Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Audit Logs provide critical visibility into who did what, when, and where within your cloud environment. These logs are essential for security monitoring, compliance reporting, and investigating potential security incidents. The Security Fundamentals Dashboards, particularly the Identity Security dashboard, leverages these OCI Audit logs to continuously monitor and improve the security posture of our customers’ OCI tenancy. By analyzing authentication patterns, permission changes, and resource access attempts captured in audit logs, the dashboard enables organizations to adopt essential cyber hygiene practices such as identifying inactive users, detecting privilege escalation, and monitoring configuration changes. This proactive approach to identity security governance helps organizations maintain compliance with security frameworks while providing actionable insights to remediate potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
The Challenge
However, OCI customers face a challenge: by default, OCI Audit Logs in the native logging service are only searchable for up to 14 days at a time, making it difficult to conduct comprehensive historical analysis. While OCI’s Service Connector Hub offers a way to continuously ingest logs from OCI Logging to OCI Log Analytics, it has a notable limitation: it only captures logs from the moment the connector is created. This presents a significant problem for organizations that need to analyze historical Audit Logs predating their connector setup.
Consider this scenario: your security team identifies suspicious activity and needs to investigate user actions across your OCI environment for the past year. With just the Service Connector Hub, you would only have logs available from when you set up the connector—leaving a potentially critical gap in your security timeline.
In today’s cybersecurity landscape, having access to historical audit data is not just a nice-to-have but a necessity. When security incidents occur, security teams need the ability to look back over extended periods—often up to a year—to understand the full scope and timeline of events.
Key Monitoring Requirements
The solution offers several key benefits:
- Complete historical coverage: Ability to collect audit logs dating back a full year
- Seamless integration: Works with existing Security Fundamentals Dashboards
- Scalable collection: Handles large volumes of historical audit data
- Automated process: Management Agent can run the collection job based on the interval and log data processing is automated
- Enhanced security: Supports OCI Resource Principal-based authentication, eliminating the need to store API keys or credentials in configuration files
Solution Design
To address this challenge, we can leverage OCI Log Analytics’ REST API log collection method to ingest historical audit logs spanning back a full year. This approach complements the Service Connector Hub by filling the historical data gap while ensuring ongoing log collection. Additionally, Log Analytics REST API log collection supports OCI Resource Principal-based authentication for searching and collecting logs using the management agent, which further solidifies the solution from a maximum security perspective. This authentication method eliminates the need for storing API keys or credentials in configuration files, reducing security risks while maintaining comprehensive audit capabilities.
Reference Architecture:
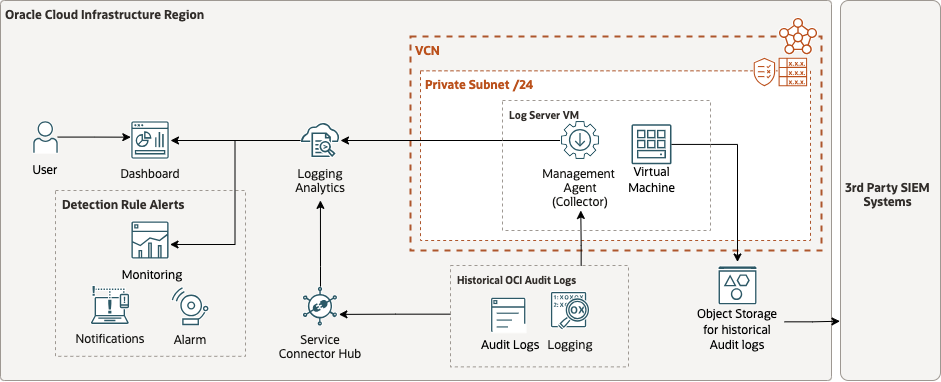
Prerequisites
- Set up service policies for Oracle Cloud Log Analytics. See Enable Access to Log Analytics and Its Resources and Prerequisite IAM Policies in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation.
- Install the Management Agent on a client host VM which has http or https access to your endpoint server, we will use this host for Log Source entity association. See Set Up Continuous Log Collection From Your Hosts.
- On Unix-based hosts, the user that installs management agent is mgmt_agent for the manually installed management agent, and oracle-cloud-agent when the management agent is a plugin enabled with Oracle Cloud Agent.
Implementation Overview
Let’s walk through the implementation process for collecting historical OCI audit logs using the REST API ingestion method.
- Create a dynamic group for the Management Agent to enable resource principal authentication
- Configure IAM policies to grant the dynamic group access to audit logs and Log Analytics resources
- Create a host entity in Log Analytics to represent the Management Agent
- Configure a custom log source and parser for historical OCI audit logs
- Associate the Management Agent with the log source using resource principal authentication
- Verify Ingestion and Use Security Fundamentals Dashboards
Step 1: Create dynmaic group for the Management Agent
-
Create Dynamic Group for the Management Agent installed on the VM or enabled via Oracle Cloud Agent:
- Navigate to the OCI Console
- Go to Identity & Security > Domains > Default domain > Dynamic Groups
- Click Create Dynamic Group
- Enter a name (e.g., ManagementAgentDynamicGroup)
- Enter a description (e.g., Dynamic group for Management Agents in specific compartment)
- In the matching rules section, add the following rule:
ALL {resource.type='managementagent', resource.compartment.id='ocid1.compartment.oc1..aaaaaa[REDACTED]'} - Click Create
-
Create OCI policy for management agent dynamic group resource principal
Note: The policy statements above use the dynamic group name ManagementAgentDynamicGroup that we created in the previous step. These policies grant the necessary permissions for the Management Agent to read audit logs and manage log groups within the tenancy.
- Navigate to the OCI Console
- Go to Identity & Security > Policies
- Click Create Policy
- Enter a name (e.g., ManagementAgentAuditLogPolicy)
- Enter a description (e.g., Policy to allow Management Agent to read audit logs and manage log groups)
- Select the compartment (typically the root compartment or tenancy)
- In the policy builder section, add the following policy statements:
allow dynamic-group ManagementAgentDynamicGroup to manage log-groups in tenancy allow dynamic-group ManagementAgentDynamicGroup to use log-content in tenancy allow dynamic-group ManagementAgentDynamicGroup to {AUDIT_EVENT_READ} in tenancy allow dynamic-group ManagementAgentDynamicGroup to {AUDIT_EVENT_READ} in tenancy allow dynamic-group ManagementAgentDynamicGroup to use metrics in tenancy allow dynamic-group ManagementAgentDynamicGroup to {LOG_ANALYTICS_LOG_GROUP_UPLOAD_LOGS} in tenancy - Click Create
Step 2: Update the Agent Configuration
To enable the Management Agent to use the REST API for log collection, you need to update its configuration properties:
-
SSH to the VM host where the Management Agent is installed:
ssh opc@<<your-vm-ip-address>> -
Switch to the root user:
sudo su - -
Navigate to the agent configuration directory:
-
If you’re using Oracle Cloud Agent:
cd /var/lib/oracle-cloud-agent/plugins/oci-managementagent/polaris/agent_inst/config/ -
If you manually installed the Management Agent (standalone installation):
cd /opt/oracle/mgmt_agent/agent_inst/config
-
-
Open the emd.properties file for editing:
vi emd.properties -
Append the following two parameters to the bottom of the file:
loganalytics.rest_api.enable_oci_api=true loganalytics.rest_api.report_interval=600Note: The
loganalytics.rest_api.report_intervalparameter sets the collection interval in seconds. The default is 300 seconds (5 minutes), but in this example, we’ve set it to 600 seconds (10 minutes). You can adjust this value based on your requirements. -
Save the file and exit the editor.
-
Restart the Management Agent to apply the changes.
-
If you’re using Oracle Cloud Agent:
-
systemctl restart oracle-cloud-agent
-
-
If you manually installed the Management Agent (standalone installation):
-
systemctl restart mgmt_agent
-
-
Step 3: Import the Audit Log Source for the Historical Logs Using REST API
- Import OCI Audit historical Log Source:
- Navigate to Log Analytics > Administration > Administration Overview
- Click Import Configuration Content
- Download the Log Source OCI_Audit_Logs_Hist from the Github repo here and drop the zip file (e.g., OCI_Audit_Logs_Hist.zip)
- Click Import
-
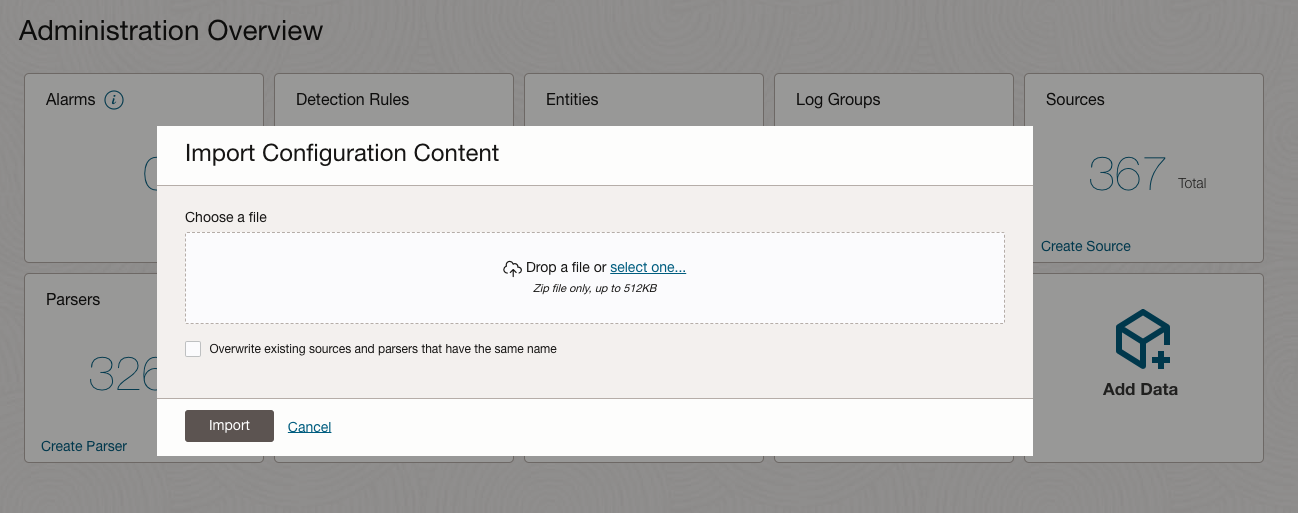
Figure 2: Import the OCI Audit historical log source
- Configure the OCI Audit Historical Log Source:
- Navigate to Log Analytics > Administration > Sources
- Search forOCI_Audit_Logs_Hist in the sources list
- Click on the log source name to open its configuration
- Click Edit in the top right
- Review and verify the following settings:
- Source Type: REST API
- Parser: Ensure OCI Audit hist logs parser is listed
- Entity Type: Host(Linux)
-
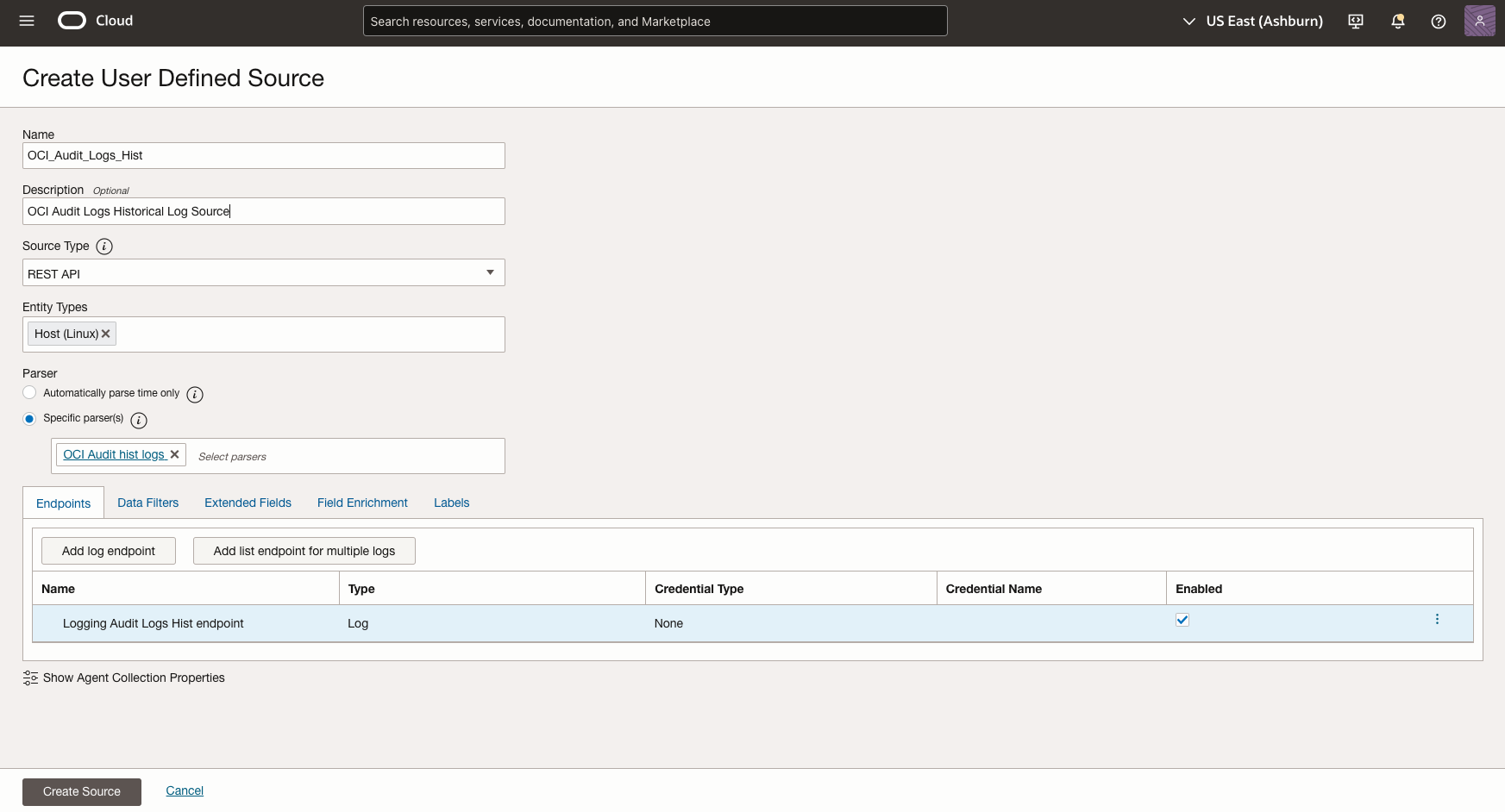
Figure 3: Review the OCI Audit historical log source configuration settings
- Update the Log endpoint for OCI Logging API:
- Navigate to Log Analytics > Administration > Collection Configuration
- Select the Log Collection tab
- Click Create Endpoint
- Enter a name (e.g., Logging Audit Logs Hist endpoint)
- For the Log URL, enter the OCI Logging service API endpoint for your region:
Replacehttps://logging.{region}.oci.oraclecloud.com/20190909/search{region}with your actual OCI region (e.g., us-ashburn-1) The variable {region} is used in endpoint instead of hardcoding the region . Based on where the agent runs it will pick the region using that parameter. - Set HTTP Method to POST
- Request content Type, select JSON
- In the POST Payload section, add the following payload
{ "timeStart": "{START_TIME:yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:00.000}Z", "timeEnd": "{START_TIME+1D:yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:00.000}Z", "isReturnFieldInfo": false, "searchQuery": "search \"ocid1.tenancy.oc1..aaapda/_Audit\" | sort by datetime desc" } - In the Request Headers section, add the following headers:
Content-Type: application/json - Leave Parameters to empty
- Set Log Credential type to None. Note: This leverages the Management Agent’s resource principal authentication, eliminating the need for explicit credentials
- Click Validate
- Click Save changes
-
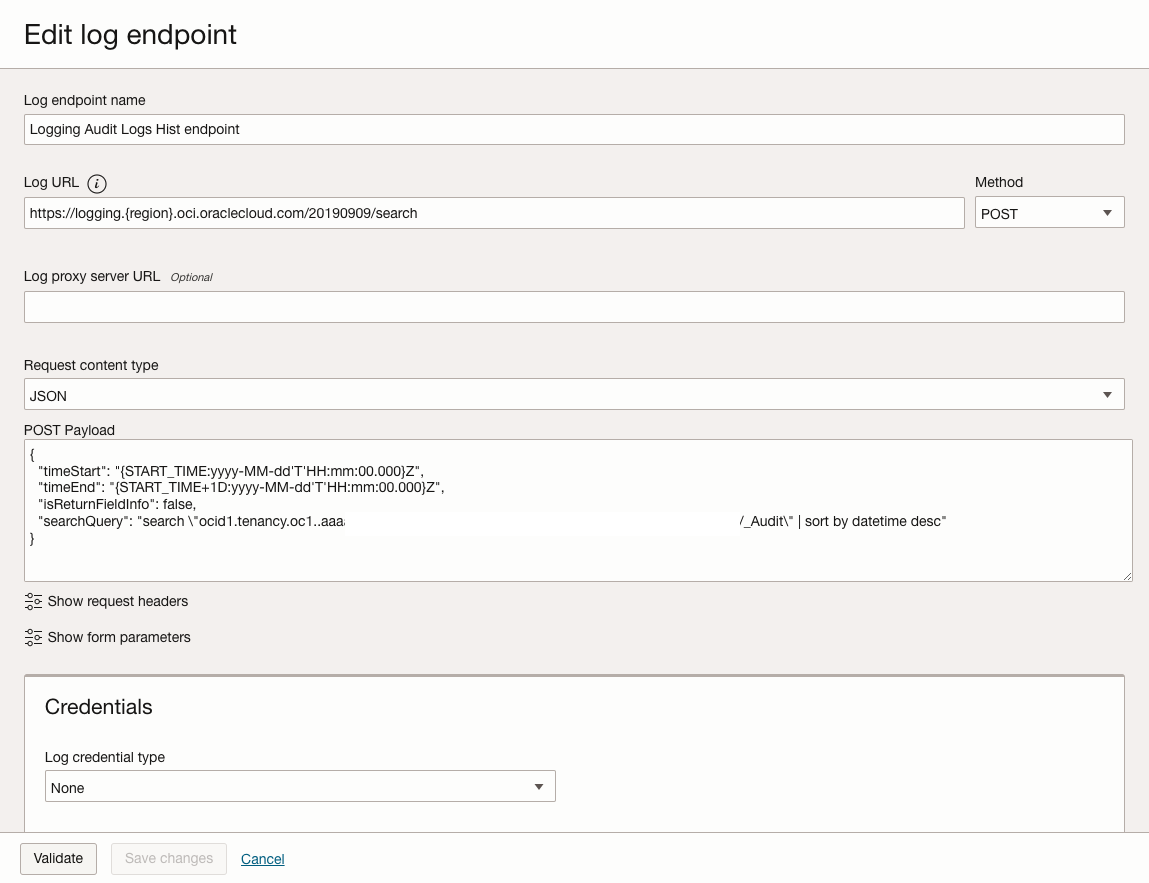
Figure 4-1 Configure the OCI Audit historical log endpoint settings -
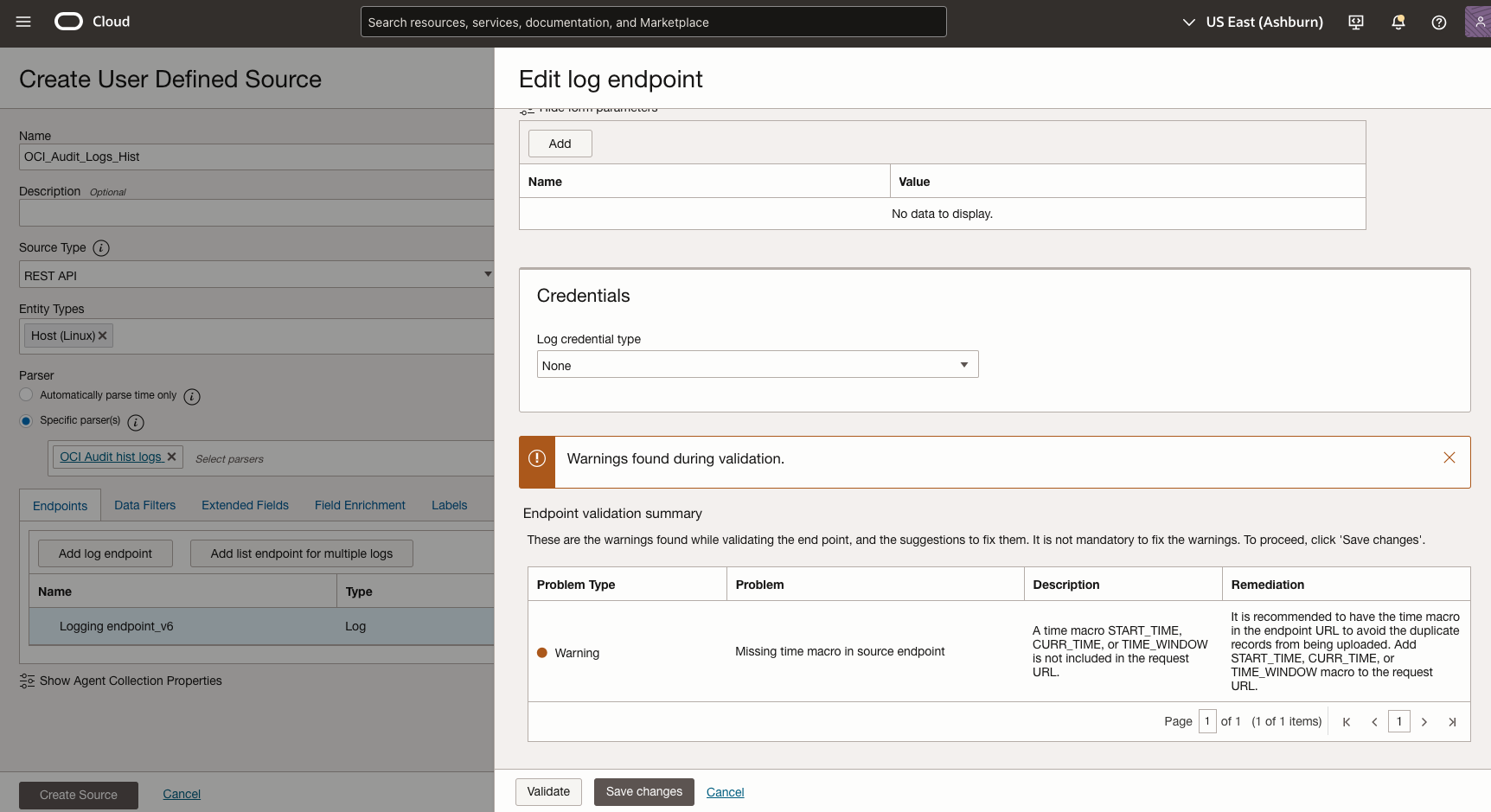
Figure 4-2: Configure the OCI Audit historical log endpoint settings
- Modify Management Agent Collection Properties for the VM Linux Host Entity:
- Navigate to Log Analytics > Administration > Collection Configuration
- Select the Entity Configuration tab
- Find and select your VM Linux Host Entity
- Click Edit
- In the Agent Collection Properties list, locate the following properties and update them:
- Set Historical Data to P365D (this configures the collection to retrieve logs for the past 365 days)
- Set Enable Filter Duplicate Records to true (this prevents duplicate log entries)
- Click Save Changes to apply the configuration
- The Management Agent will now be configured to collect historical audit logs for up to one year while filtering out any duplicate records
-
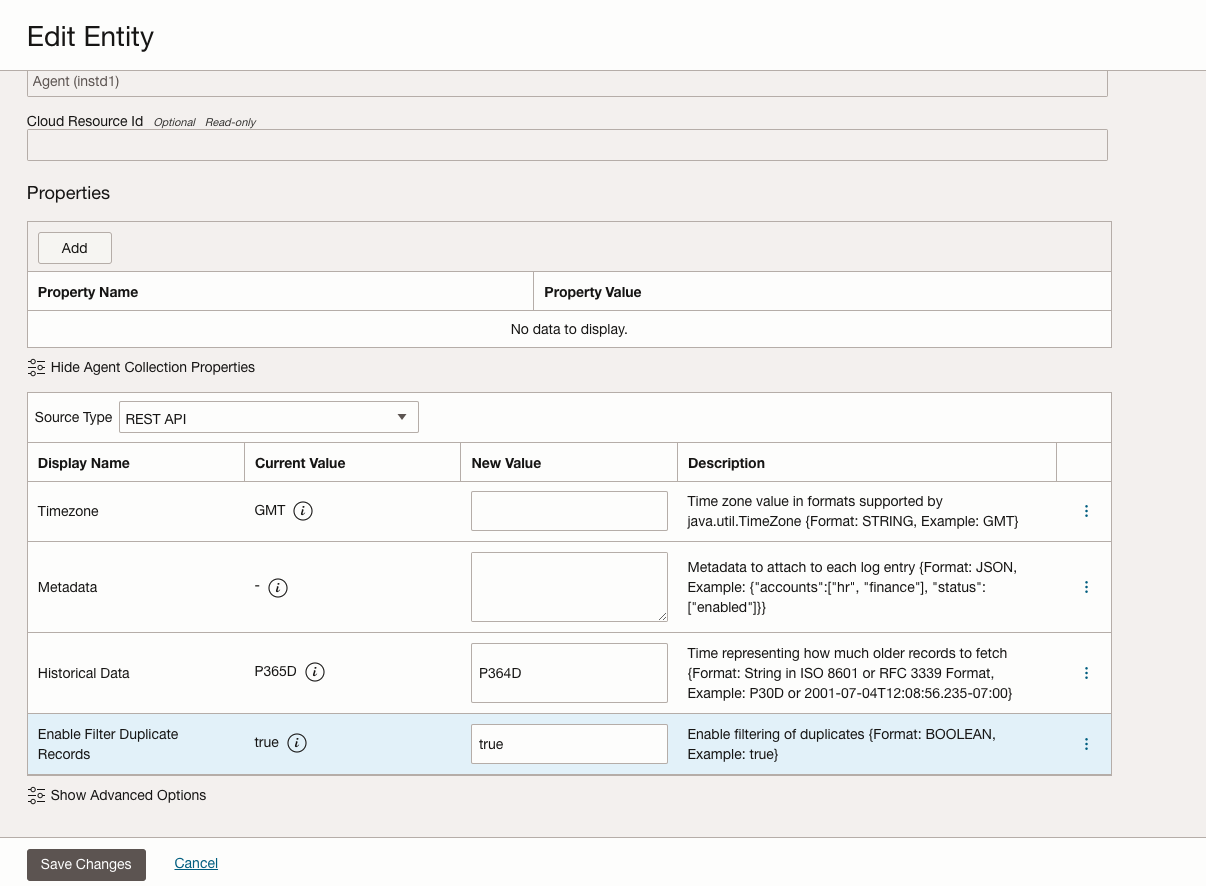
Figure 5: Update the Management Agent collection properties to enable historical data collection and duplicate filtering
- Associate the Entity with your log source and configure log group:
- Navigate to Log Analytics > Administration > Sources
- Select Log Source OCI_Audit_Logs_Hist
- Select the Unassociated Entities menu
- Click Add Association
- Select your Management Agent host entity
- In the Log Group section, select an existing log group or create a new one for your historical audit logs
- Click Create to finalize the association
- Note: This association will push the REST API configuration to the Management Agent, initiating the collection of historical audit logs according to your specified schedule. The Management Agent will use its resource principal authentication to access the logs and ingest them into the selected log group.
-
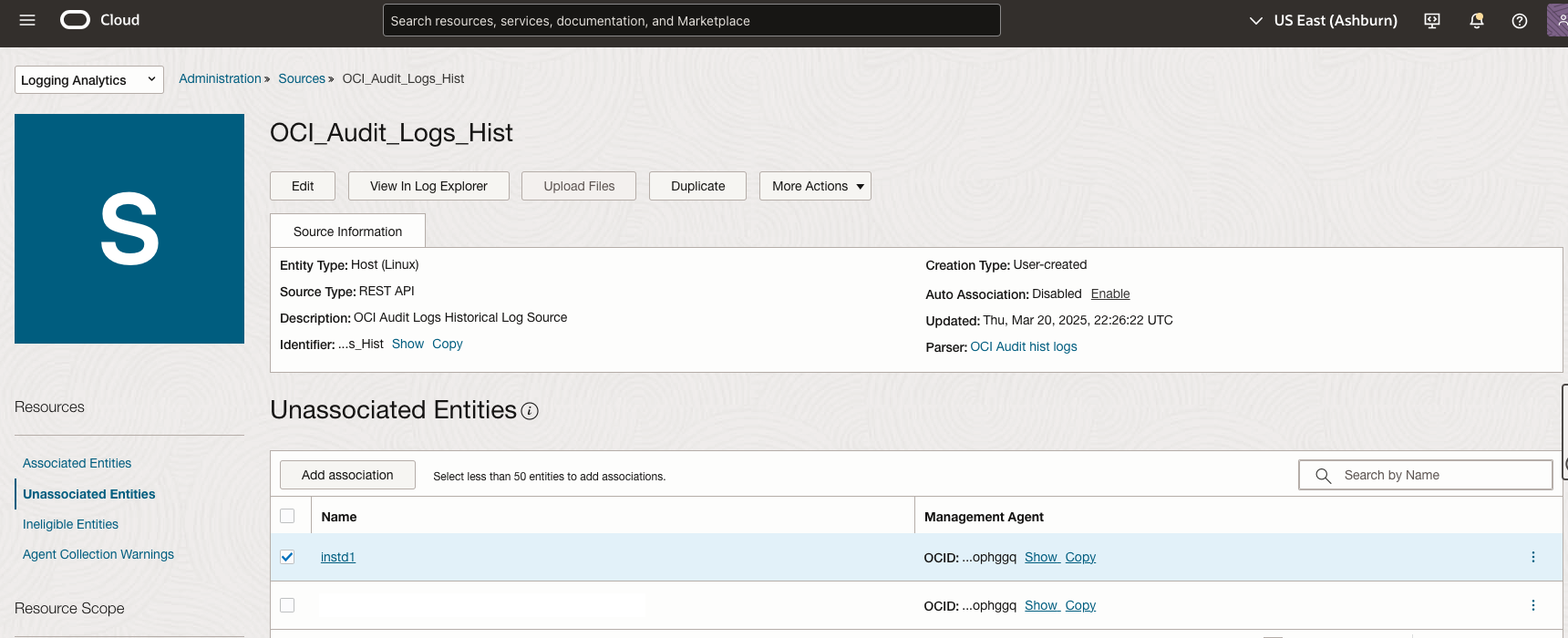
Figure 6: Associate the Management Agent host entity with the OCI_Audit_Logs_Hist log source and configure log group
Step 4: Verify Ingestion and Use Security Fundamentals Dashboards
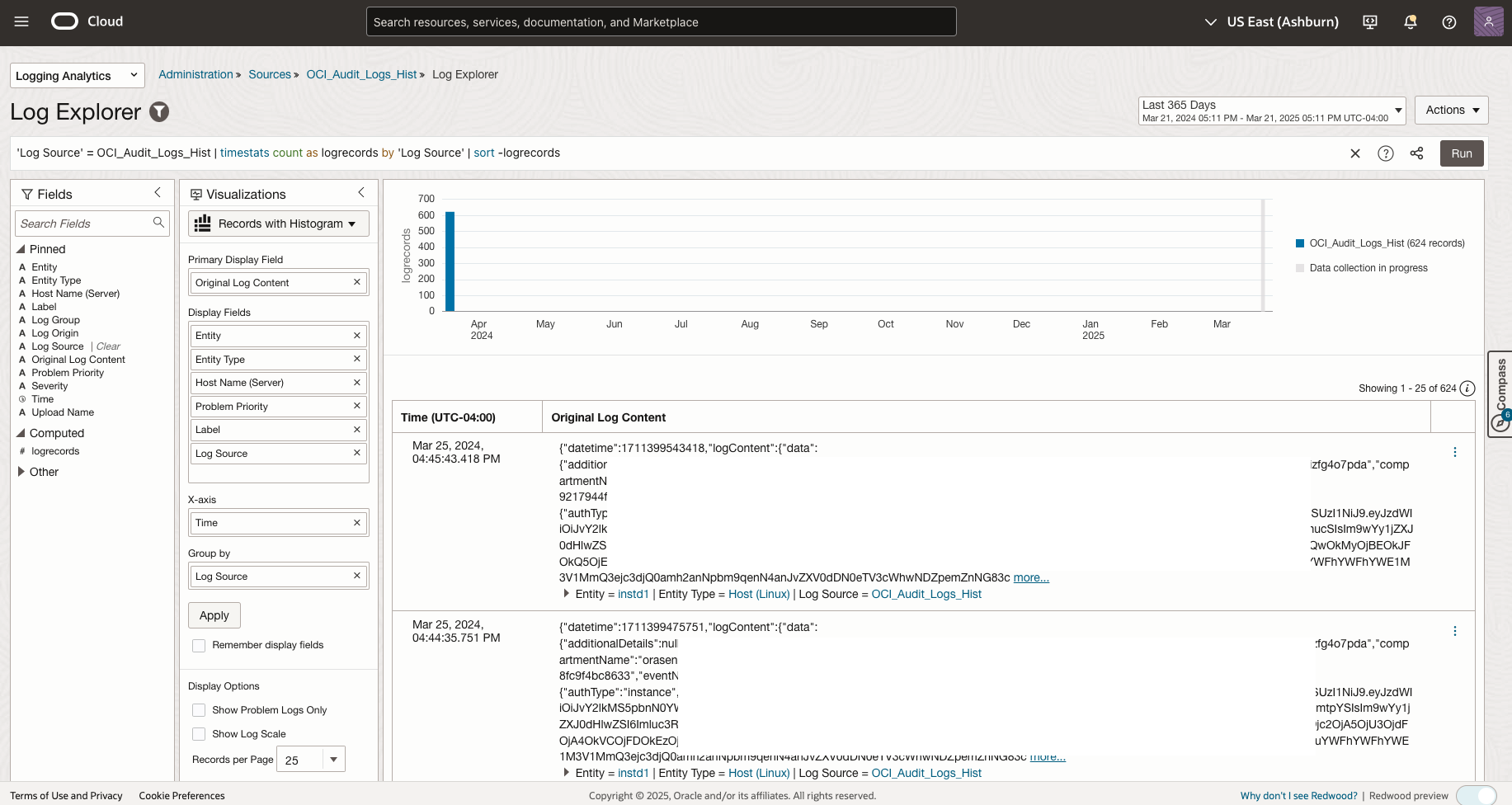
Once you’ve successfully ingested the historical audit logs, you can verify them in the OCI Console:
- Navigate to Log Analytics > Log Explorer
- Create a query to view your ingested audit logs
Log Source = 'OCI_Audit_Logs_Hist' | timestats count as logrecords by 'Log Source' | sort -logrecords - Check that historical data is present and properly structured
With the historical data now available in Log Analytics, you can leverage the Security Fundamentals dashboards to analyze this extended dataset.
Integration with Security Fundamentals Dashboards
The OCI Security Fundamentals Dashboards provide pre-built visualizations for security monitoring and compliance reporting. With your historical audit logs now ingested, these dashboards can display a complete picture of activity across your OCI environment.
Identity Security Plus Dashboard Github download link here
Key security insights include:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Insights:
- User password reset activities and trends
- User creation, modification, and deactivation patterns
- Identification of dormant users (inactive for 30+ days)
- Group membership changes and policy modifications
- Identity Provider (IdP) configuration changes and group mappings
- Authentication patterns including successful and failed login attempts
- API key creation and management
- Top identity event producers across your environment
-
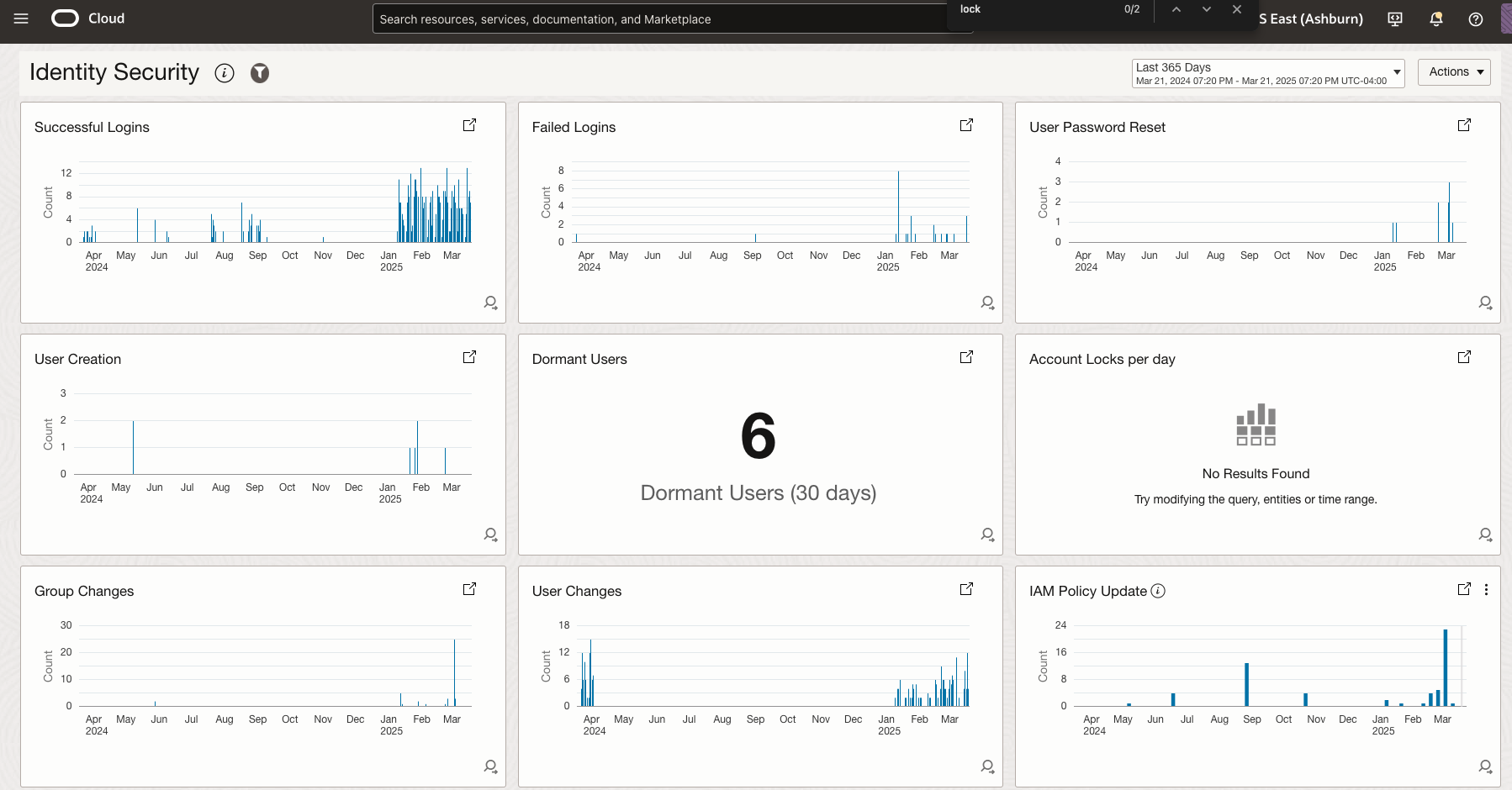
Figure 8: Security Fundamentals Dashboard visualizing historical audit logs in OCI Log Analytics
Alternative Approaches for CSV Export
It’s worth noting that there are existing tools specifically designed for exporting OCI audit logs to CSV format:
- OCI Audit Analyzer: Thanks to the great work and contribution from Josh Hammer, his GitHub repository contains a useful script for querying OCI Audit data for a user’s activity during a specific date range, outputting the activities into a CSV file. This is particularly useful for focused analysis of individual user actions.
- Example usage:
python3 analyze-oci-audit.py --startdate 2024-12-02 --enddate 2024-12-03 --userid ocid1.user.oc1..
- Example usage:
- Export OCI Audit Logs in CSV format for a custom time range: Oracle also provides a custom Python script for exporting OCI Audit Logs in CSV format for any time range up to 365 days. This script handles the pagination of results and can be scheduled for regular execution.
While these tools are excellent for exporting audit logs to CSV for analysis, our REST API approach focuses on ingesting the historical logs directly into OCI Log Analytics, enabling integration with Security Fundamentals Dashboards and more advanced querying capabilities.
Extending Beyond OCI Audit Logs: A Versatile Paradigm for Historical Data Collection
While this solution was designed specifically for OCI Audit Logs, the underlying pattern of using Management Agent with Resource Principal authentication for REST API-based historical data collection can be extended to many other OCI services. This creates opportunities for organizations to build comprehensive historical datasets across their cloud environment without being limited by default retention windows.
Some compelling use cases include:
-
Monitoring Metrics Historical Archive
- Collect and analyze long-term performance trends
- Workround the 90 days Monitoring service Storage limits
- Build historical baselines for anomaly detection
-
Database Backup and Recovery Analytics
- Track backup and recovery operations over extended periods
- Analyze recovery time objectives (RTO) trends
- Support compliance requirements with comprehensive backup history
- Optimize backup strategies based on historical patterns
-
Cloud Guard Problem History
- Maintain historical records of security findings over 180 days
- Track remediation effectiveness across time
- Support security posture trending analysis
By leveraging the same architectural approach demonstrated here – combining Management Agent’s Resource Principal authentication with REST API ingestion – organizations can create a unified historical data platform within OCI Log Analytics. This enables comprehensive historical analysis across multiple services while maintaining strict security controls and eliminating the need for credential management.
Conclusion
By implementing this unified approach that combines Service Connector Hub for real-time log collection with REST API ingestion for historical analysis, organizations can establish a seamless OCI Audit Logs security solution that delivers complete visibility across their cloud environment. Maintaining a full year of audit history addresses critical security requirements for threat hunting, compliance audits, and forensic investigations – particularly when analyzing sophisticated attacks that may have dormant periods between initial compromise and active exploitation.
For organizations using external SIEM solutions, this approach provides enriched OCI audit data that can correlate with other security telemetry while avoiding cloud-native visibility gaps. The solution complements SIEM architectures by serving as either a primary audit data source or a historical reference repository, particularly valuable for investigations requiring cross-platform analysis.
The included OCI Audit Logs export tools (OCI Audit Analyzer and Export OCI Audit Logs in CSV format for a custom time range) remain available for targeted exports analysis scenarios, ensuring flexibility for security teams with diverse operational requirements.
References
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Security Fundamentals Dashboards Using OCI Log Analytics
- OCI Log Analytics: Collect Logs Using REST API Collection Method
- Generate Identity and Access Management Reports in OCI Log Analytics
- OCI Audit Analyzer on GitHub
- Export OCI Audit Logs in CSV Format Tutorial
- OCI Documentation: Log Analytics API
- OCI Documentation: Audit API
- OCI Documentation: Set Up REST API Log Collection
- ZFS Storage Appliance Observability and Monitoring
- Identity Security Plus Dashboard
- Log Source: OCI_Audit_Logs_Hist
Acknowledgments
- Kumar Varun, Log Analytics Product Management
- Xin Xu, Log Analytics Development
- Satinder Singh, Log Analytics Development
- Guru Poosamalai, Log Analytics Development
- Josh Hammer, Field CISO
- Waymon Whiting, North America Cloud Infrastructure Engineering
