Introduction
Welcome to part 9 of our blog series on enhancing SaaS applications with AI and machine learning capabilities. In this post, we’ll go through how to utilize Machine Learning in Oracle Database (OML) to generate vector embeddings and train a classification model using SaaS data.
Machine Learning in Oracle Database
Oracle provides over 30 high-performance, in-database algorithms, enabling immediate use of models in your applications. By keeping the data inside the database, organizations can simplify their infrastructure while ensuring better data synchronization and security. Oracle Machine Learning Notebooks support various languages such as SQL, PL/SQL, Python, R, and Conda. In addition, OML supports bringing your own models in Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) format. You can import text transformer, classification, regression, and clustering models in ONNX format to use in OML.
The Vector data type is introduced with the release of Oracle Database 23ai. Using embedding models, you can transform unstructured data into vector embeddings. You can then provide Vector emeddings as input to Oracle Machine Learning in-database algorithms to complement other structured data or be used alone. The Vector data type is supported for clustering, classification, anomaly detection, and feature extraction.
In this article, we’ll focus on training a classification model using OML. The classification model will use Vector embeddings generated using an imported HuggingFace ONNX model. For details on the dataset used for classification, refer to Part 2 of this blog series. To learn more about loading data into an autonomous database, check out Part 6.
Steps
Step 1: Create a database user with OML privileges
To use OML for training the model, do the following:
- On the Autonomous Database Details page, click Database Actions and select Database Users.
Alternatively, select Database Actions and click View All Database Actions to access the Database Actions Launchpad. From the launchpad, under Administration, click Database Users.
- Click + Create User.
- In the Username field, enter a username for the account (e.g.,
OML_USER). - In the Password field, enter a password for the user.
- In the Confirm Password field, re-enter the password to confirm it.
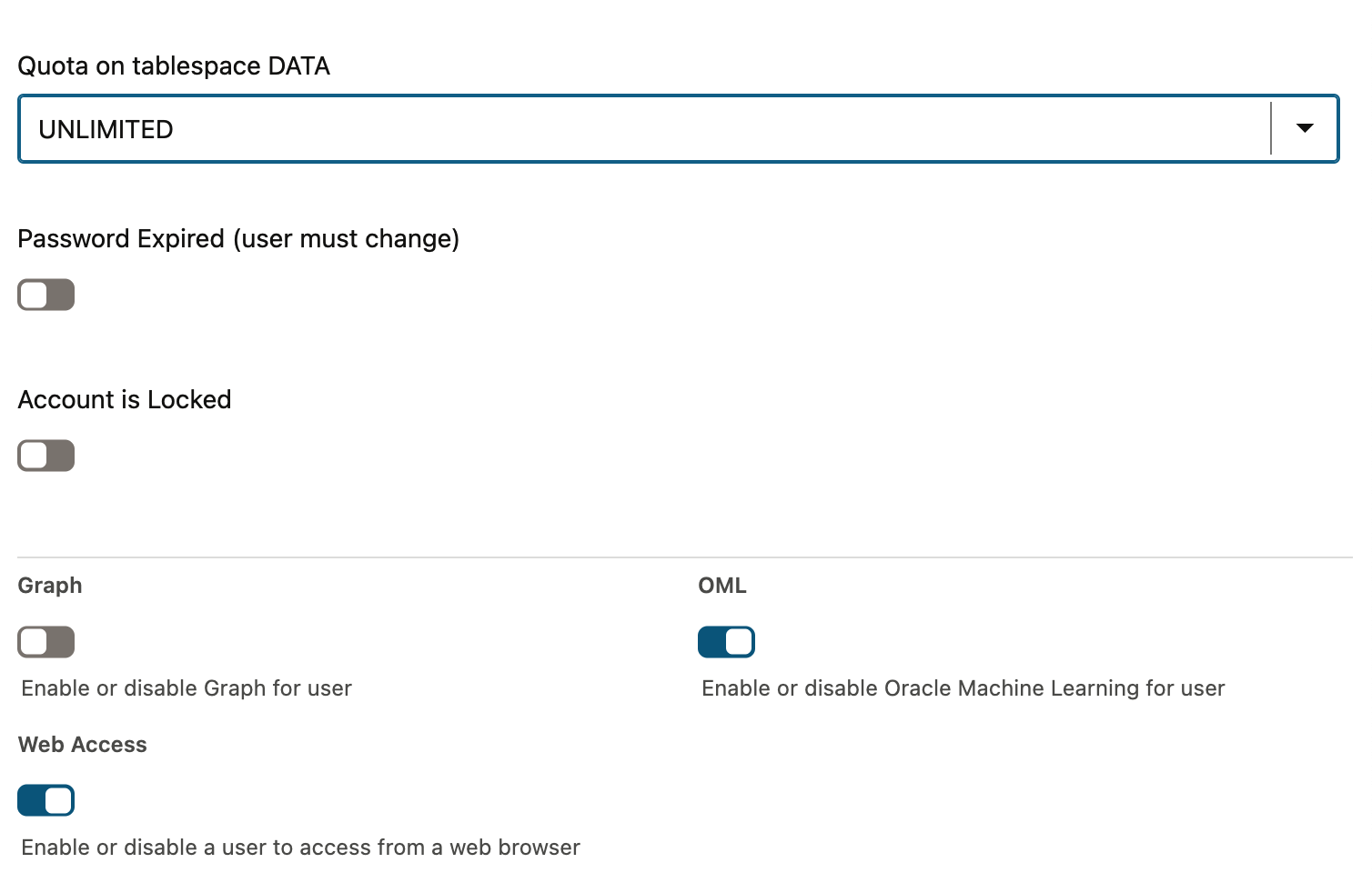
- Select OML to enable Oracle Machine Learning for this user. Optionally, enable Web Access to allow web-based access.
Step 2: Create a database table for storing the dataset
- On the Autonomous Database Details page, click Database Actions.
- Use the credentials of the
OML_USERyou just created to log in. - Create a table named
ITEMSto store the dataset for item classification. This table has the following 3 columns:
-
ITEM_CLASS_NAMEVARCHAR2(100) (the target label) -
ITEM_DESCRIPTIONVARCHAR2(4000) (the feature used for prediction) -
ID NUMBER ( Primary Key Column)
The model we create will predict the ITEM_CLASS_NAME based on the ITEM_DESCRIPTION feature.
Step 3: Import a HuggingFace Model for Generating Embedding
Steps to Download and Load the Model into Oracle Database
- Download the HuggingFace model from here, Hugging Face all-MiniLM-L12-v2 model and extract the zip file.
- Upload the
.onnxfile to an Object Storage bucket. - Create a pre-authenticated request of the
.onnxfile in the bucket.
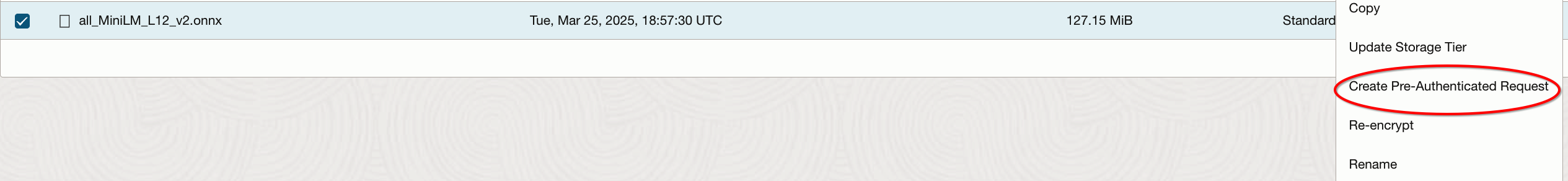
4. Select Permit object reads option, set an expiration date for the URL, generate and copy the Pre-Authenticated URL.
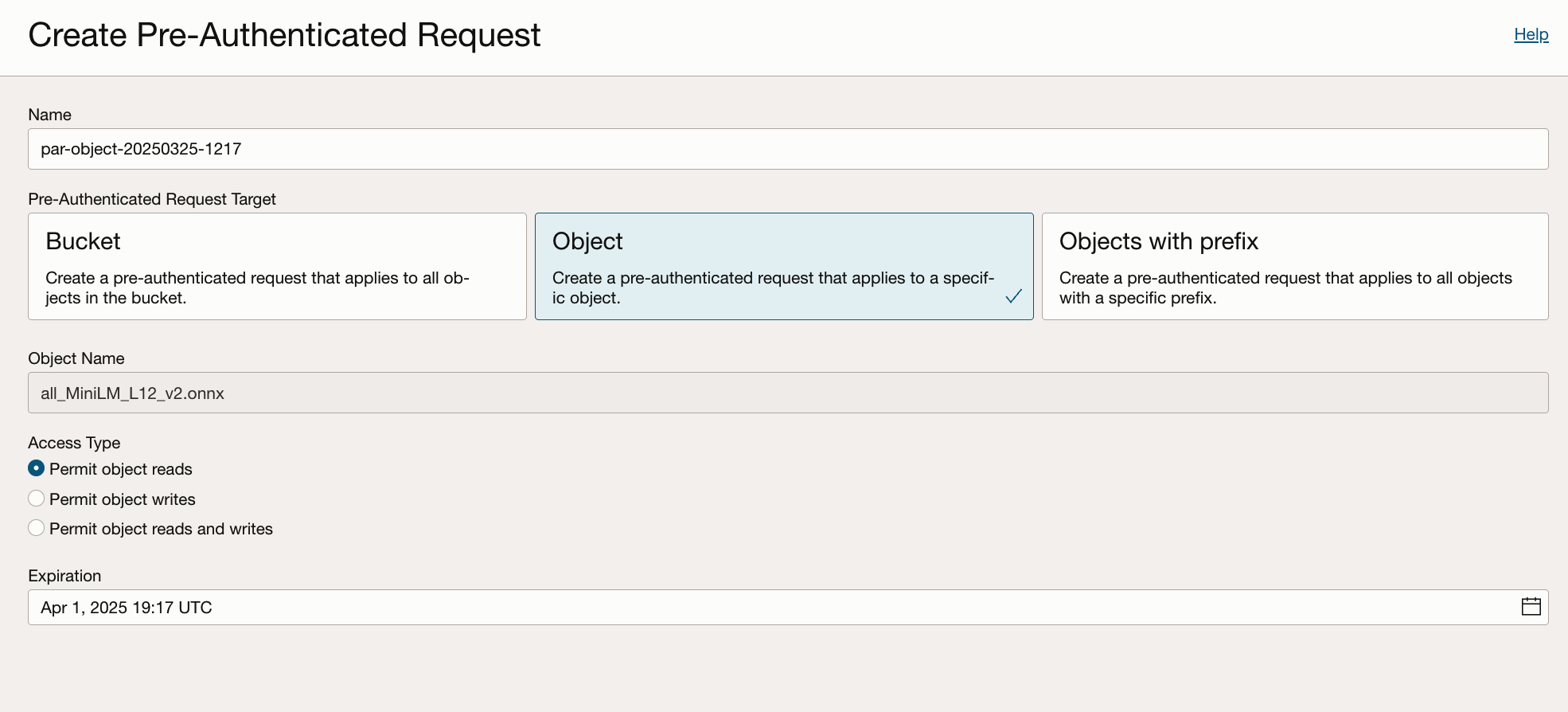
5. Connect to the database as oml_user, execute the following script, replacing LOCATION_URI with the Pre-Authenticated URL from the previous step.
DECLARE
ONNX_MOD_FILE VARCHAR2(100) := 'all_MiniLM_L12_v2.onnx';
MODNAME VARCHAR2(500);
-- Set the LOCATION_URI
LOCATION_URI VARCHAR2(200) := 'https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/p/nVX....n/idprle0k7dv3/b/bucket-20250110-1032/o/';
BEGIN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('ONNX model file name in Object Storage is: '||ONNX_MOD_FILE);
-- Define a model name for the loaded model
SELECT UPPER(REGEXP_SUBSTR(ONNX_MOD_FILE, '[^.]+'))
INTO MODNAME
FROM DUAL;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Model will be loaded and saved with name: '||MODNAME);
-- Read the ONNX model file from Object Storage into
-- the Autonomous Database data pump directory
BEGIN
DBMS_DATA_MINING.DROP_MODEL(model_name => MODNAME);
EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN
NULL;
END;
DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT(
credential_name => NULL,
directory_name => 'DATA_PUMP_DIR',
object_uri => LOCATION_URI || ONNX_MOD_FILE
);
-- Load the ONNX model to the database
DBMS_VECTOR.LOAD_ONNX_MODEL(
directory => 'DATA_PUMP_DIR',
file_name => ONNX_MOD_FILE,
model_name => MODNAME
);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('New model successfully loaded with name: '||MODNAME);
END;
6. The above step should give the results as below if successfully completed.
ONNX model file name in Object Storage is: all_MiniLM_L12_v2.onnx Model will be loaded and saved with name: ALL_MINILM_L12_V2 New model successfully loaded with name: ALL_MINILM_L12_V2
Step 4: Train a Classification Model
To train the model, we’ll use OML Notebooks. OML Notebooks is an advanced web-based platform designed for data analysts and data scientists. It enables users to write code, create visualizations, and perform data analytics and machine learning.
To connect to the OML notebook, follow the steps below:
- On the Autonomous Database Details page, click Database Actions.

2. Use the credentials of OML_USER you just created to log in.
3. In the left navigation pane of Oracle Machine Learning, expand Project and click on Notebooks. Click Create, then provide a name for the notebook.

To train a machine learning model, follow the steps below:
1. Open the notebook you just created.
2. Create Training and Test Data Sets from the ITEMS Table.
For a supervised learning model such as classification, it is essential to split the data into training and test sets before building the model. The training set is used to train the model, while the test set is used to evaluate its accuracy through prediction queries.
For our classification model, we will use the vector embeddings of the ITEM_DESCRIPTION column to predict the ITEM_CLASS_NAME.The vector embeddings are generated using the VECTOR_EMBEDDING function. This function requires a model name as a parameter, which corresponds to the imported Hugging Face embedding model that performs the embedding function. The embeddings are then stored in the ITEM_DESCRIPTION_V column of the training and test data set.
Create embeddings and store training data set in a table
%script CREATE TABLE TRAIN_DATA_SET AS SELECT ID, ITEM_CLASS_NAME, (SELECT VECTOR_EMBEDDING(ALL_MINILM_L12_V2 USING ITEM_DESCRIPTION AS data)) AS ITEM_DESCRIPTION_V FROM ITEMS SAMPLE (60) SEED (1); %script DESC TRAIN_DATA_SET; Name Null? Type ------------------ ----- ------------- ID NUMBER ITEM_CLASS_NAME VARCHAR2(100) ITEM_DESCRIPTION_V VECTOR
Create embeddings and store test data set in a table
%script
CREATE TABLE TEST_DATA_SET AS
SELECT
ID,
(SELECT VECTOR_EMBEDDING(ALL_MINILM_L12_V2 USING ITEM_DESCRIPTION AS data)) ITEM_DESCRIPTION_V
FROM ITEMS
WHERE ITEMS.ID NOT IN (SELECT ID FROM TRAIN_DATA_SET);
Name Null? Type ------------------ ----- ------ ID NUMBER ITEM_DESCRIPTION_V VECTOR
Build an SVM Classifier Model
To build the model,use the CREATE_MODEL2 procedure in OML. It has the following parameters,
-
DATA_QUERYparameter specifies a query that provides training data for building the model. -
SET_LISTparameter defines model settings. -
MODEL_NAMEparameter specifies the model name. -
Since we are using classification, the
MINING_FUNCTIONparameter is set toCLASSIFICATION.
A sample script to train the model is given below:
%script
BEGIN
DBMS_DATA_MINING.DROP_MODEL('SVM_CLASSIFICATION_MODEL');
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN NULL;
END;
/
DECLARE
v_settings DBMS_DATA_MINING.SETTING_LIST;
BEGIN
-- Settings of the SVM model
v_settings('PREP_AUTO') := 'ON';
v_settings('ALGO_NAME') := dbms_data_mining.algo_support_vector_machines;
v_settings('SVMS_KERNEL_FUNCTION') := 'SVMS_LINEAR';
v_settings('SVMS_CONV_TOLERANCE') := '0.001';
v_settings('SVMS_BATCH_ROWS') := '2000';
v_settings('SVMS_REGULARIZER') := 'SVMS_REGULARIZER_L1';
v_settings('SVMS_SOLVER') := 'SVMS_SOLVER_SGD';
-- Train the model
DBMS_DATA_MINING.CREATE_MODEL2(
MODEL_NAME => 'SVM_CLASSIFICATION_MODEL',
MINING_FUNCTION => 'CLASSIFICATION',
DATA_QUERY => 'SELECT * FROM TRAIN_DATA_SET',
SET_LIST => v_settings,
CASE_ID_COLUMN_NAME => 'ID',
TARGET_COLUMN_NAME => 'ITEM_CLASS_NAME'
);
END;
Make Predictions using the Model
The APPLY procedure in DBMS_DATA_MINING is a batch apply operation that writes the results of scoring directly to a table. Classification produces a prediction and a probability for each case.
%script
--Drop Existing Results Table (If Any) and Apply model prediction
BEGIN
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'DROP TABLE SVM_RESULT PURGE';
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN NULL;
END;
/
-- Apply the model to the test data set
BEGIN
DBMS_DATA_MINING.APPLY('SVM_CLASSIFICATION_MODEL','TEST_DATA_SET','ID','SVM_RESULT');
END;
/
-- Select from the SVM_RESULT to see the predictions
SELECT * FROM svm_result;
/
Step 5: Create an Oracle Machine Learning Services model endpoint for scoring
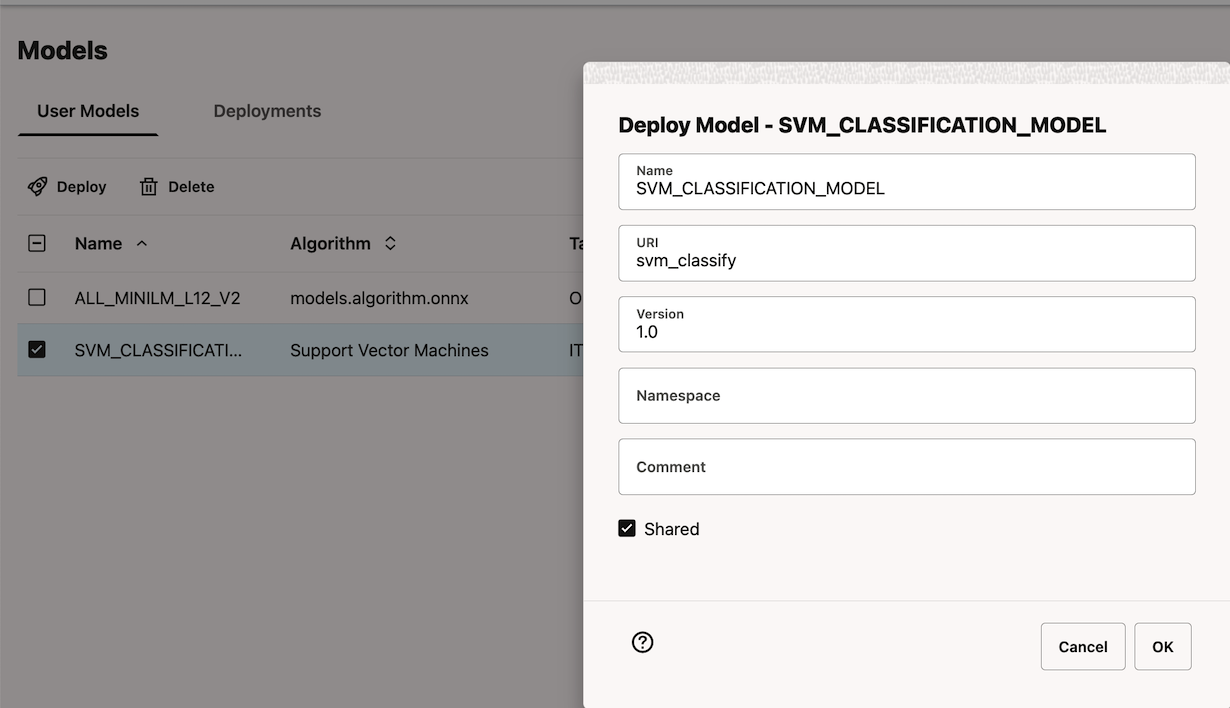
Once the model is trained, it will be available under the Models menu in Oracle Machine Learning.

Deploy the model using the Deploy button on the Models page. After a model is successfully deployed, it is listed in the Deployments tab.
To get the model invocation URL, select a deployed model and click the link under URI to view the REST API URI of the model.
Conclusion
By leveraging Oracle Machine Learning (OML), you gain access to a platform that accelerates the development and deployment of machine learning solutions for enterprise business challenges. You can run machine learning algorithms within the database kernel, bypassing the complexities and performance issues associated with transferring large enterprise datasets between external tools.
