In this new blog post, we will explore the firewall throughput we can get in different scenarios using the Palo Alto VM Series on OCI.
Palo Alto VM-Series firewall supports the PacketMMAP and Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) drivers to communicate with the drivers on the host. On OCI, the networking launch type consists of: PARAVIRTUALIZED Networking for general purpose workloads and Hardware-Assisted SR-IOV Networking for low-latency workloads.
Below, I will run the traffic tests using iperf3 to measure the firewall throughput when the traffic passes through the Palo Alto VM-Series configured as an inspection point.
All the VMs used in this scenario (test VMs and Palo Alto OCI VM) are VM.Standard2.8.
I will start our tests by using the default Palo Alto VM mode, PARAVIRTUALIZED and DPDK, we will observe the performance and after this test I will switch the networking mode to the SR-IOV and PacketMMAP on the Palo Alto VM. The scope is to conclude if we can obtain better performance.
Important note: Palo Alto Support offers assistance for any issues running the PA NGFW in SR-IOV Networking and PacketMMAP mode only if the software version is 10.x.x.
Networking Topology
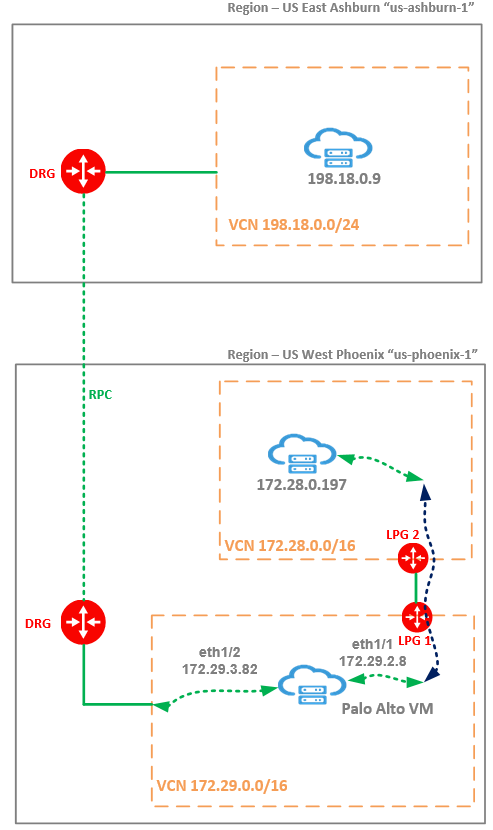
Palo Alto VM is running in a VCN from Phoenix region and all the traffic between Ashburn and Phoenix regions is passing through the PA. In this test scenario PA is configured with two VNICs configured in two different security zones. Between the two security zones the traffic is permitted. No other traffic inspection feature is enabled on the PA NGFW.
I will run the iperf3 using multiple TCP threads from the test VM at 198.18.0.9 on Ashburn to the test VM at 172.28.0.197 on Phoenix. The traffic sent from Ashburn is received on eth1/2 on the PA and it is forwarded out using eth1/1 toward 172.28.0.197 – as noted, we are using two interfaces for this testing scenario.
Traffic path from Ashburn to Phoenix: 198.18.0.9 -> Ashburn DRG -> RPC -> Phoenix DRG -> PA eth1/2 -> PA eth1/1 -> LPG 1 -> LPG 2 -> 172.28.0.197.
Traffic path from Phoenix to Ashburn: 172.28.0.197 -> LPG 2 -> LPG 1 -> PA eth1/1 -> PA eth1/2 -> Phoenix DRG -> RPC -> Ashburn DRG -> 198.18.0.9.
Probably, a relevant question is: Why you use LPGs instead of attaching both VCNs from Phoenix to the DRG and use the DRG routing functions to deliver the traffic received from Ashburn to the PA and from the PA back to the DRG and from there to the 198.18.0.9? The answer for sure is related to the fact that the goal is to obtain the lowest possible latency offered by OCI.
Throughput Test
1. PA NGFW PARAVIRTUALIZED and DPDK (the default mode)
1.1 9000 MTU for the entire path: 198.18.0.9 (9000 MTU) – PA (9000 MTU) – 172.28.0.197 (9000 MTU)
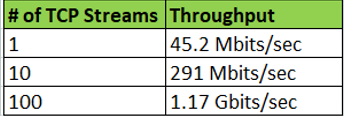
1.2 1500 MTU for the entire path: 198.18.0.9 (1500 MTU) – PA (1500 MTU) – 172.28.0.197 (1500 MTU)
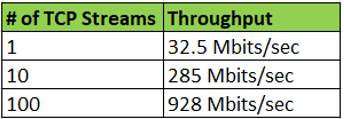
2. SR-IOV and packet MMAP mode
We need to perform some configuration changes in order to activate the SR-IOV and packet MMAP mode.
The step-by-step procedure to enable the SR-IOV and packet MMAP mode is listed below.
2.1 Save the PA configuration;
2.2 Run the command to check the current running mode: show system setting dpdk-pkt-io
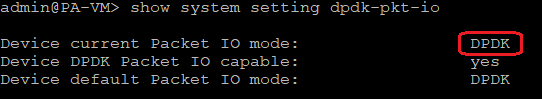
2.3 Disable the DPDK mode: set system setting dpdk-pkt-io off
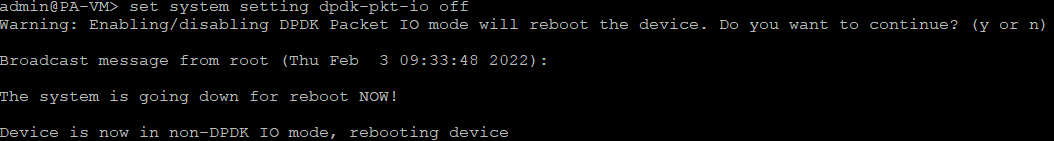
Once we continue with yes, the device will reboot.
2.4 After PA booted successfully we need to verify if the packet MMAP mode is enabled:
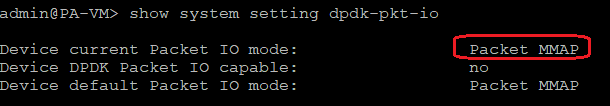
2.5 Login to OCI WebUI and detach all the PA VNICs except for the primary VNIC (note down the private IP addresses of the detached VNICs – we will add the VNICs later);
2.6 Edit the PA instance and change the networking mode to SR-IOV:
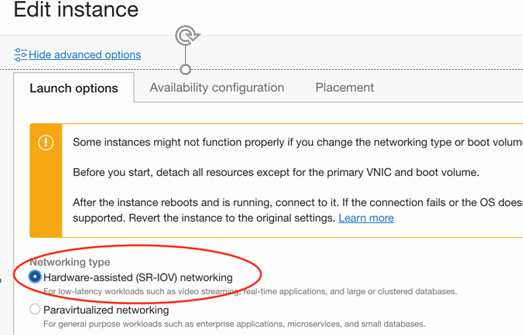
2.7 Save the changes and confirm to reboot the VM;
2.8 Once the PA has fully booted, confirm that it’s running in the SR-IOV mode and attach all the VNICs detached at step 2.5 adding the same private IP addresses – in this way, no configuration changes needs to be done on the PA for interfaces and routing;
Now, it is the time to perform the iperf3 test once the PA is running in SR-IOV mode and packet MMAP.
2.9 9000 MTU for the entire path: 198.18.0.9 (9000 MTU) – PA (9000 MTU) – 172.28.0.197 (9000 MTU)
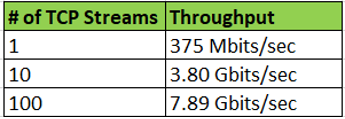
2.10 1500 MTU for the entire path: 198.18.0.9 (1500 MTU) – PA (1500 MTU) – 172.28.0.197 (1500 MTU)
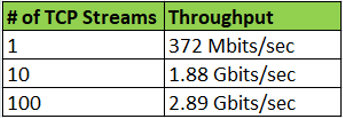
The numbers above clearly shows a big difference between the two modes. Definitively going with SR-IOV and packet MMAP the firewall throughput was significantly improved.
