3. OCI Internet Gateway
• Internet Gateway introduction and creation
The Internet Gateway allows bi-directional connectivity, so I mean by that, we could egress out of the cloud infrastructure towards the internet. Likewise, we can make connections back onto the public IP of a given instance that resides in a public subnet to manage the instance, like an SSH connection request.
There are some Key points to consider:
• Resources that need to connect to the Internet must be in a public subnet and have a public IP address.
• Each public subnet that uses the internet gateway must have a routing table Specify security rules to control the types of traffic allowed in and out of resources in that subnet.
• A VCN can be attached to only one Internet Gateway.
Let’s go back to the OCI service menu, Virtual Cloud Network, Networking, and then click on your created VCN (Blog-VCN-London)
From the Resources menu, click on Internet Gateways and then create Internet Gateway.
Please enter a name and click on Create Internet Gateway.
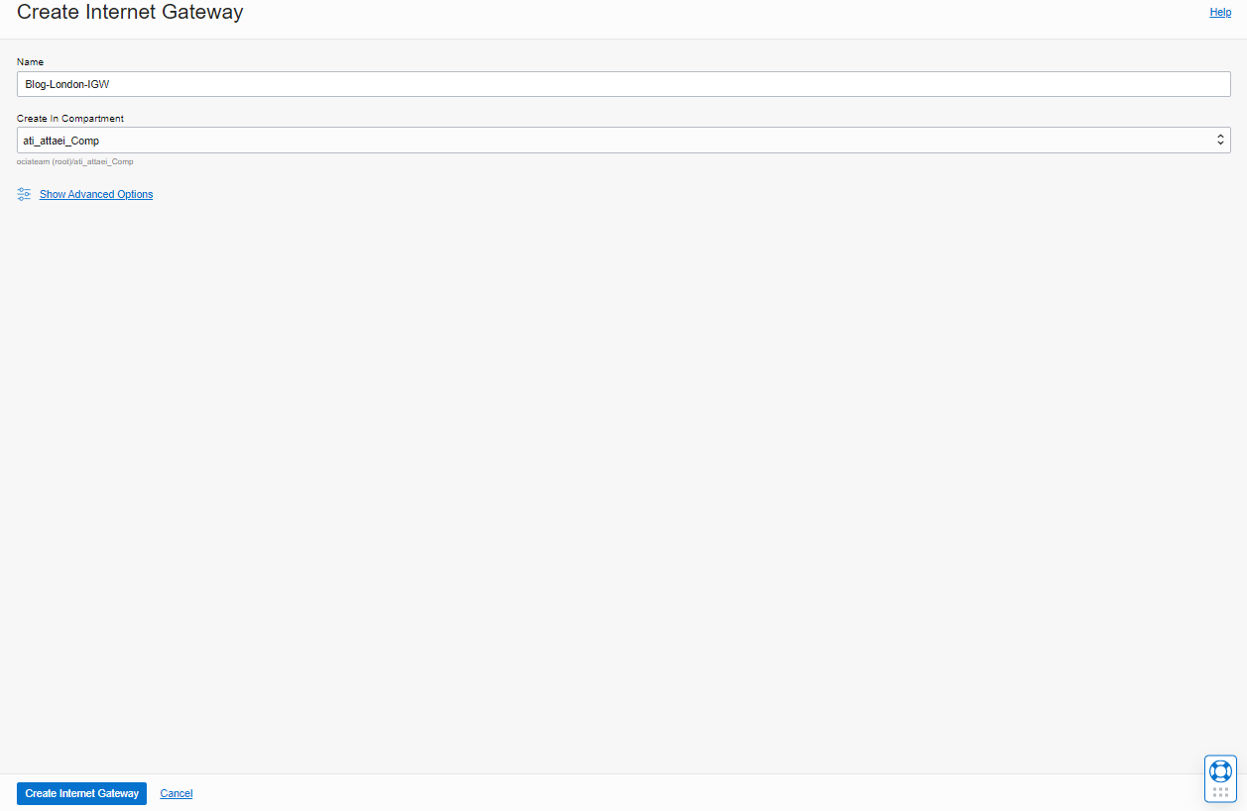
• Update the default route table to use the IGW
After we created our first gateway, Internet Gateway, we need to associate that with the VCN route table.
From the left side of the screen, under the Resources menu, Click on Route Table, Default Route Table for Blog-VCN-London As you see on the screenshot below, there is no Number of Rules available there, and we’ll go to add them now.
Click on the default route table and then Add Route Rules.
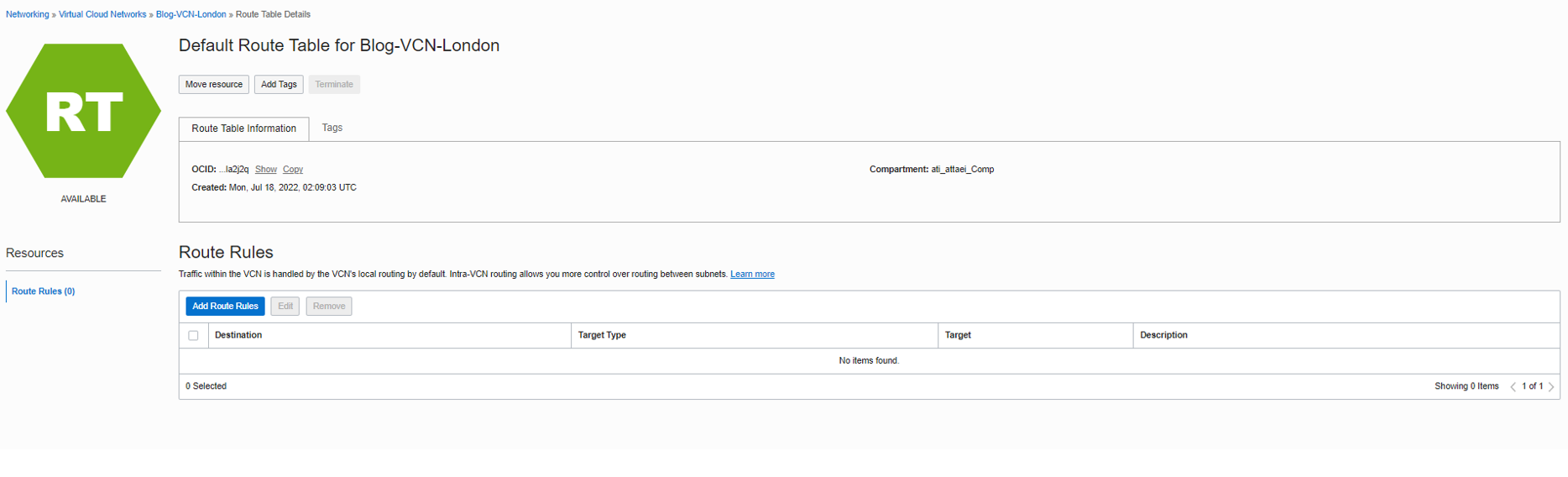
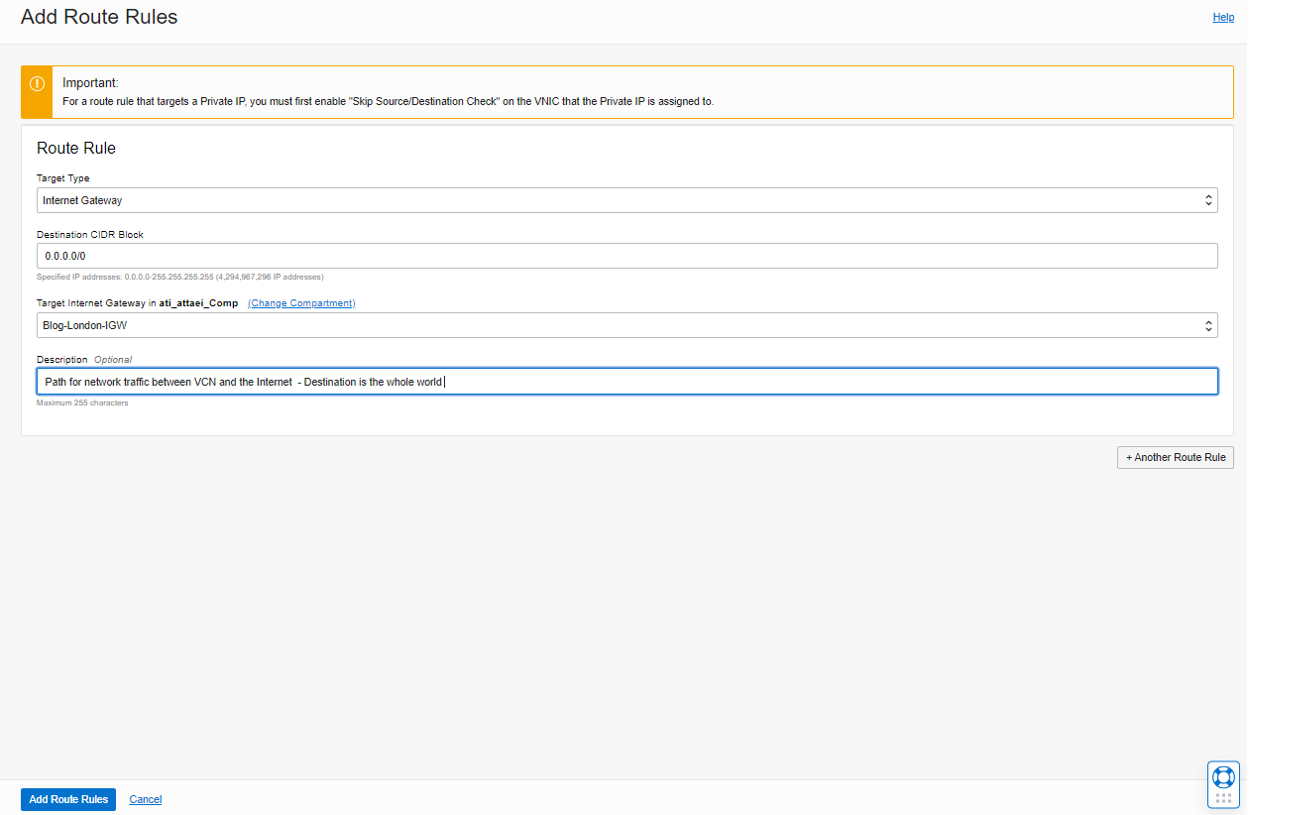
As you see in the screenshot above, click Add Route Rules.
• Update the default security list
When we finish the route table part, we need to check the Security List rules attached to the public subnet assigned to our Public VM to ensure SSH port 22 is allowed there.
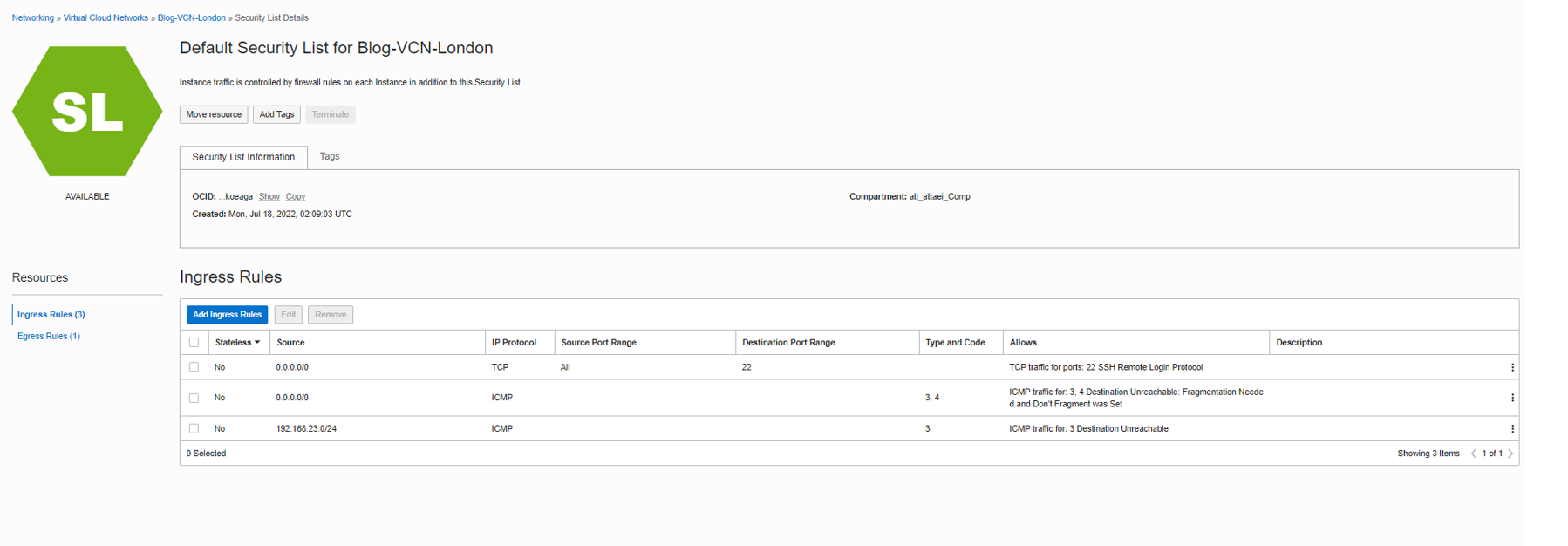
• Test connectivity
Now it’s time to try SSH to our public VM again.
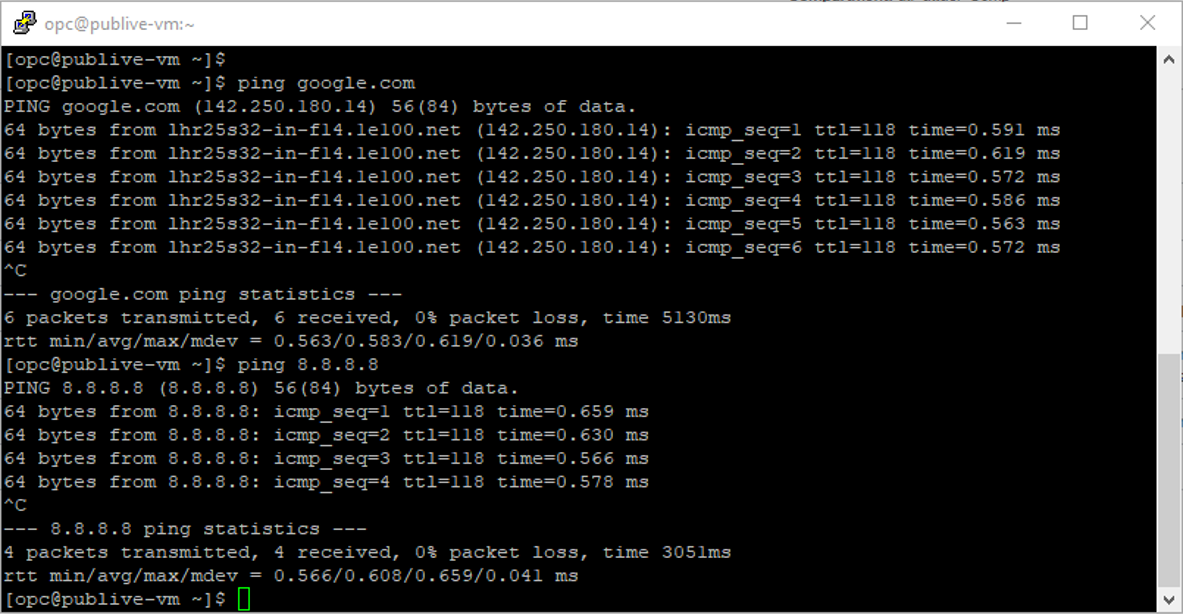
As you see, we can connect to the public VM and ping Google.com (Username is opc).
Note: You can have only one IGW per VCN.
Now, let’s try to connect to the Private VM and test the connectivity.
Note: Private subnet means VNICs in the subnet can’t have public IPv4 addresses.
First, connect to a public VM, create a file (I called my file blog. key) and use one of the Linux editors.
I used “nano”; see below.

Please copy and Paste the Private key we saved when we created our private VM (click on the private key and copy it).
Press Ctrl+x and then save and close the file.
Now connect to the Private VM, and use the command mentioned below.
” ssh -i blog.key opc@192.168.23.9 ”
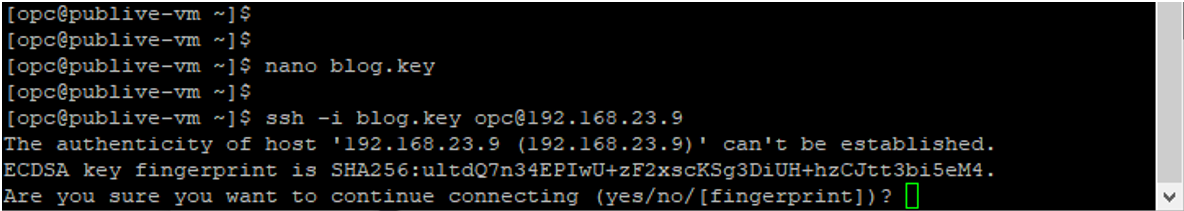
Accept the fingerprint.
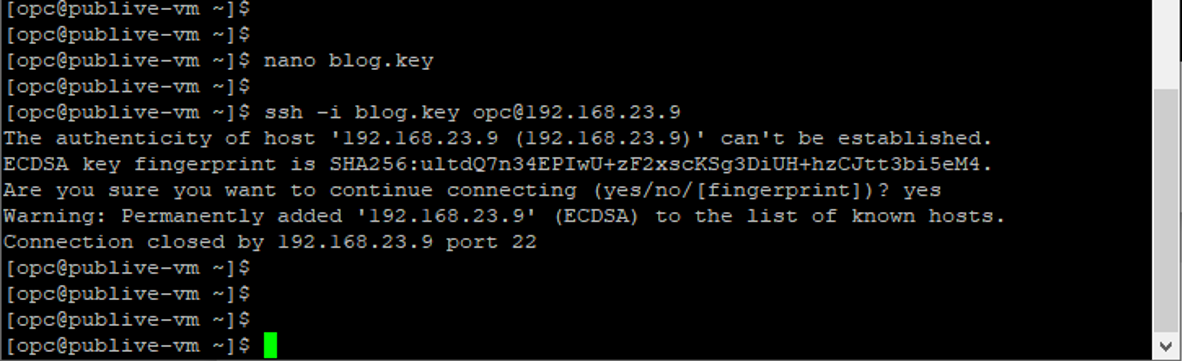
As you see in the screenshot above, we got a security error.
Adjust the security for the key by running the chmod 600 blog.key command.
Note: chmod 600 permissions means that only the file owner has full read and write access to it.
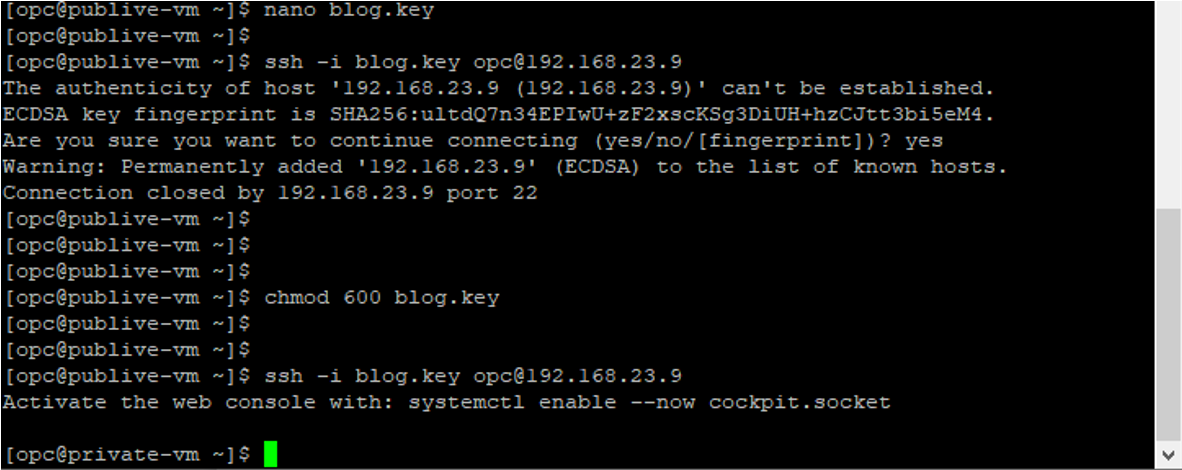
Test the connectivity one more time.
Now you are connected to your private VM.
It’s time to ping google.com again to test our VM connectivity.
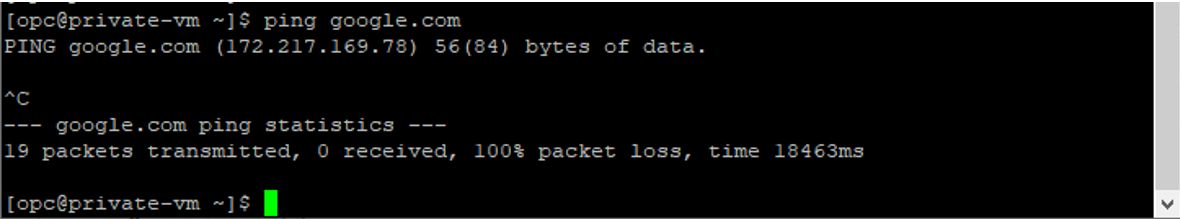
As you see above, the ping didn’t go through because there is no proper gateway attached to the blog VCN, which is NAT Gateway.
4. OCI NAT Gateway
• OCI NAT Gateway Introduction and Creation
NAT gateway gives private subnet access to the Internet without assigning the host a public IP address. It only enables outbound connections to the private subnets like performing patches, updates, or just resources that need general internet connectivity outbound.
Key points to note:
• NAT gateway is added to give instances in private subnet access to the internet.
• With the NAT gateway, these instances can initiate connections to the internet and receive responses, but they cannot receive any incoming connections from the internet.
• NAT gateways are highly available and support TCP, UDP, and ICMP ping traffic.
Let’s go back to the Virtual Cloud Network tab, and from the Resources menu, click on NAT Gateways and create NAT Gateway.
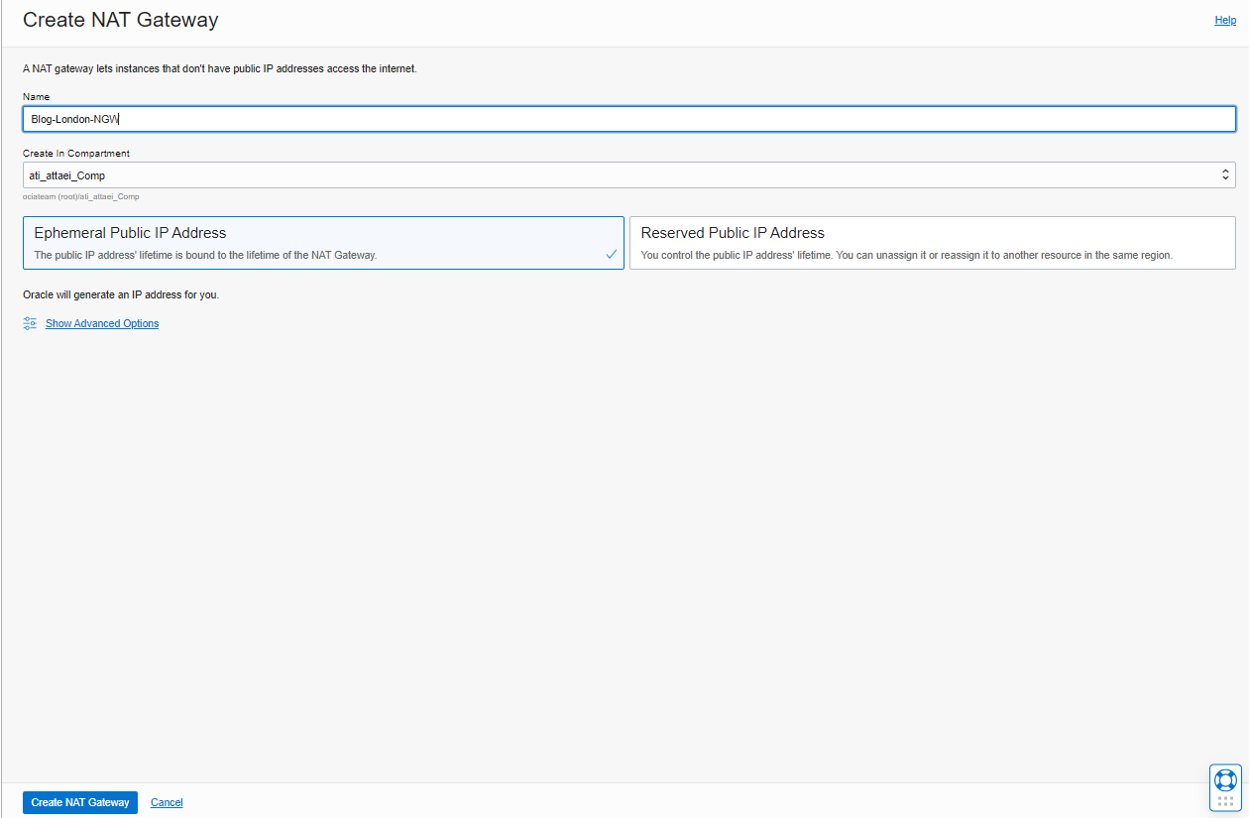
As you see above, I entered a name and chose an Ephemeral Public IP Address.
Note: Ephemeral IP address is temporary and exists for the instance’s lifetime.
Note: Choose this option to specify an existing reserved IP address by name or create a new one by assigning a name and selecting a source IP pool for the address. The default Oracle IP pool is used if you don’t choose a pool you’ve created.
• Create a specific route table for the private subnet
We’ll create a new route table for the private subnet to target it to NAT Gateway.
Note: The best practice is to create two separate public and private route tables once we create our subnets at the beginning of our design.
Let’s go back to the Virtual Cloud Network tab, and from the Resources menu, click on Route Tables and create Route Table.
Please enter a name and create.
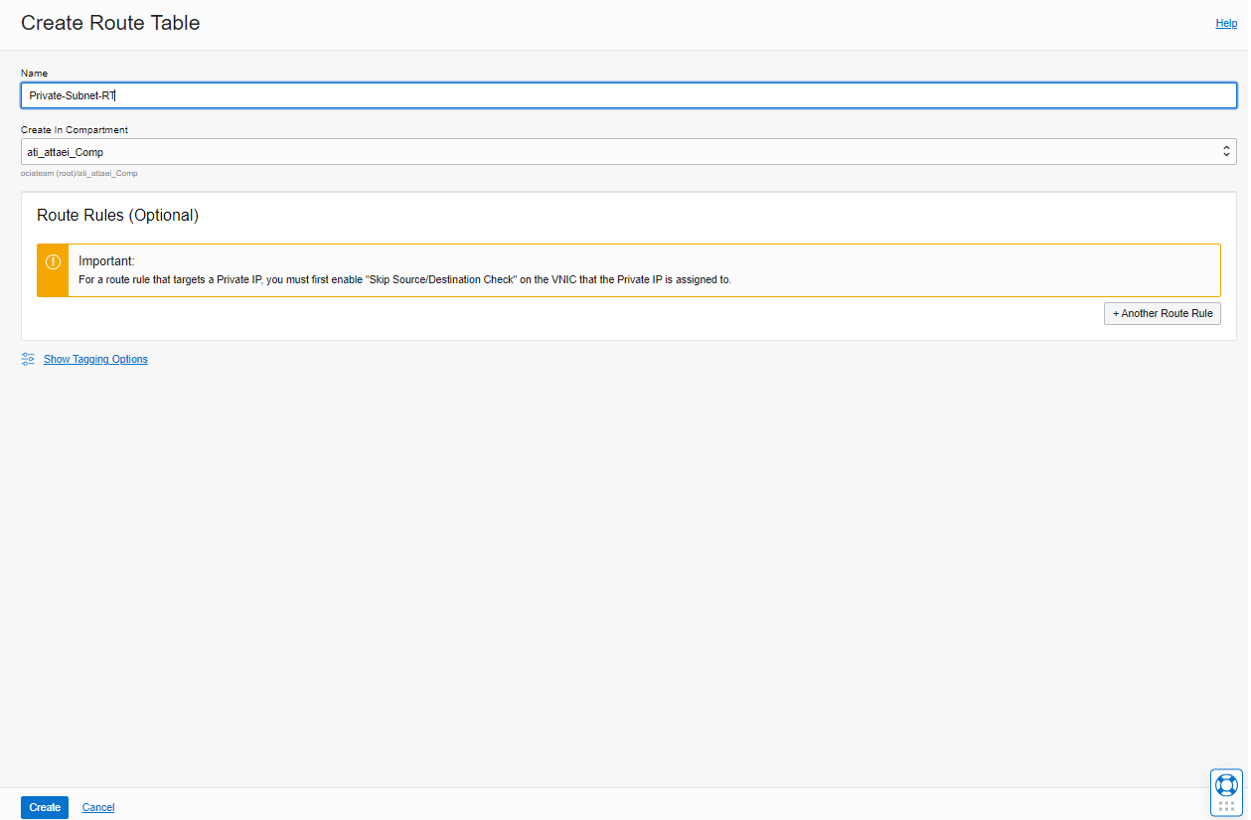
Now go to the Route Tables, Private-Subnet-RT.(The route table we just created)
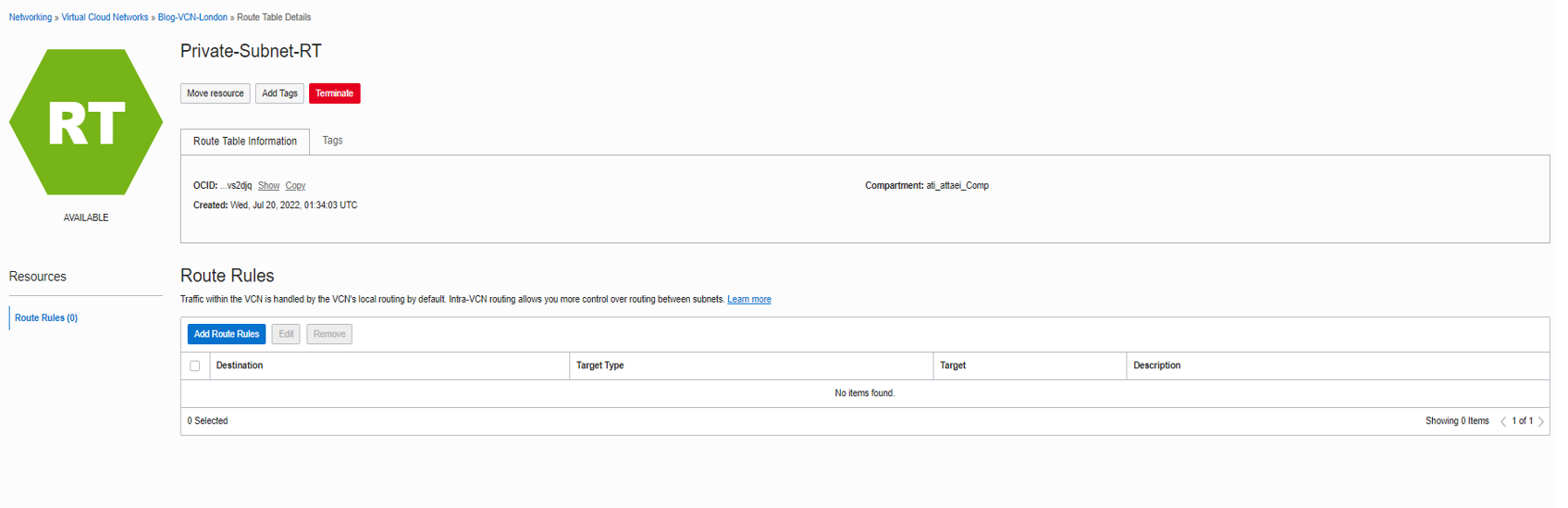
Click on Add Route Rules, as seen in the screenshot below.
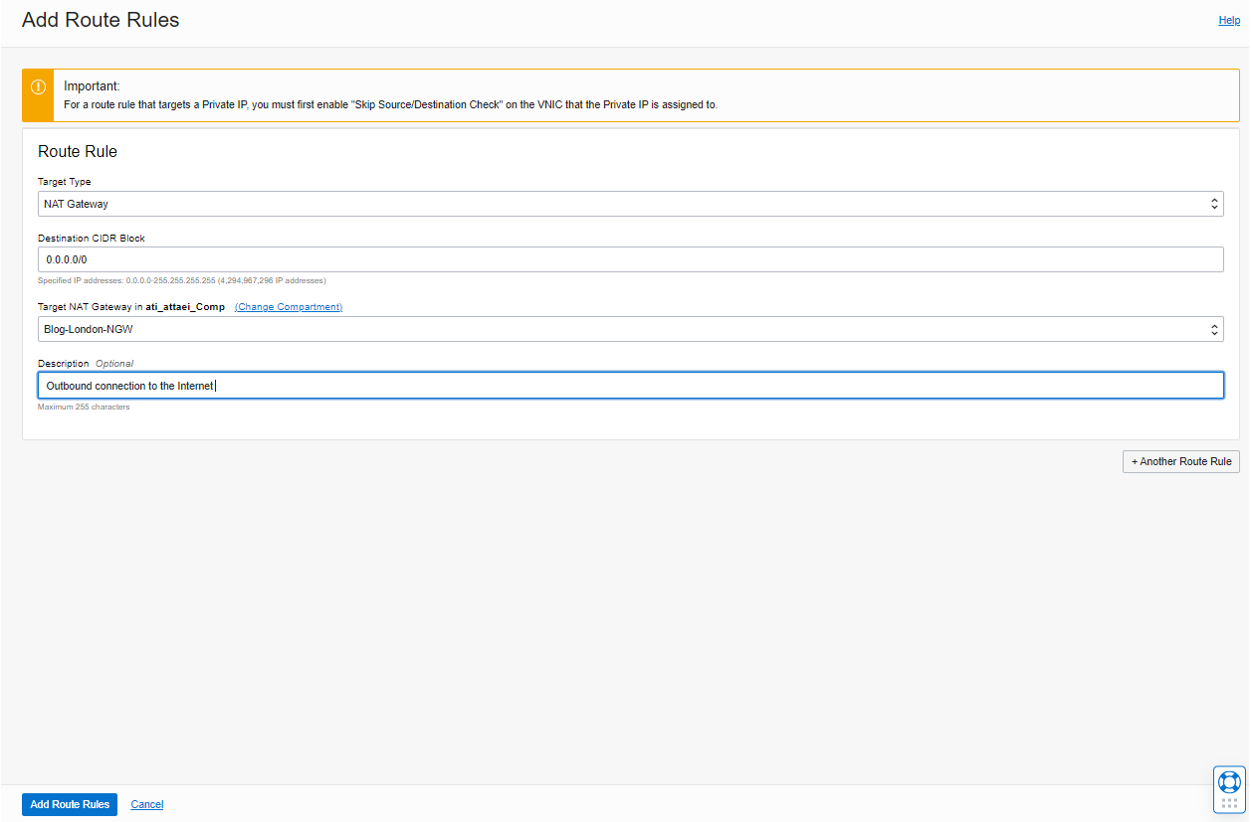
And create a “Route Rules”
We should now associate our newly created Private route table with our private subnet.
Go to the Virtual Cloud Network Details page from the left side Resources menu, Subnets, and click on Private-Subnet.
Edit the Private Subnet and change the routing table from Default Route Table to Private-Subnet-RT.
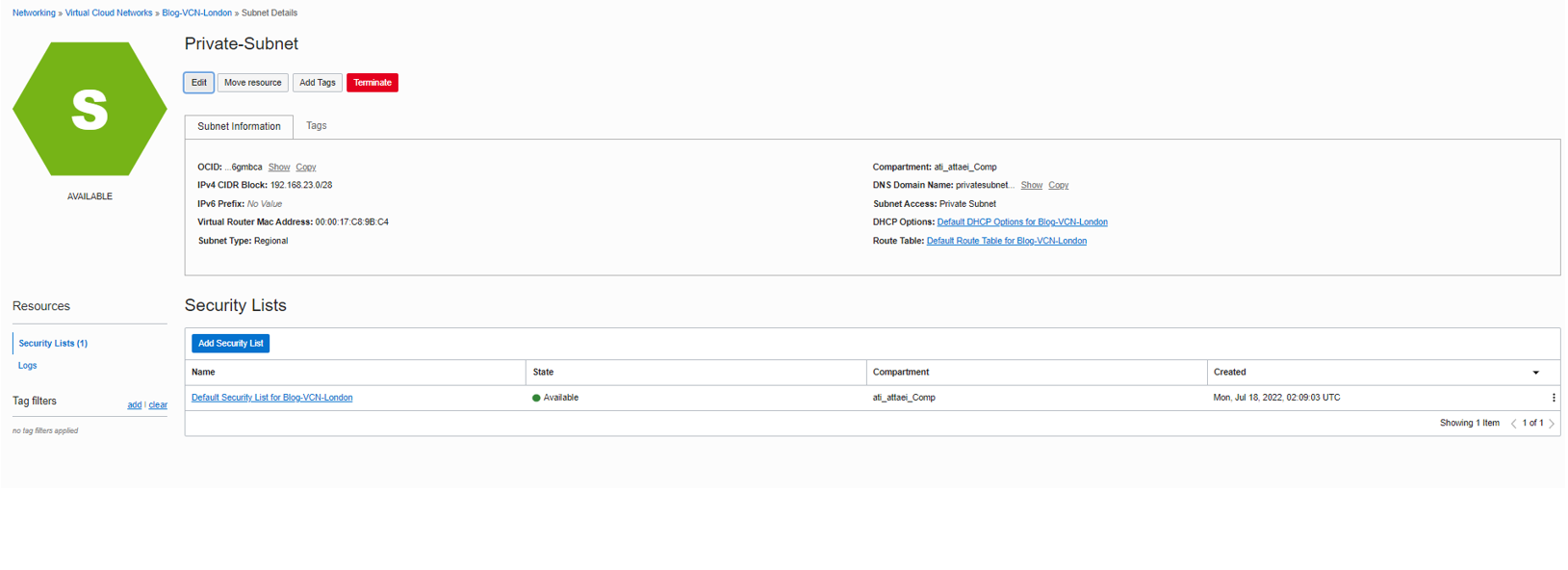
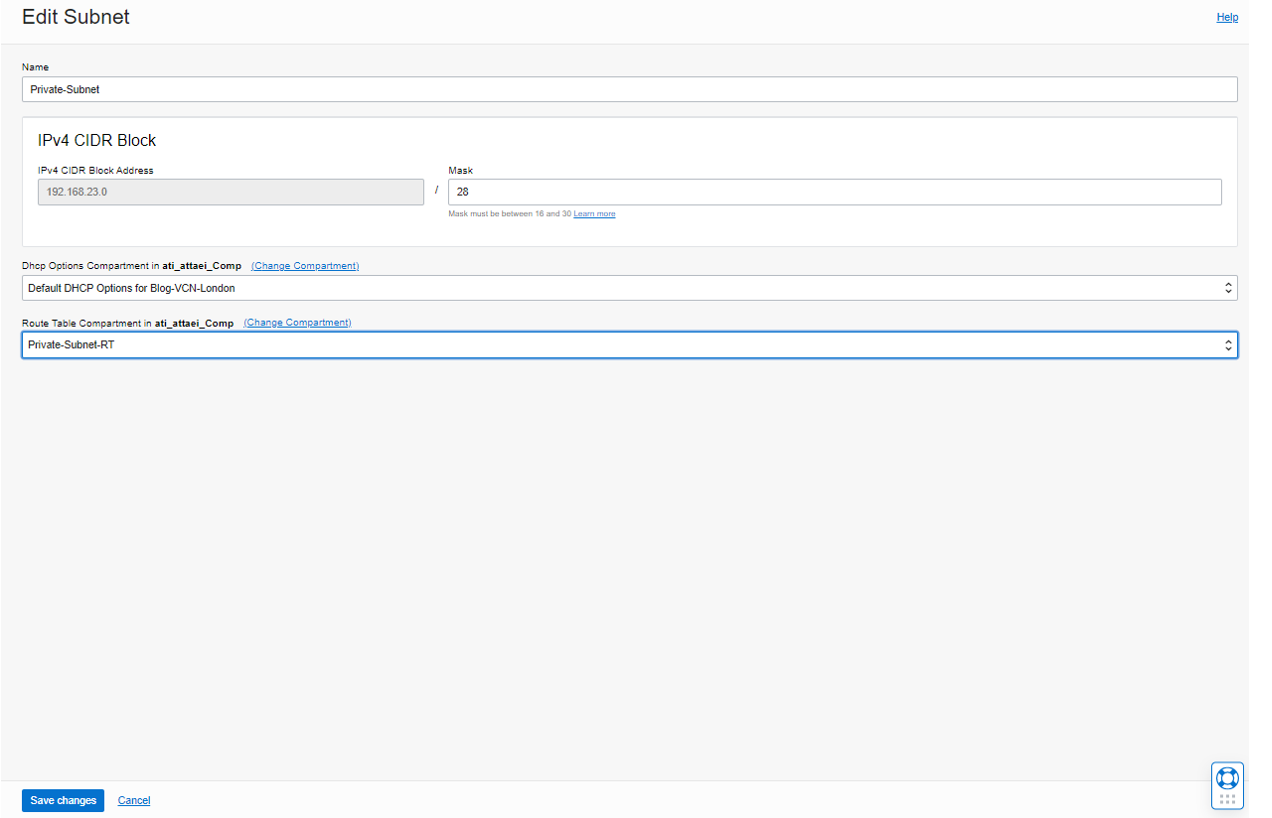
Save the changes.
• Test Connection
Please try to connect to the VM with No Public IPv4 assigned (Private VM).
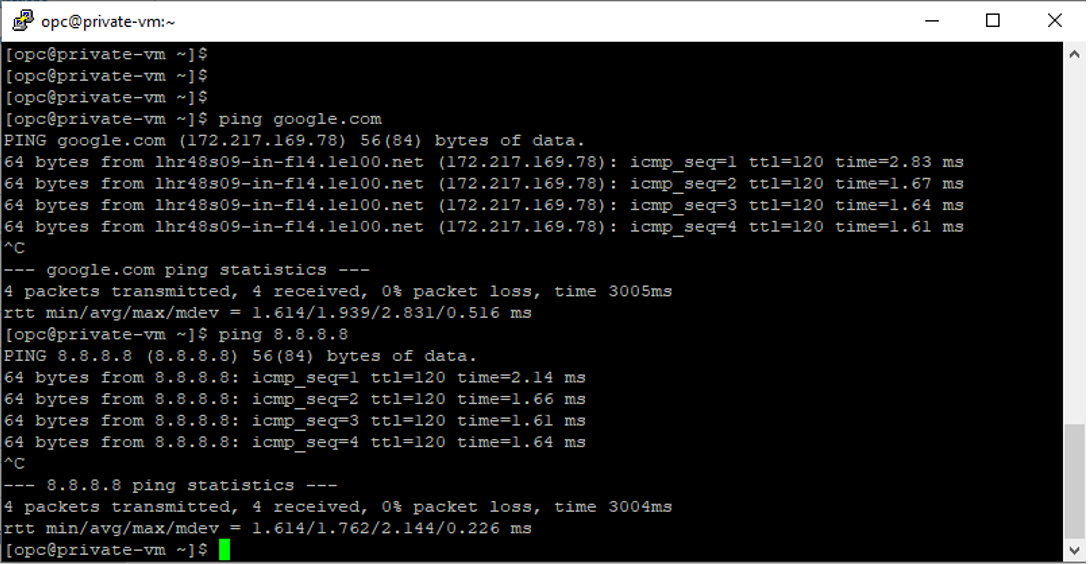
As you have seen above, the successful ping request to Google.com.
Note: We can have more than one NAT Gateway per VCN.
Note: The host can initiate outbound connections to the internet and receive responses, but no inbound connection can be initiated from the Internet (Use case: Updates, patches).
4.Conclusion
Like a traditional Data Center network, a VCN provides complete control over your network environment.This includes creating subnets, IP address space, required gateways, creating route tables, and many more components in your VCN. This blog contains basic but essential cloud architecture concepts that I tried to explain as efficiently as possible!
I hope you enjoyed it!
Blog links
OCI Public and Private Subnets in association with Internet and NAT Gateways (Part-1)
OCI Public and Private Subnets in association with Internet and NAT Gateways (Part-2)
