process works for each of the scenarios mentioned above. Click on “Actions“
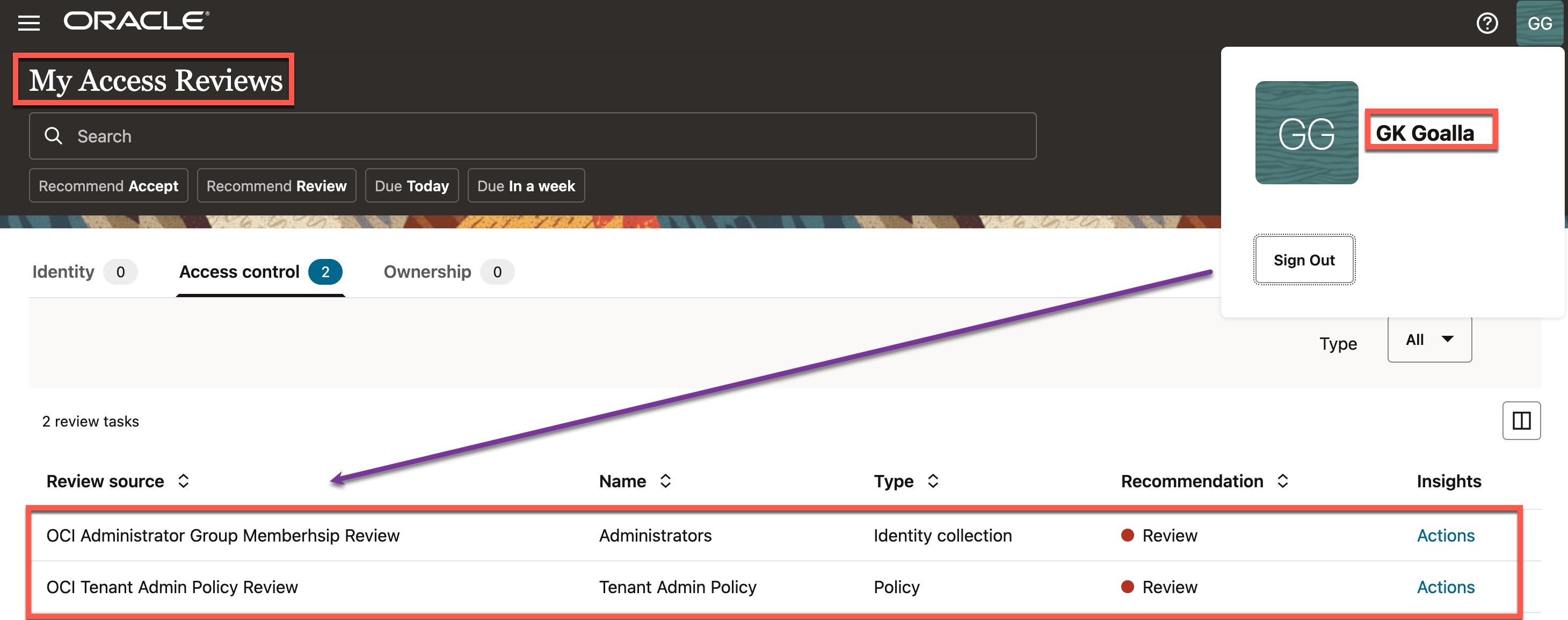
Access review of OCI Tenancy Admin Policy
The policy under review here is the “Tenant Admin Policy,” which comes by default with every OCI tenancy.
You can see a policy statement that grants full administrative access to all resources in your OCI tenancy for users who are in the “Administrators” group. As a reviewer, you can choose to either “Accept” or “Revoke” this policy statement to part of the policy. Accepting indicates that you agree the statement is appropriate, while revoking it will trigger Access Governance to remove the policy statement from that policy as part of the remediation process.
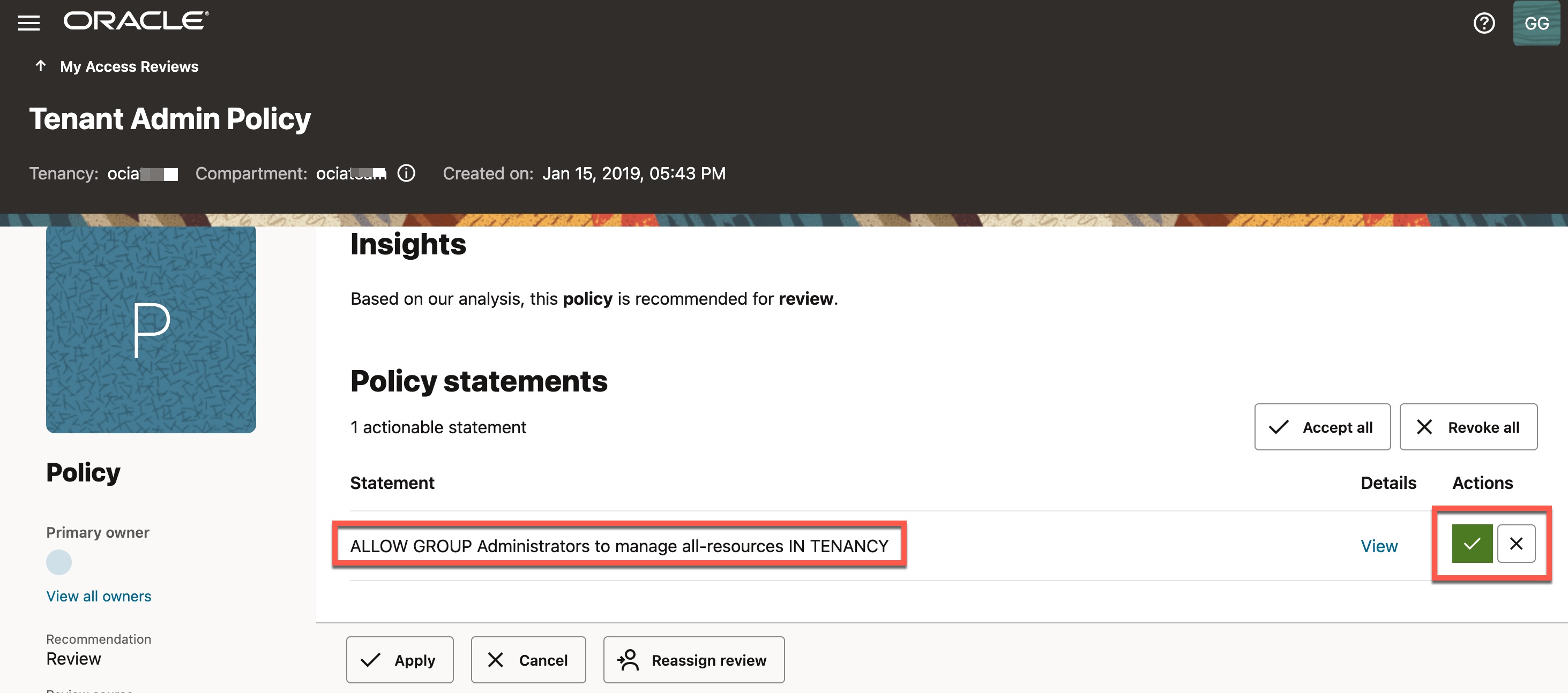
Before making an access decision, optioally, reviewer can click on “View” to see how many users are in the Administrators group and what resources they currently have access to because of this policy.
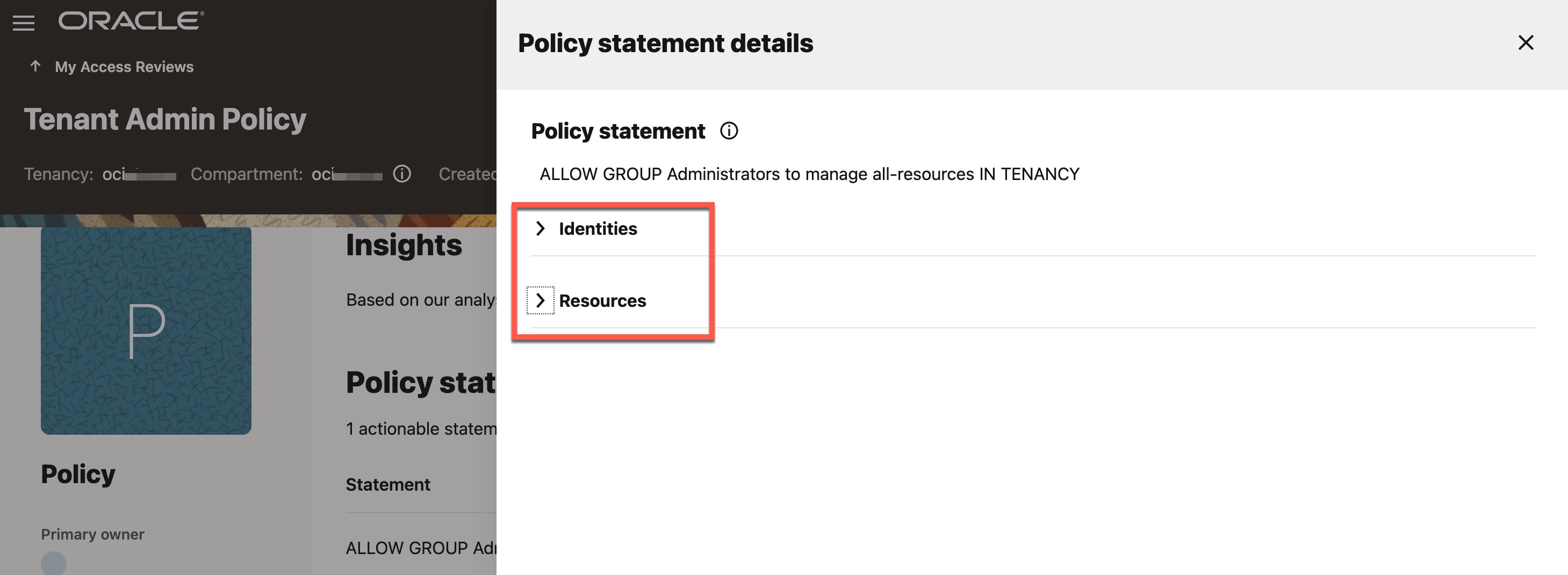
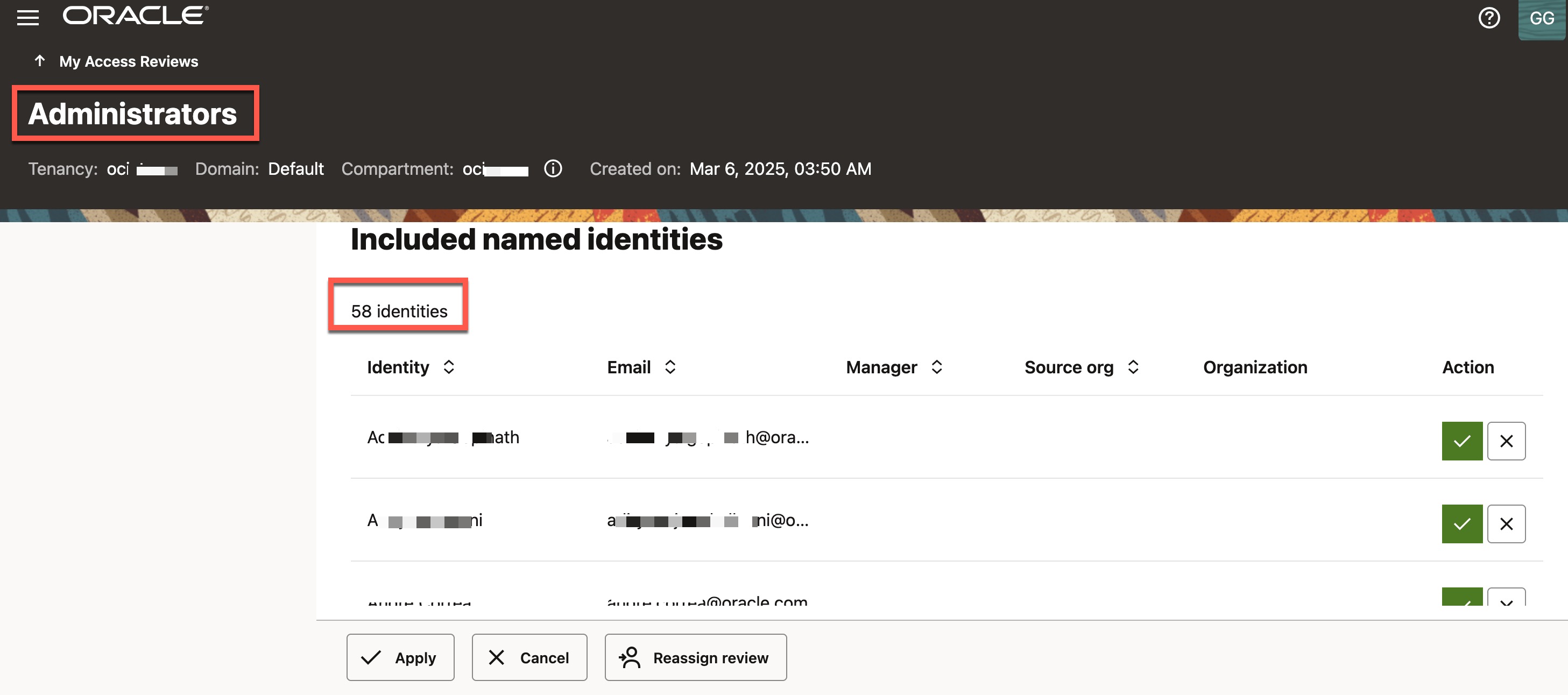
Access review of OCI Administrator Group
This access review is similar to the previous one, but here you are reviewing the membership of the OCI “Administrators” group, which holds significant privileges by granting full administrative access to all its members. It is crucial to regularly review and certify that only eligible users are assigned to this group. Refer to the image below, which is self-explanatory.
Use Case # 4 : Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege to Prevent Toxic Combinations (SoDs)
To support compliance and reduce risk, Oracle Access Governance enables the enforcement of Segregation of Duties (SoDs) by applying metadata-driven rules through Access Guardrails, which define criteria to automatically detect and remediate risky access combinations—ensuring a secure and compliant access control environment.
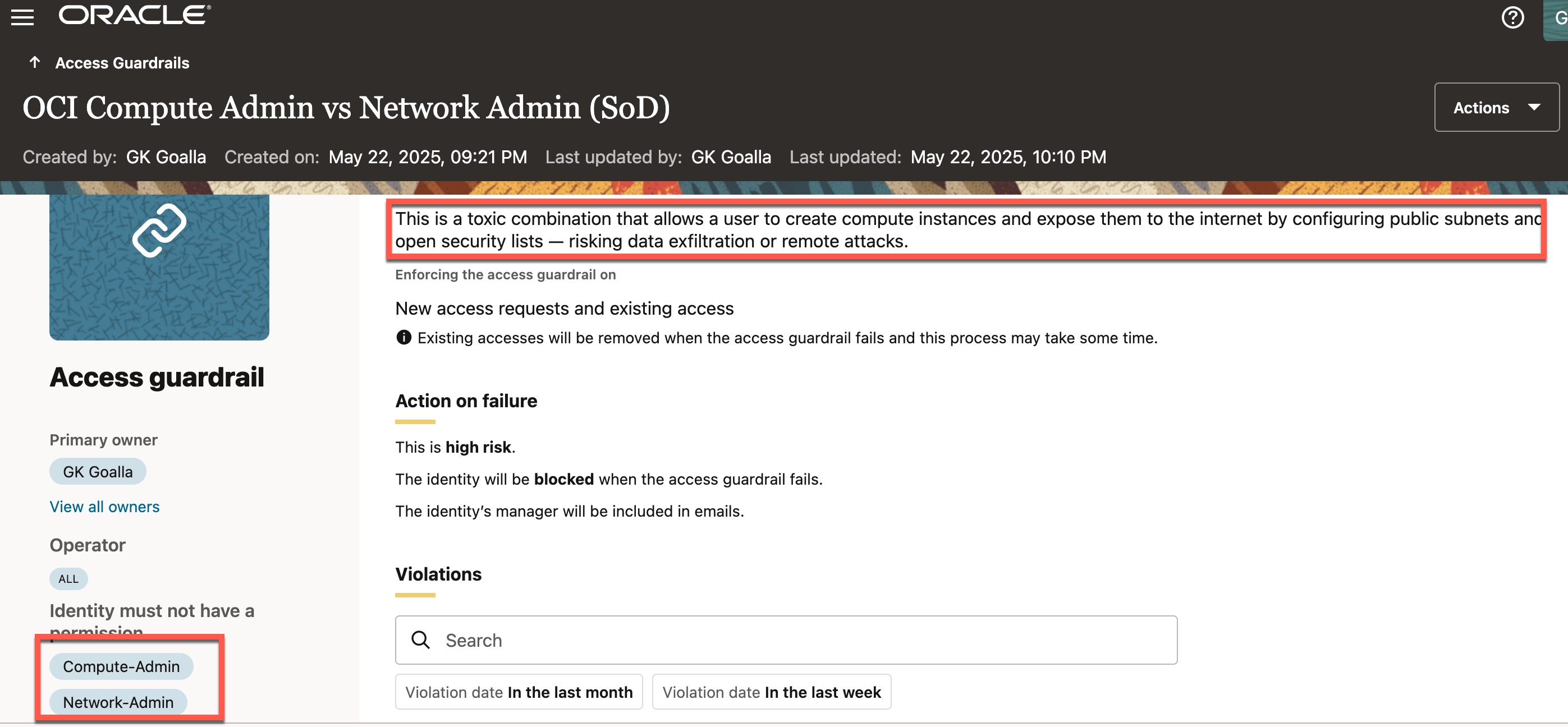
A common example of a toxic access combination is when a user has full access to both Networking and Compute resources. This poses a significant security risk, as the user can launch compute instances and expose them to the internet via public subnets and permissive security lists—risking data exfiltration or remote attacks.
Here is the definition of an access guardrail for this example. This guardrail essentially states that a user cannot have both “Compute-Admin” and “Network-Admin” permissions in OCI, as having both results in excessive and risky access.
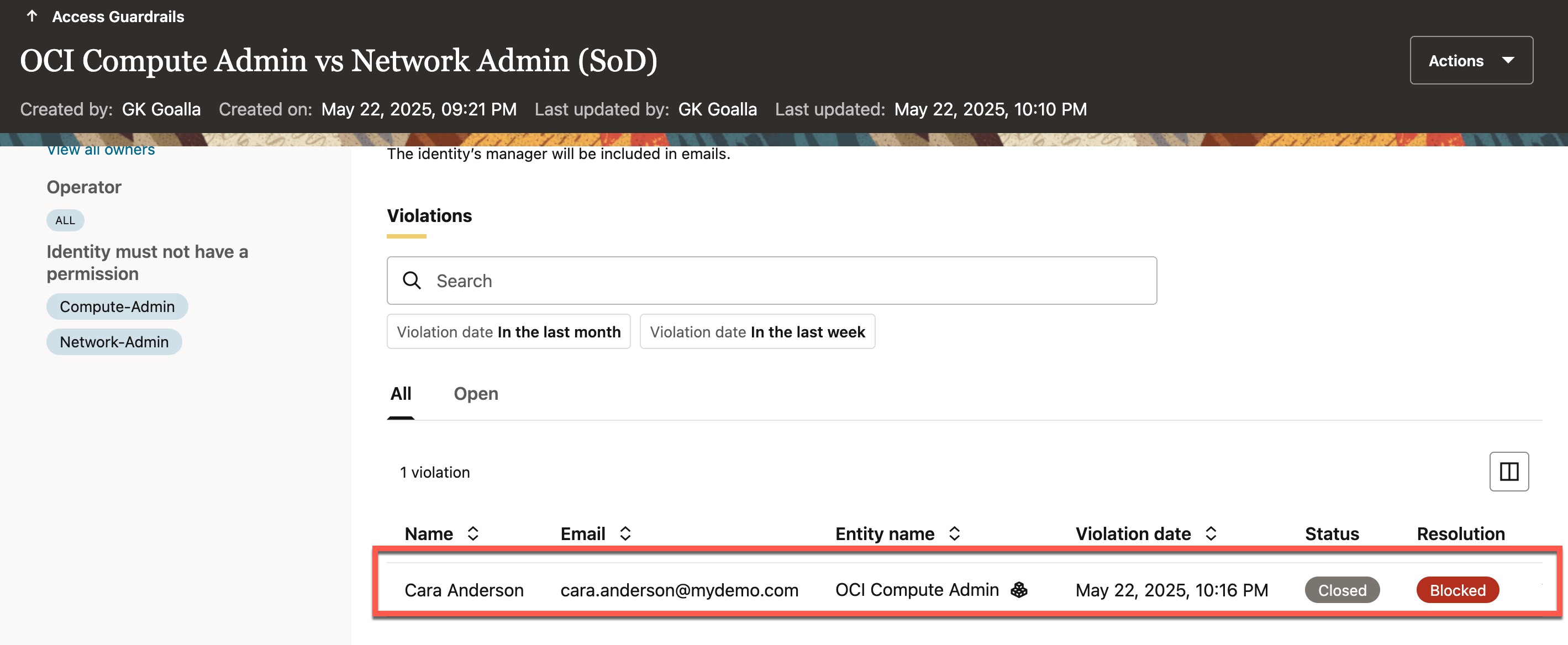
If a user who already holds one of these permissions attempts to request the other, the access guardrail immediately detects the violation and blocks the request. The image below shows an access violation for “Cara Anderson,” who already has the “Network-Admin” permission and tries to request “Compute-Admin” access—promptly blocked by the access guardrail.
This wraps up the four key access governance use cases for OCI—hope you found it insightful!
By the way, what we’ve explored here is just scratching the surface of Access Governance—it can help address many more use cases beyond what we’ve covered
To summarize, this blog post covered how to integrate an OCI tenancy with Access Governance and highlighted the key use cases it supports to enhance access visibility and ensure compliance.
Final Thoughts:
Oracle Access Governance for OCI empowers organizations to manage access with confidence—enhancing visibility, enforcing least privilege, and ensuring compliance. It’s a key step toward securing your cloud environment efficiently and effectively.
Next Step : If you’re using OCI and haven’t yet implemented Oracle Access Governance, now is the time! See the Access Governance pricing for OCI here and it’s just $0.10 per OCI user per month.
