Introduction
Oracle Analytics Cloud is a scalable and secure Public Cloud Service that provides a full set of capabilities to explore and perform collaborative analytics for you, your workgroup, and your enterprise. In this blog entry, the focus will be on the various ways the OAC service can be used and integrated with OCI IaaS, mainly VCNs and Fast Connect or IPSEC connectivity to customer datacenters. We will not cover the exact steps on how to deploy the OAC service. For more details on OAC please visit these blog entries:
https://www.ateam-oracle.com/post/provisioning-oracle-analytics-cloud-with-a-private-end-point
OAC components needed:
-
One or more OAC instances per OCI cloud region – clients can deploy multiple OAC instances in each OCI region.
-
One global IDCS instance – OAC relies on Oracle’s Identity Cloud Service (IDCS) which is a required component for this setup. If possible, it is a best practice to deploy IDCS and OAC in the same OCI region, but it is not mandatory.
Solution Description
Each service from the OCI PaaS and SaaS portfolio is deployed in a dedicated services network that exists in every OCI Region.
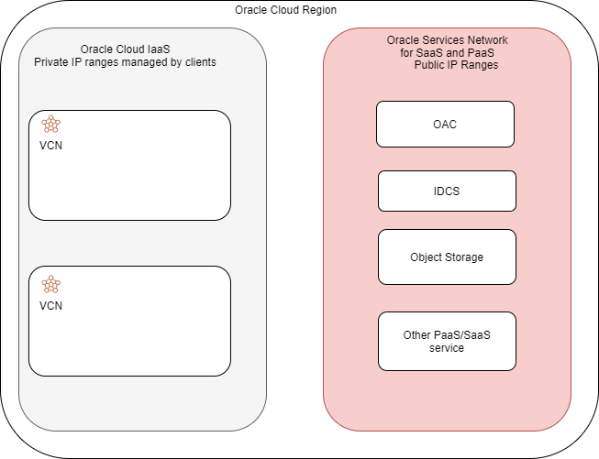
When deploying an OAC instance we can select Public or Private mode. Let’s explore each type of deployment by focusing on the network components and flows involved.
We will cover the following scenarios:
Oracle Analytics Cloud – Public Instance
By default, an OAC instance is deployed with a Public Endpoint. Once deployed, the OAC instance will receive the following network resources:
-
One Public IP Address:
-
Assigned from a regional pool of IP ranges.
-
Ephemeral – If the OAC instance is deleted, the assigned IP address will go back to the pool and be available for someone else’s OAC instance
-
Used only for incoming connections from users.
-
-
One Public Gateway IP Address:
-
Assigned from a regional pool of IP ranges.
-
Ephemeral – If the OAC instance is deleted, the assigned IP address will go back to the pool and be available for someone else’s OAC instance
-
Used only for outgoing connections to OAC data sources such as Internet reachable databases or OCI database services with public IPs.
-
-
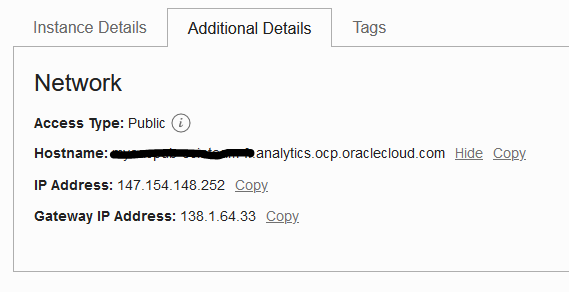
One Public DNS entry in the analytics.ocp.oraclecloud.com subdomain which will resolve to the Public IP address.
This information can be seen in the details page of the instance:
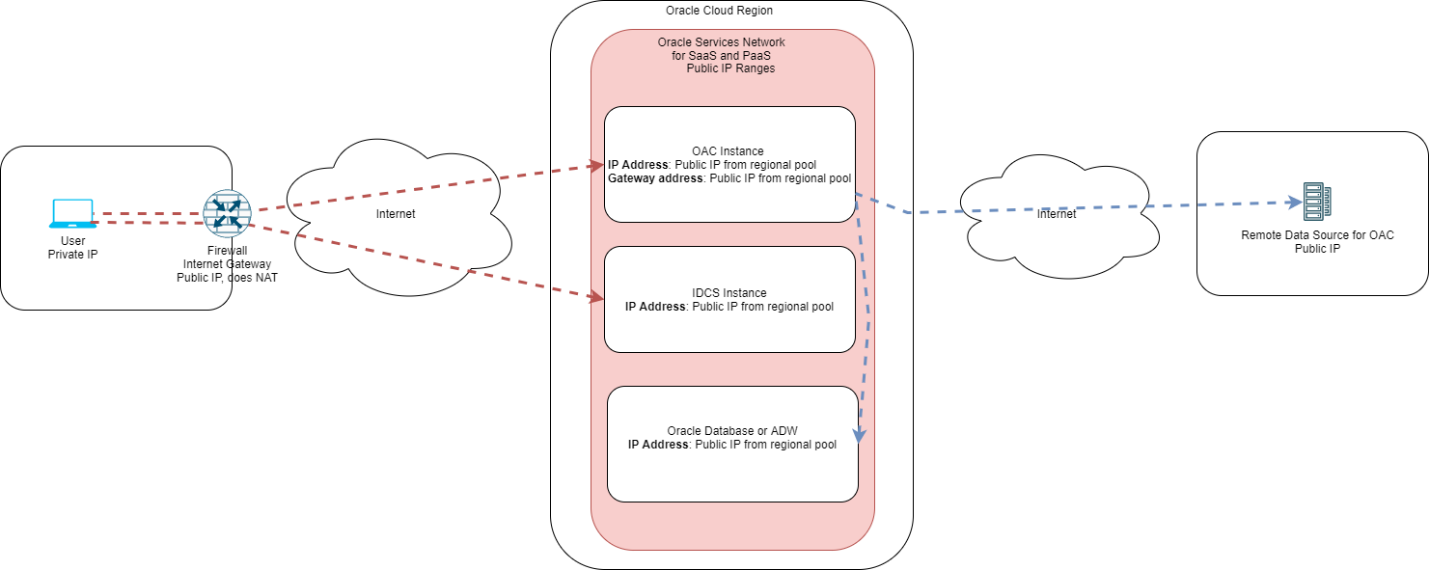
Access to the new instance can be done via Public Internet or via Private links:
-
-
Public access over the Internet
-
After the deployment is complete users can connect to the OAC instance via the Public IP. The gateway IP will be used by the OAC instance as the source IP to connect to remote data sources.
Access to this instance can be restricted via the advanced options in the deployment menu or later on, in the settings tab.
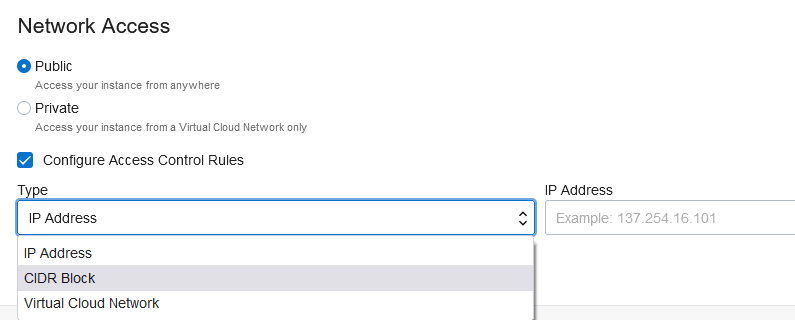
These restrictions can be:
- IP Address : Individual IP addresses of OAC users
- CIDR Block: Network subnets where OAC users exist
- Virtual Cloud Network: Limits access to IPs part of a defined VCN. This 3rd option needs a Service Gateway deployed in the VCN which will create connectivity between the VCN and the Oracle Services Network where the OAC instance is deployed.
-
-
Private access using VPN or FastConnect
-
Even though the OAC instance was deployed in a Public mode, access to it can be kept private by leveraging the following network components:
-
Virtual Cloud Networks
-
Services Gateways – network constructs that allow connectivity between IaaS and SaaS/PaaS networks
-
Optional, for connections from the client datacenter:
-
Dynamic routing gateway.
-
IPSEC tunnel (with BGP) or Fast Connect.
-
A generic connectivity diagram can be seen below:
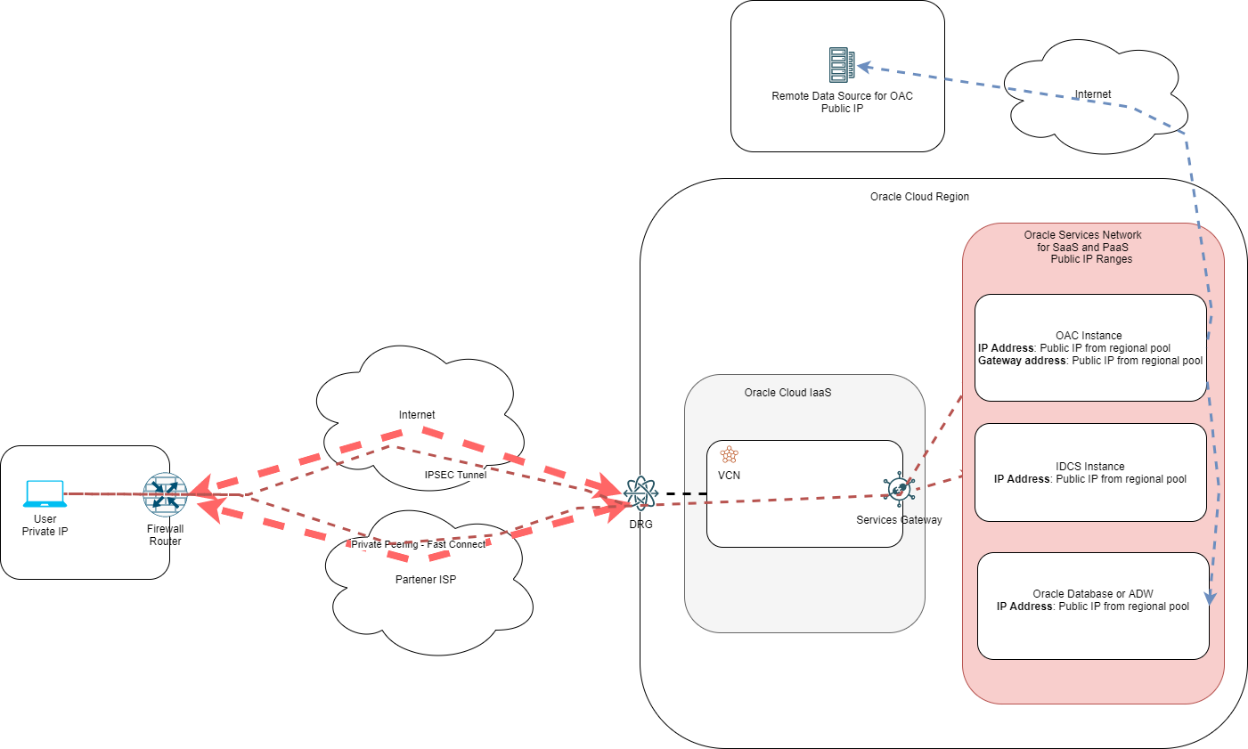
Step-by-step configuration for Public OAC with private access:
- Create one VCN in the same region as the OAC instance.
- Create one Service Gateway for all regional services inside the VCN
- Create one route table in the VCN with the following entries:
- Target type: Service Gateway
- Destination Service: All [Region] Services in Oracle Services Network
- Target Service Gateway – the SGW from above
- Create one new Dynamic Routing Gateway or use an existing one.
- In the DRG, select Virtual Cloud Networks Attachment and click Create. In the menu that opens select the VCN created at step i) and click Show Advanced Options. In the Advanced options menu select the VCN route table tab and select the route table created at step iii). Click Create.
- Go back to the VCN from point i) and create a new route table with the following entries:
- Target type: Dynamic Routing Gateway
- Destination CIDR block: your On-Premises subnet
- Target DRG – auto-selected or manual select if you have multiple DRGs in the region
- Go to the Service Gateway menu inside the VCN details and click the 3 dots on the right end of the row of the Service Gateway deployed at step ii). Select Associate route table and select the route table from step vi).
- Connect your data center to the DRG via IPSEC or Fast Connect.
Important considerations:
- The moment you finish connecting the DRG to the datacenter (via IPSEC or Fast Connect) Oracle will advertise over BGP all Public Subnets dedicated to the Services Network in that region. For a full list of advertised subnets, please download and check this JSON file:
- https://docs.oracle.com/iaas/tools/public_ip_ranges.json and look for subnets marked with “OSN” in the region of interest.
- Clients can minimize the number of imported prefixes by creating an import policy on their datacenter routers to allow only the IPs or subnets of the OAC and IDCS instances
- This scenario is focused on user access to the OAC instance. The connectivity between OAC and its data sources remains over the Public Internet.
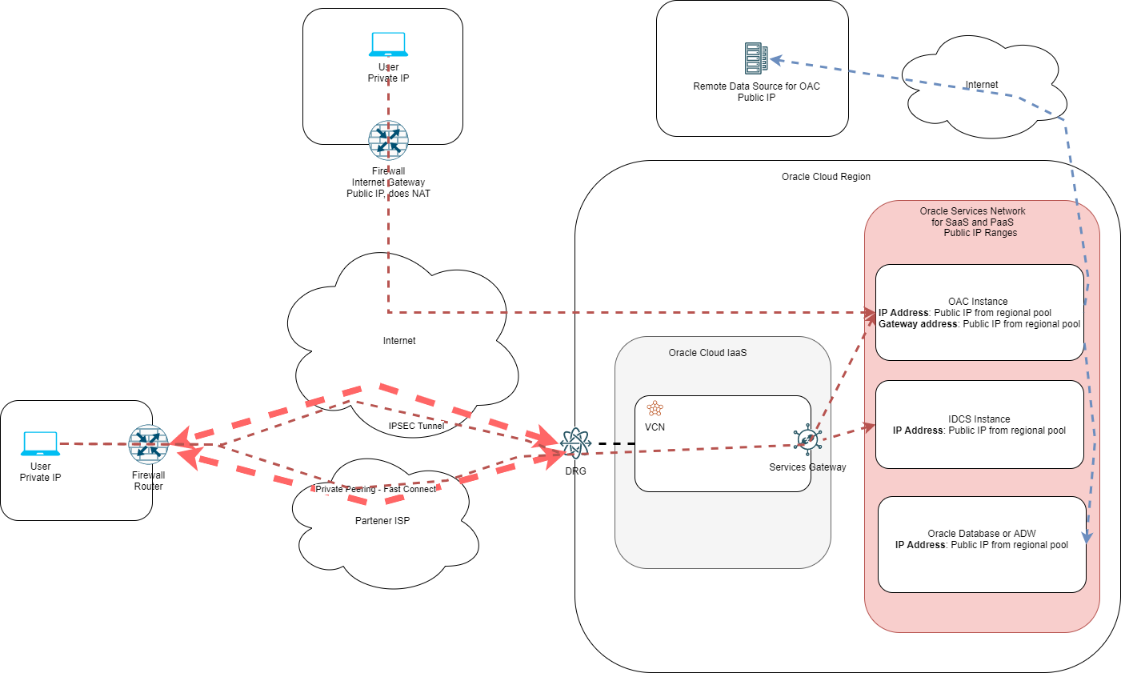
As a final point on this topic please note that both Private and Public connectivity concepts can be used at the same time meaning some clients can leverage the private path and others the public path, as shown in the diagram below:
Oracle Analytics Cloud – Private Instance
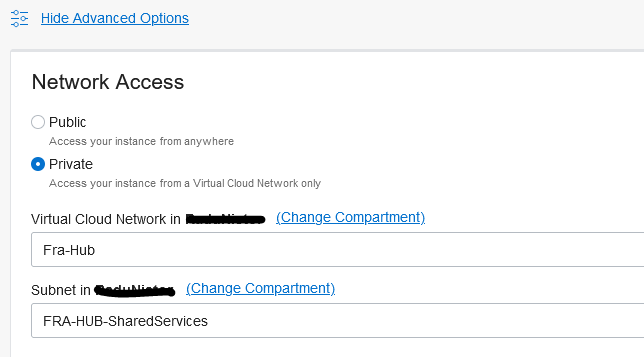
The OAC instance can be deployed with a private endpoint meaning it will have a private IP from a VCN private subnet. To deploy a private OAC instance, select Advanced Options in the deployment page and select “Private” under Network Access. You need a VCN and a Subnet in the same region.
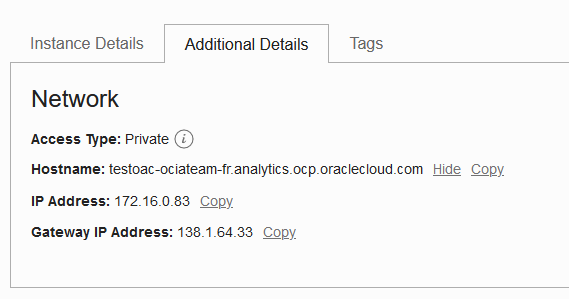
Once deployed, the OAC instance will receive the following network resources:
- One Private IP Address:
- Allocated from the chosen subnet.
- Used only for incoming connections from users.
- One Public Gateway IP Address:
- Allocated from a regional pool of IP ranges.
- Ephemeral – If the OAC instance is deleted, the assigned IP address will go back to the pool and be available for someone else’s OAC instance.
- Used only for outgoing connections to OAC data sources such as Internet reachable databases or OCI database services with public IPs.
- One Hostname entry in the analytics.ocp.oraclecloud.com subdomain which will NOT be resolvable.
Please see the diagram below for a generic architecture related to private access.
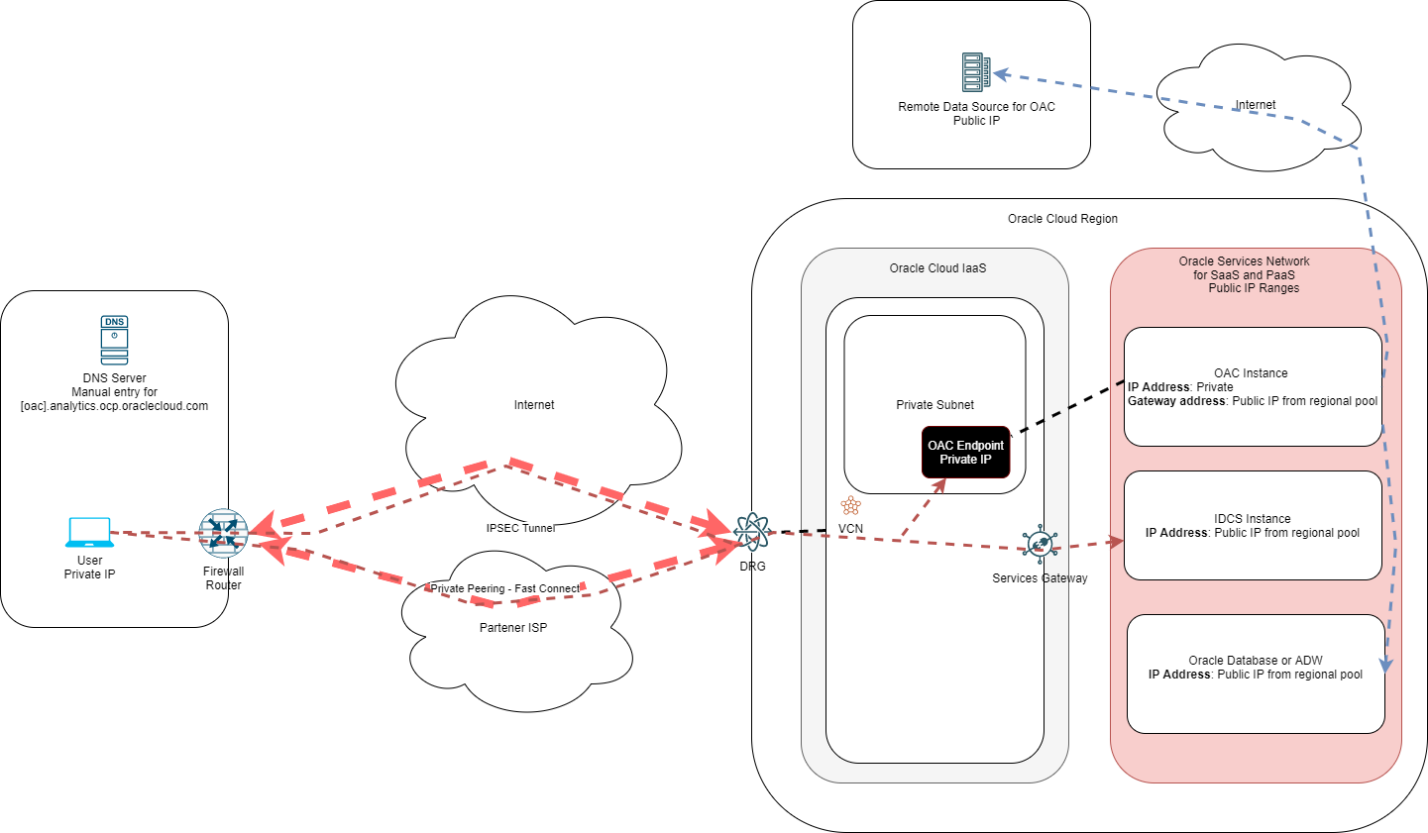
When using this scenario please consider the following:
- Only users that can reach the Private IP of the endpoint can use the service as there is no Public address.
- The users still need to reach the IDCS service Public IP; they can do that either directly, over the Internet, or via the Service Gateway deployed in the VCN as explained in the previous chapter.
- Because the service is now private, Oracle will not create a public DNS entry, so a manual entry must be created in the customer DNS to pinpoint the service DNS:
- Example: oac-name.analytics.ocp.oraclecloud.com pointing to the private IP.
- The OAC Endpoint follows the routing and security rules like any other IP in the VCN so appropriate routes and security rules must be configured to allow connectivity.
- Again, this scenario is focused on client connectivity to the OAC service. Connections from OAC to remote data sources will be over Public Internet as the OAC instance still has a Public Gateway Address.
Oracle Analytics Cloud – Private Access Channel (PAC)
In the previous chapters, we explored the various ways of connecting to the OAC service deployed on Oracle Cloud. However, all scenarios focused on client connectivity to the service while OAC connectivity to the data sources remained always public, over the Internet. Oracle provides a component named Private Access Channel (PAC) that allows connectivity of the OAC service to private data sources residing inside a VCN or in a client data center.
PAC can be leveraged regardless of the OAC instance mode, private or public. The service deploys two endpoints inside a private subnet in an existing VCN in the same region as the OAC instance. The two endpoints will follow the routing and security rules defined in the VCN.
One important aspect is that PAC sources can only be defined with DNS names (FQDNs) so the VCN DNS Resolver must be able to resolve the target. This implies a DNS integration must be configured between the VCN DNS and the client’s local DNS.
An example diagram can be seen below:
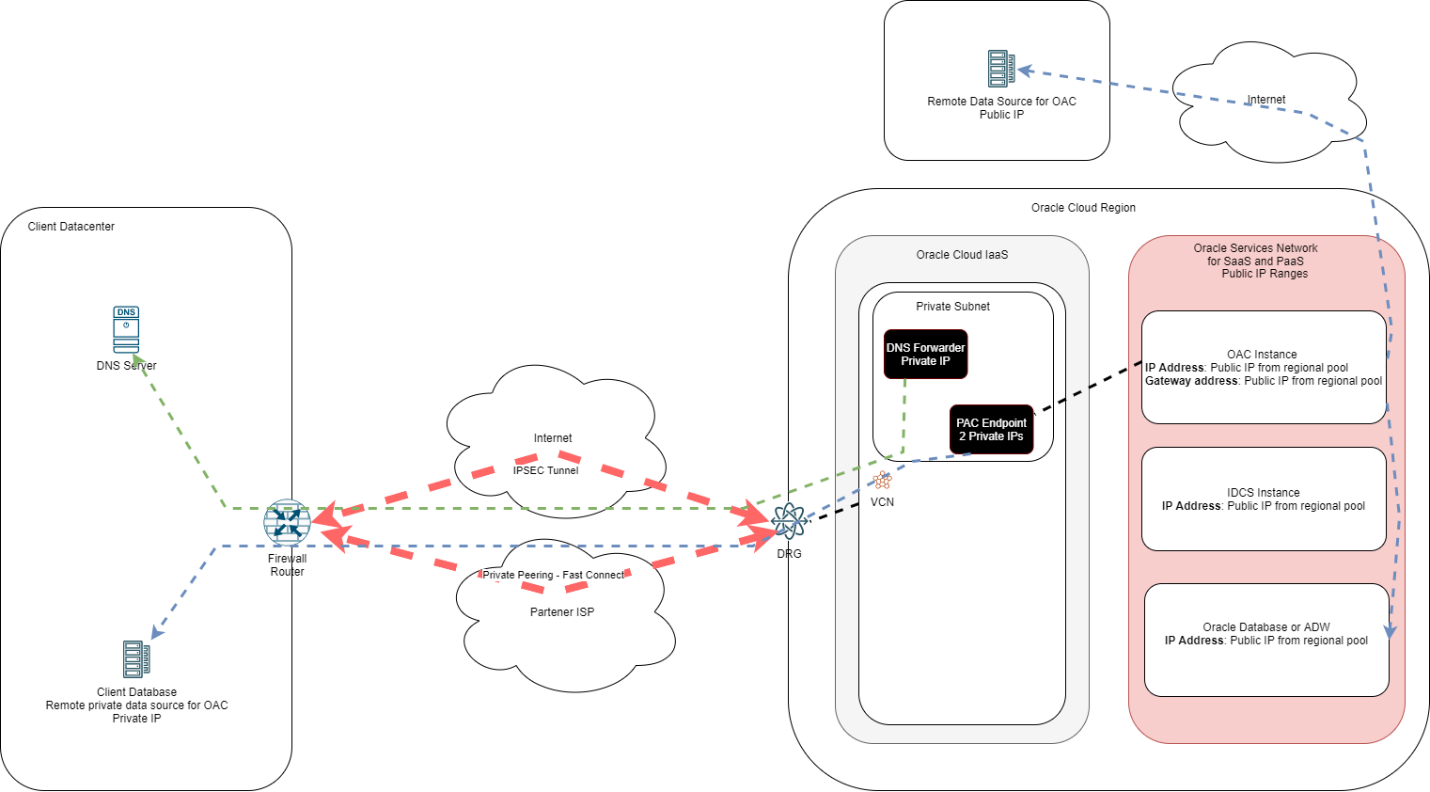
Steps to implement PAC:
- In the OAC instance details select Private Access Channel on the left – note that you need Enterprise Analytics to be able to see the menu.
- Click Configure Private Access Channel and select the VCN and the subnet where the two endpoints will be deployed.
- Under DNS input the DNS zone where your remote data sources live. Let’s say the database is deployed in the databases.clientdomain.com subdomain:
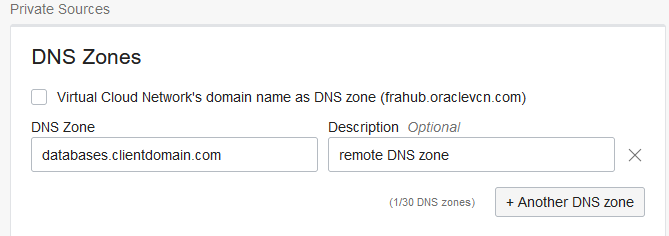
Next, we need to configure the DNS portion:
- Go to Networking -> Virtual Cloud Networks and click the VCN where the PAC endpoints are deployed.
- On the overview page – click the DNS Resolver name on the right.
- In the menu that opens click Endpoints on the left and click “Create Endpoint” -> Give it a name, select a subnet in which to deploy the DNS endpoint (can be the same as the PAC endpoints or different), endpoint type is “Forwarding”, click Create. Take a note of the endpoint IP.
- Next click Rules on the left and click Manage Rules. Select “Domains”, input the domain defined in the PAC set up, select the source (the endpoint created earlier), and input the IP of the DNS server in your data center that can resolve that domain:
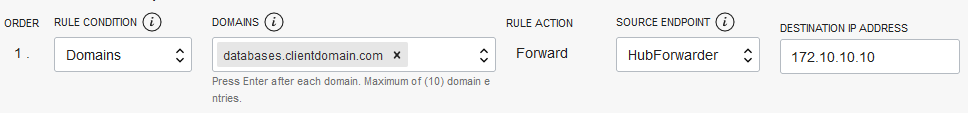
Click Save changes. Now, the VCN Resolver can forward any request for databases.clientdomain.com to the On-Premises DNS. Please note that routing and security rules must be put in place to allow UDP port 53 connectivity between the DNS Resolver endpoint and the target DNS system.
Conclusion
As a final note, the Private Access Channel will only be used for targets that match the DNS Zone declared at PAC deployment, any other target (remote database) will be accessed with the Public Gateway IP address.
Oracle Analytics Cloud official documentation can be found at:
https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/paas/analytics-cloud/index.html
