When you’re working with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) at scale, you quickly move beyond a single tenancy. Organizations split workloads across multiple tenancies for billing separation, regional compliance, environment isolation, or to enforce organizational boundaries between business units. OCI Organizations help consolidate billing and commitments, but they don’t automatically solve the challenge of access governance.
Each tenancy remains an independent security boundary with its own users, groups, compartments, and IAM policies even when federated to the same corporate IdP. This means managing IAM in multiple tenancies typically results in managing multiple silos.
That’s exactly where Access Governance (AG) comes in. By onboarding multiple OCI tenancies, including parent and child tenancies in an Organization, into a single AG instance, you can establish a single centralized access governance control plane.
Onboarding Multiple Tenancies to a Single AG Instance
The first step is onboarding each tenancy into the AG instance. This isn’t automatic, you explicitly integrate each tenancy by setting up the required OCI IAM policies and service users in that tenancy.
This design preserves tenancy isolation:
- Child tenancies must grant the needed permissions (like manage policies, manage domains, read audit-events, inspect all-resources) to the AG integration user
By doing this, you enable the AG instance (which might live in your parent tenancy) to manage access governance consistently across all onboarded tenancies.
Including “cloudAccountName” as part of User Correlation Rules
One challenge when unifying multiple tenancies is correctly correlating identities that might share the same username or email across tenancies.
The OCI integration in AG provides various attributes and one of the key ones is cloudAccountName, which captures the OCI tenancy name.
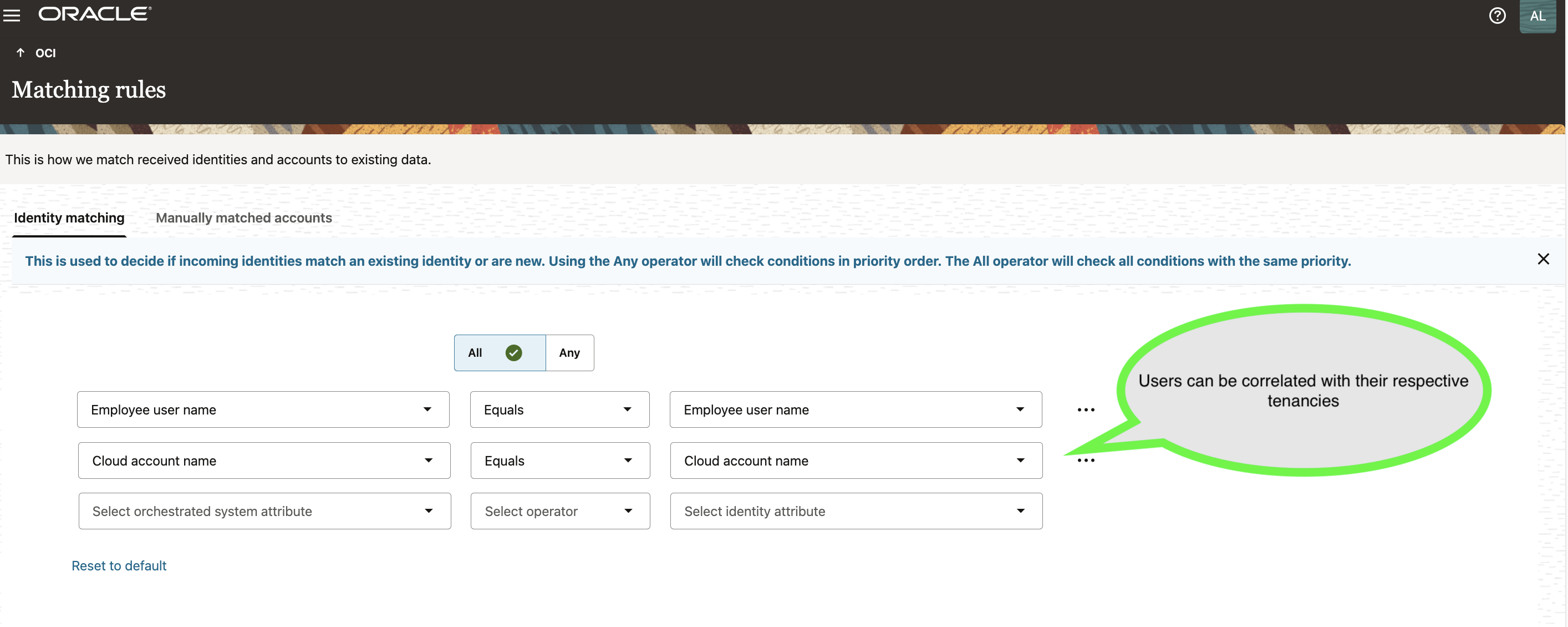
During onboarding, you define matching rules that include the cloudAccountName attribute:
- Ensures that users are uniquely correlated with their tenancy of origin
- Prevents ambiguous identity matches
The image shows matching rule configuration that includes cloudAccountName to ensure correct user correlation per tenancy.
Configuring “cloudAccountName” as an Identity Attribute
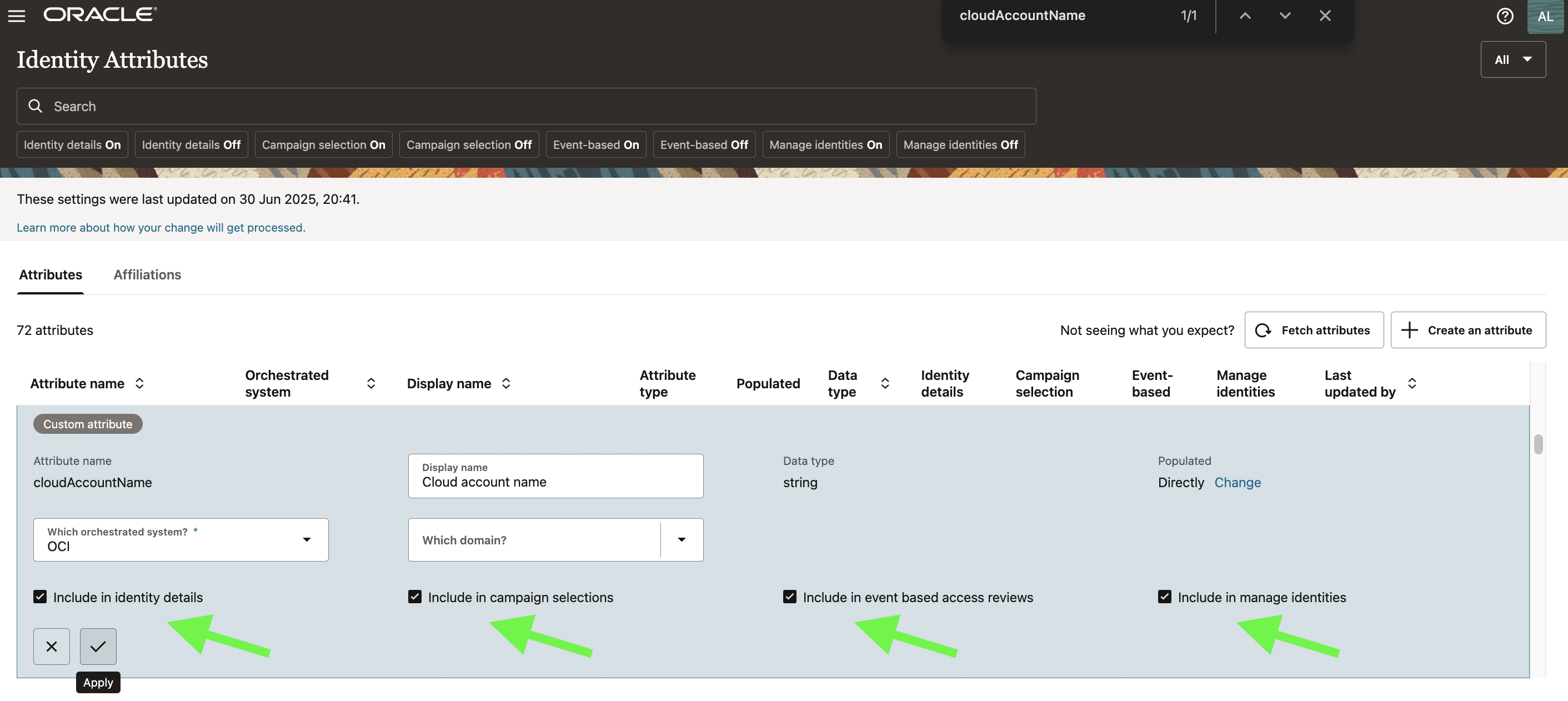
To make tenancy context usable throughout AG, you configure cloudAccountName in the Identity Attributes section:
This enables the tenancy label to show up in:
- Identity details
- Campaign selection
- Event-based reviews
- Manage Identities views
The image shows enabling cloudAccountName in Identity Attributes so it’s visible in all the key AG views.
Enterprise-Wide Browser and Tenancy Filtering
Once tenancies are onboarded, AG presents all users, groups, policies, and resources in a single enterprise-wide view.
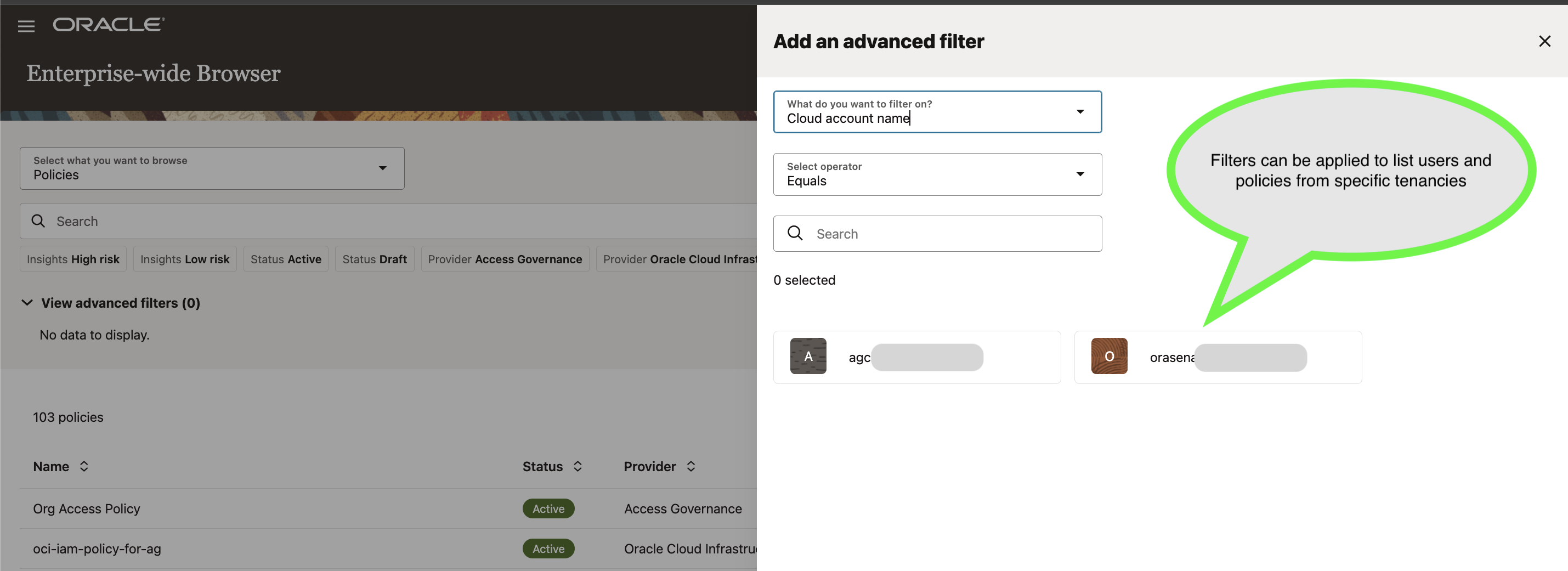
The important part here is the filtering:
- Use cloudAccountName to slice the data by specific tenancy
- Supports both broad organizational views and tenancy-specific deep-dives
The image shows using advanced filters on cloudAccountName to see users/groups/policies/resources specific to a tenancy.
Defining Identity Collections Targeted by Tenancy
AG supports defining Identity Collections, which represent logical groupings of users that share attributes.
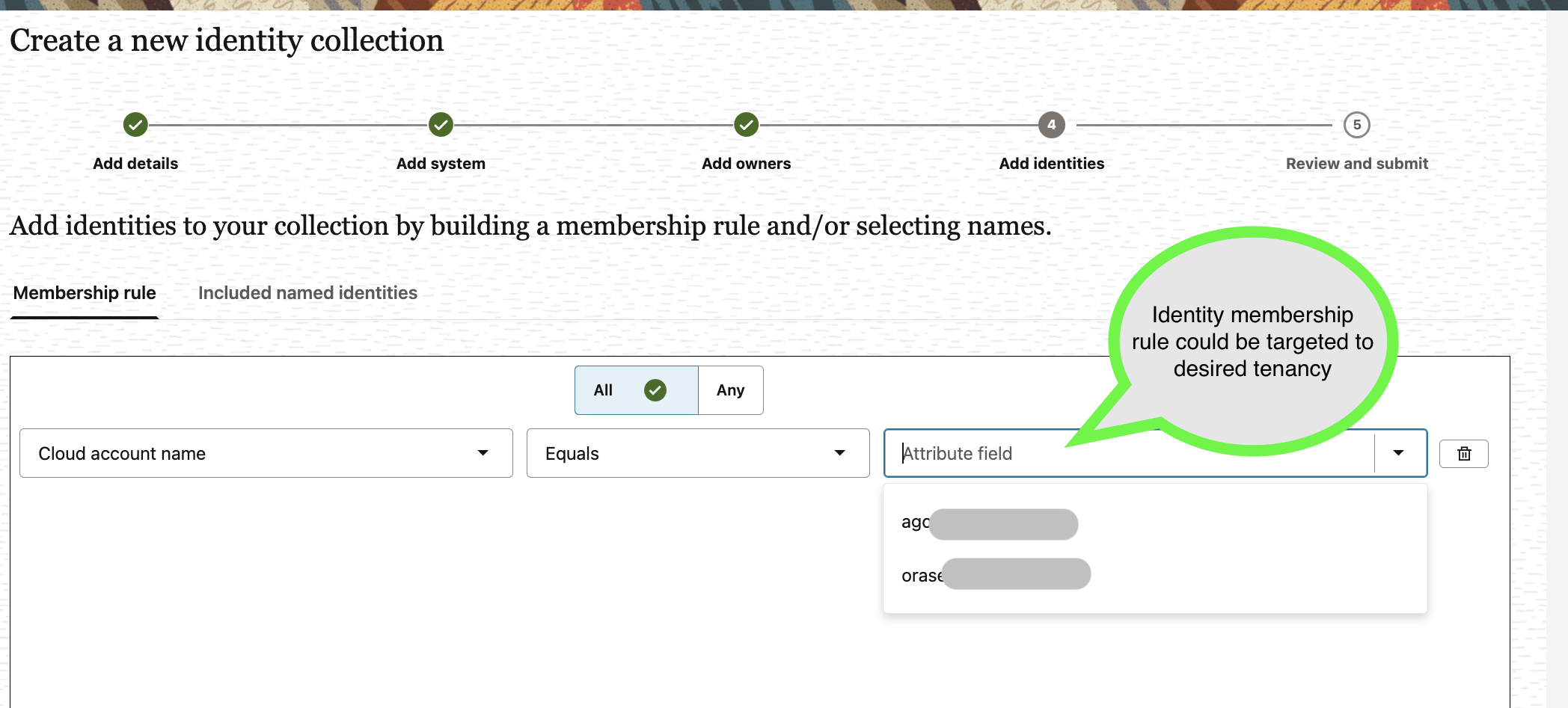
By including cloudAccountName in collection membership rules, you can:
- Target users from specific tenancies
- Build collections that mirror your actual business unit or regional structure
The image below shows Identity collection rule using cloudAccountName to target a specific tenancy’s users.
Managing Access Control Policies Across Tenancies
Access Bundles, Roles, and Policies in AG can include OCI groups and app roles from specific tenancies.
Your access control models can stay tenancy-aware:
- Assign users to tenancy-specific OCI groups via bundles
- Include tenancy context in provisioning decisions
This respects OCI tenancy isolation while delivering central governance over lifecycle management.
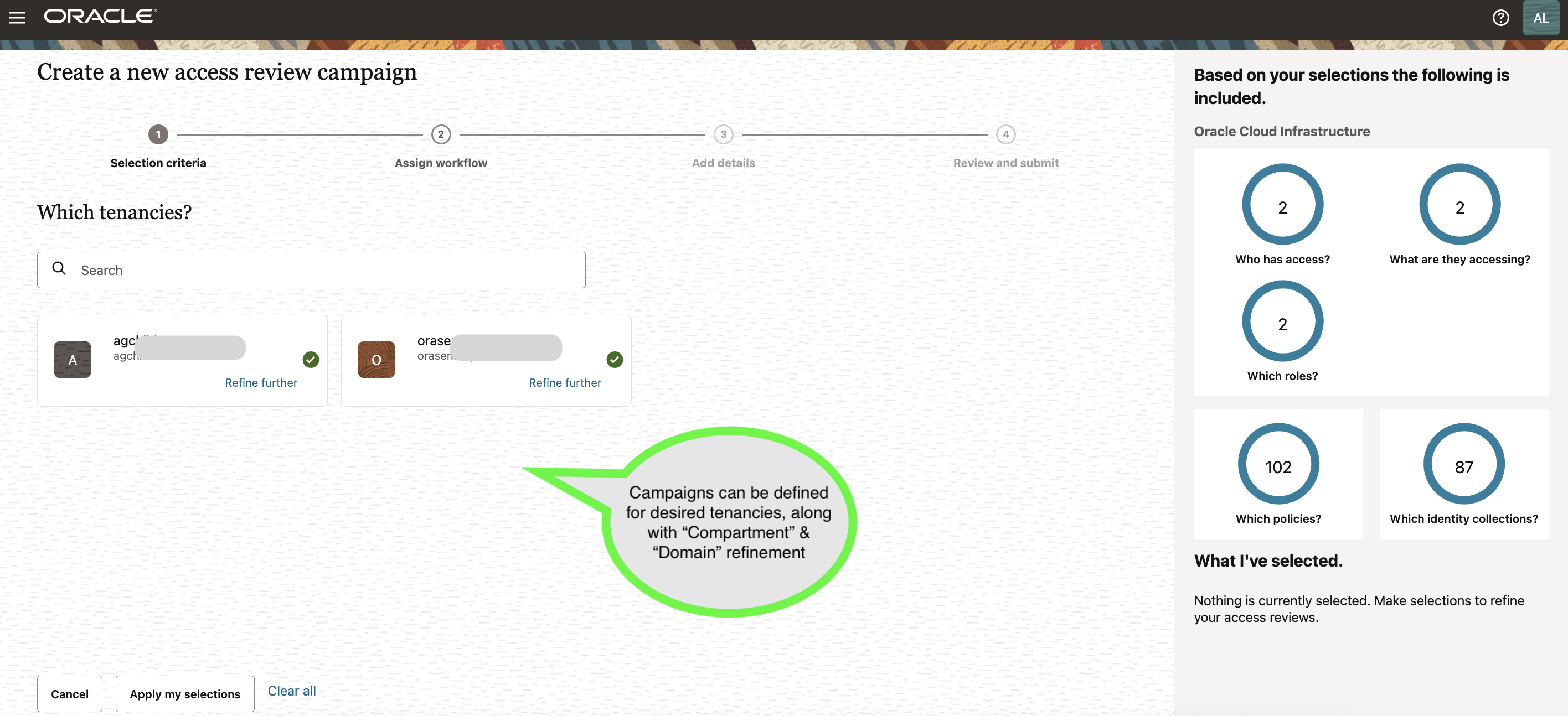
Running Access Reviews Across Tenancies
AG also enables consistent access review campaigns across one or more OCI tenancies.
You can:
- Run reviews scoped to a specific tenancy
- Combine multiple tenancies in a single campaign
- Filter and refine by compartment, domain, or tenancy
The image below shows an access review campaign that could span specific tenancies with the ability to be refined further.
Closing Thoughts
Using a single Oracle Access Governance instance to manage multiple OCI tenancies doesn’t break tenancy isolation – it requires explicit delegation of IAM management permissions during onboarding.
This model gives central security and compliance teams the visibility and control they need to:
- See who has access to what across the entire OCI Organization
- Define and enforce consistent access governance policies
- Run centralized, auditable access reviews
Granting this level of central authority is a strategic governance decision. However, adopting centralized visibility and control simplifies user and access governance, providing organizations with a more consistent, secure, and compliant framework that enhances overall oversight and efficiency.

