Hi! In this blog entry, we will talk about a common network architecture for the Oracle Database@GCP product, mainly how to connect to the Oracle Database from a remote location, via Google Interconnect.
Oracle Database@GCP
Oracle Databases of various types can now be deployed in AWS, Azure and GCP. Since the database now lives in that Cloud Service Provider, it has to follow the network rules and constructs defined there. Particularly for GCP, we have the following details:
- The database(s) will live in a new network construct called an ODB Network.
- The ODB Network will be automatically connected to a VPC through 4x Partner Interconnect which end up in a dedicated VPC Cloud Router, deployed automatically.
- The automation will make sure than any resource in the Peered VPC can connect to the database without any additional configuration.
Let’s look at what happens at the routing layer, through this diagram:
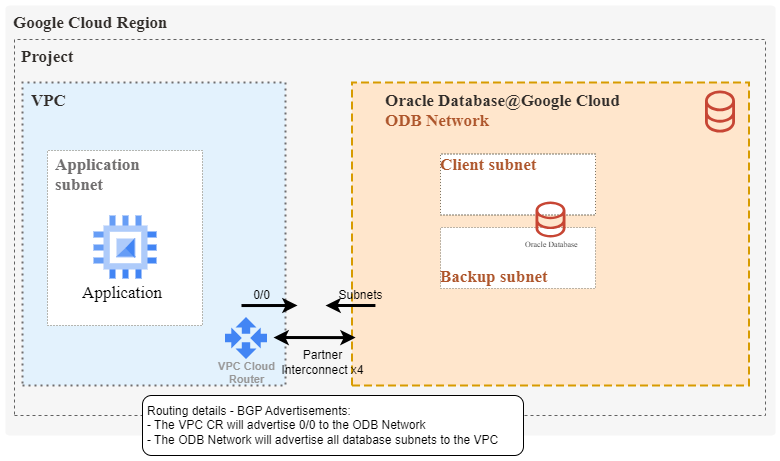
Looking into the initial routing setup, things are quite simple:
- A VPC Cloud Router will automatically be deployed in the VPC that was selected during ODB Network creation.
- The Cloud Router will have 4x Interconnect links to the ODB Deployment.
- Since this is Interconnect, all routing will be handled by BGP:
- The VPC cloud router will advertise 0/0 to the Oracle Database
- The Oracle Database will advertise all deployed subnets. Note that up to five subnets can be deployed in an ODB Network.
For more information about the network fundamentals of the product, please take a look at this blog.
The initial setup will create all needed constructs for routing, security, and DNS so connections from the initial VPC to the ODB Network will work seamlessly. However, what happens if there is an existing Hub-and-Spoke design which has a HUB VPC with connections to other locations (Datacenter, other Cloud Service Providers, etc.) and we want to leverage those connections for connectivity to the database? Google’s VPC Peering mechanism allows for route advertisements between the Cloud Routers of each VPC thus ensuring the required reachability. Let’s look at a diagram:
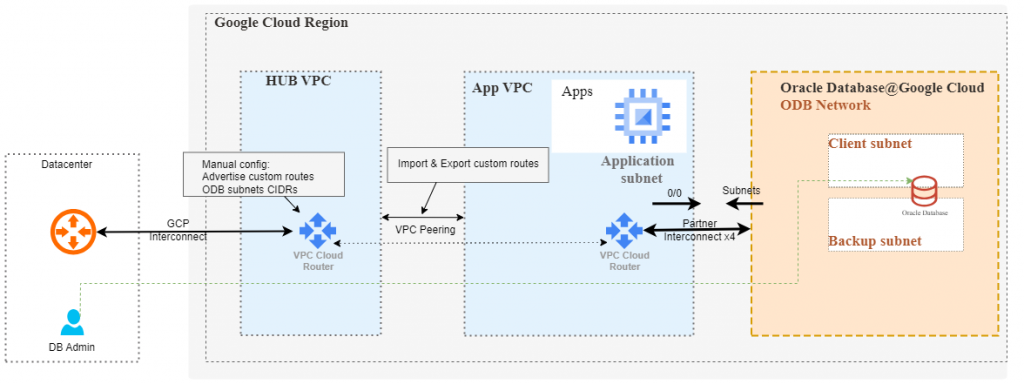
As some GCP Networking experience is expected, we will only discuss the important parts:
- When creating the peering between the HUB and the VPC connected to the ODB, you will need to enable importing and exporting of custom routes so that the ODB networks are advertised to the HUB.
- The VPC Cloud router in the HUB will need a manual configuration to advertise the ODB Networks to the remote location, via Interconnect.
And that’s pretty much it, the remote location should be able to connect to the Oracle Databases. Let’s do a quick demo and see where the relevant menus are.
DEMO
To make things more interesting, we will simulate the remote location with an OCI deployment and use the OCI – GCP Interconnect product, thus covering the use case where you want OCI workloads to connect to an Oracle Database deployed in GCP. As a note, the OCI – GCP Interconnect works like any other Interconnect so the steps described here will work on Interconnect connections to a datacenter too.
First, let’s put all the details on a diagram.
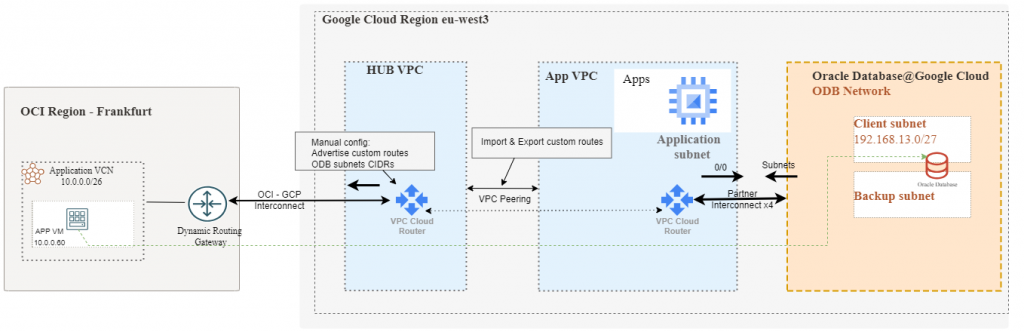
As there are many pieces involved, showing a detailed guide for all steps would make this blog too long. Most of the steps will be provided as a summary and we will focus only on the key parts.
A. The GCP VPCs
Before creating an ODB Network in GCP you need to have a VPC as it’s a required input for the ODB creation. I have 2 VPCs with subnets in GCP region eu-west3:
- naci-netw-vpc01 will be used for the ODB Peering
- naci-netw-hub01 will be used to connect to OCI and simulate a “hub”.
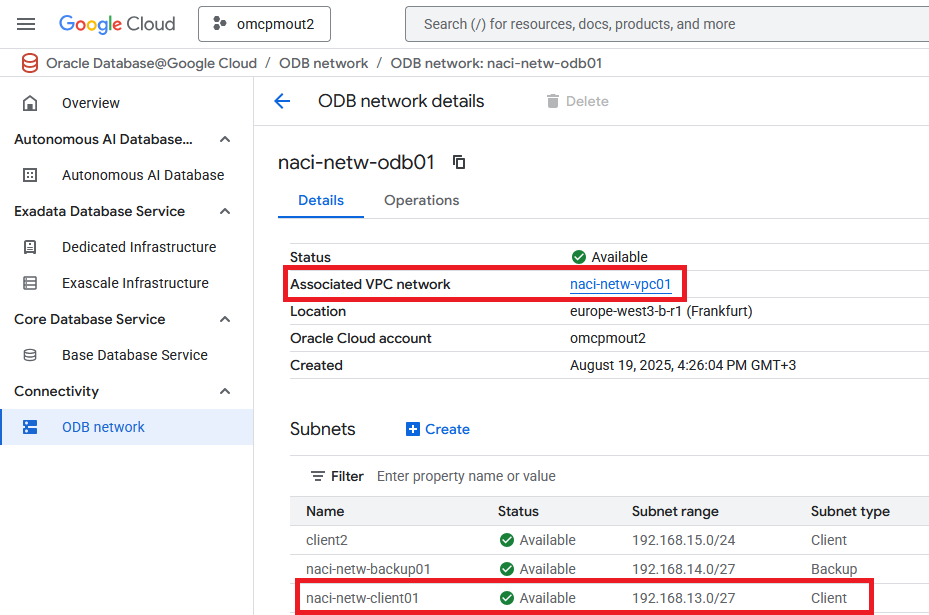
B. The ODB Network
I created an ODB Network and peered it to the VPC. I also created 3 subnets, one of them with the 192.168.13.0/27 CIDR and assigned it as a “client” subnet.
C. VPC Peering
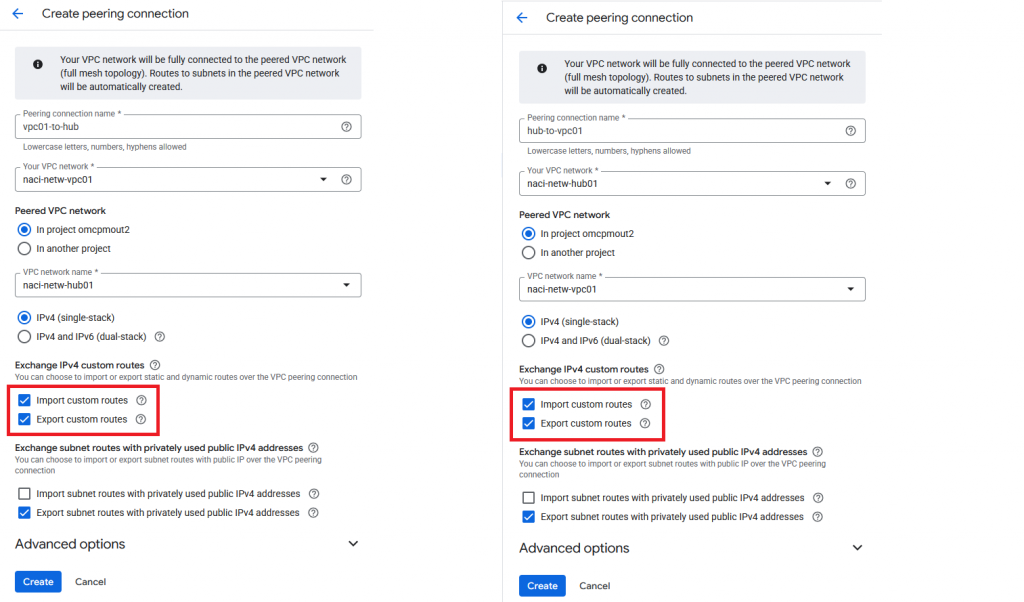
The next step is to create VPC Peering between the HUB and the ODB VPC (VPC01). As you know, VPC Peering has to be created from both sides, for everything to work properly. The most important thing here is to make sure you enable “Import custom routes” and “Export custom routes”.

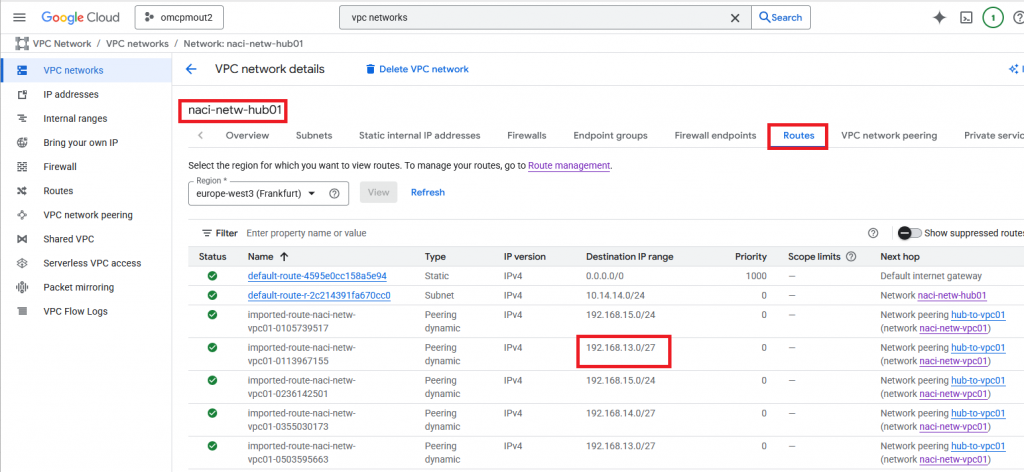
To make sure that everything went well, you should be able to see the ODB subnets in the Hub routes.
D. OCI – GCP Interconnect
The step-by-step procedure to deploy the OCI-GCP Interconnect would take too much space. Please follow the excellent guide written here. As discussed before, this Interconnect to OCI is just an example, any Google Interconnect will work.
Before starting the procedure, make sure you have a VPC Cloud Router deployed in your HUB. Since my HUB VPC is new, I will need to create one.
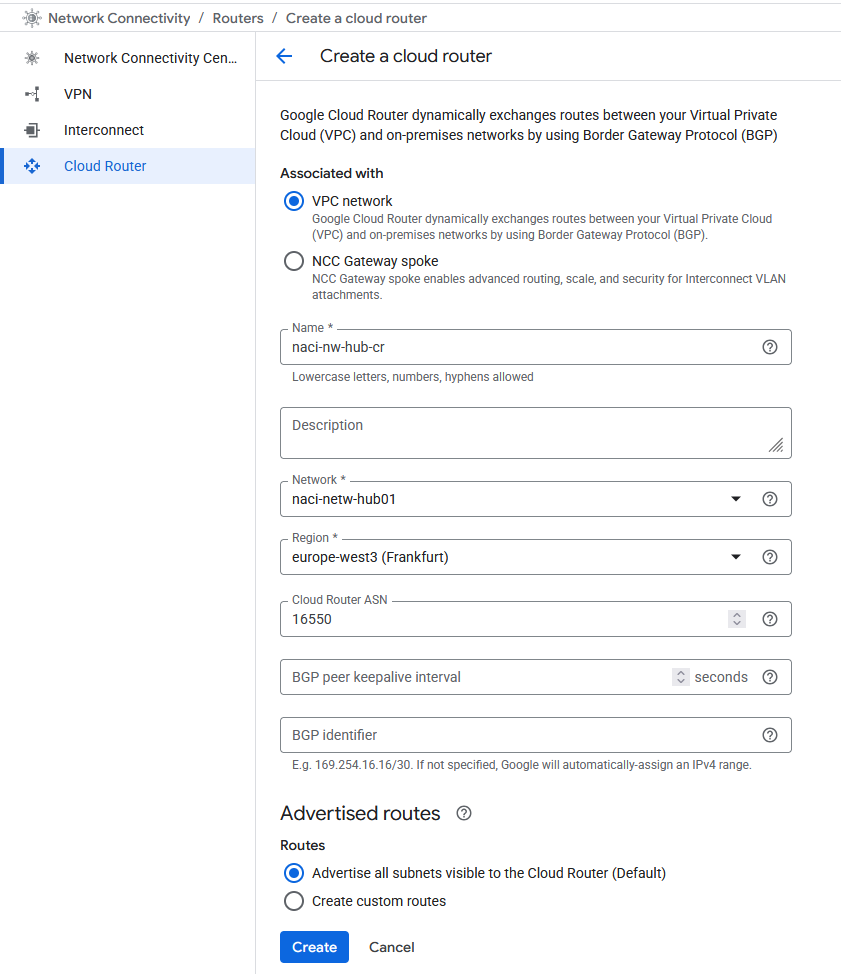
After the Cloud Router is deployed, we can start with the Interconnect deployment.
- Start on the GCP side with a new VLAN Attachment -> this will give you a service key.
- Input the service key on the OCI Portal FastConnect menu and wait for the deployment to complete.
When you are done, you should see the connection UP.
On the GCP side:
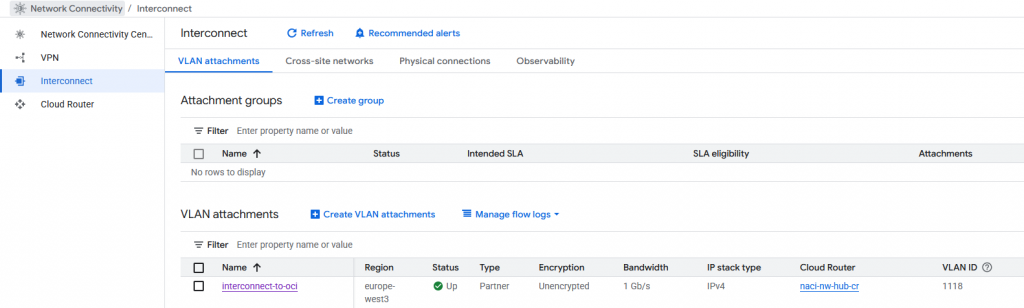
On the Oracle side:
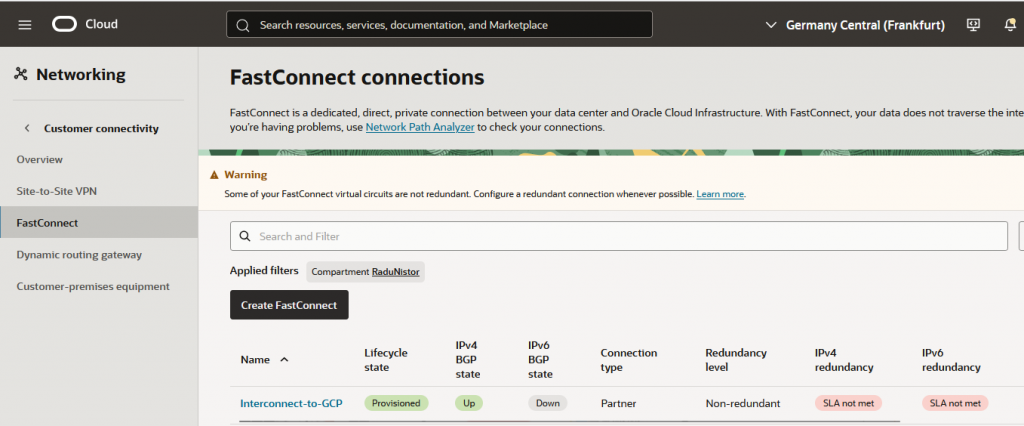
E. The OCI Infra side
All the infrastructure on the OCI side is out of scope of this blog. I have a VCN, a subnet, a Dynamic Routing Gateway and all the required configuration to allow connections to GCP.
F. The static advertisement from GCP
By default, GCP will advertise only the VPC subnets, over the Interconnect. In my example, I have a subnet in the HUB VPC with the allocated CIDR 10.14.14.0/24 and it’s only that subnet being advertised by GCP.
This is what OCI sees as routes advertised by GCP:
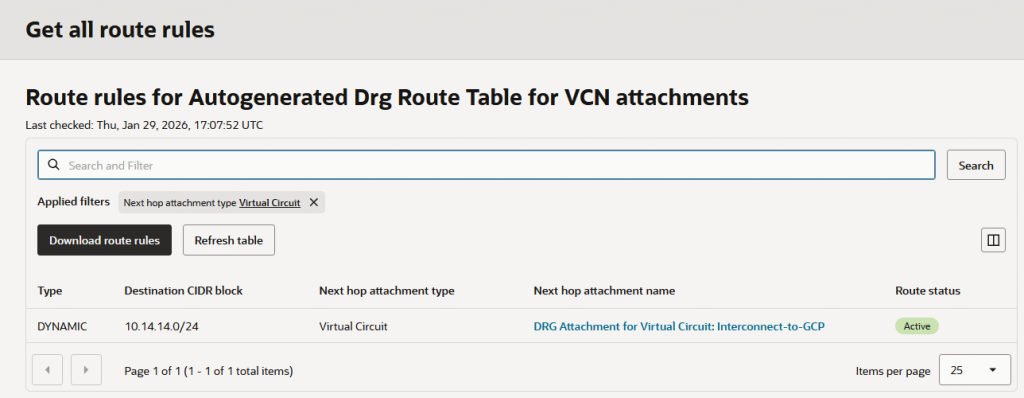
For GCP to advertise the ODB Networks via this Interconnect, we will need to configure the GCP Cloud Router in the HUB with Custom Routes.
Go to the HUB’s Cloud Router and edit it:
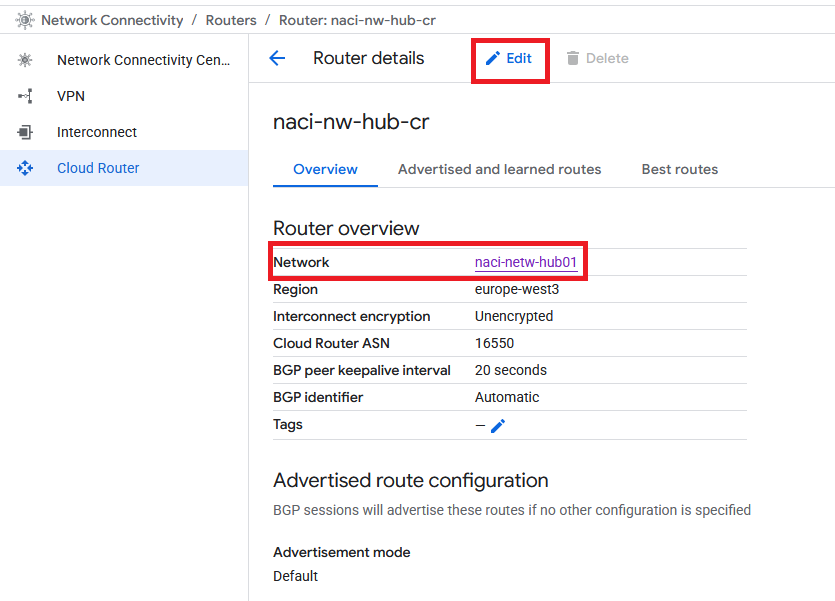
Add each ODB Subnet that you want to advertise as a Custom route.
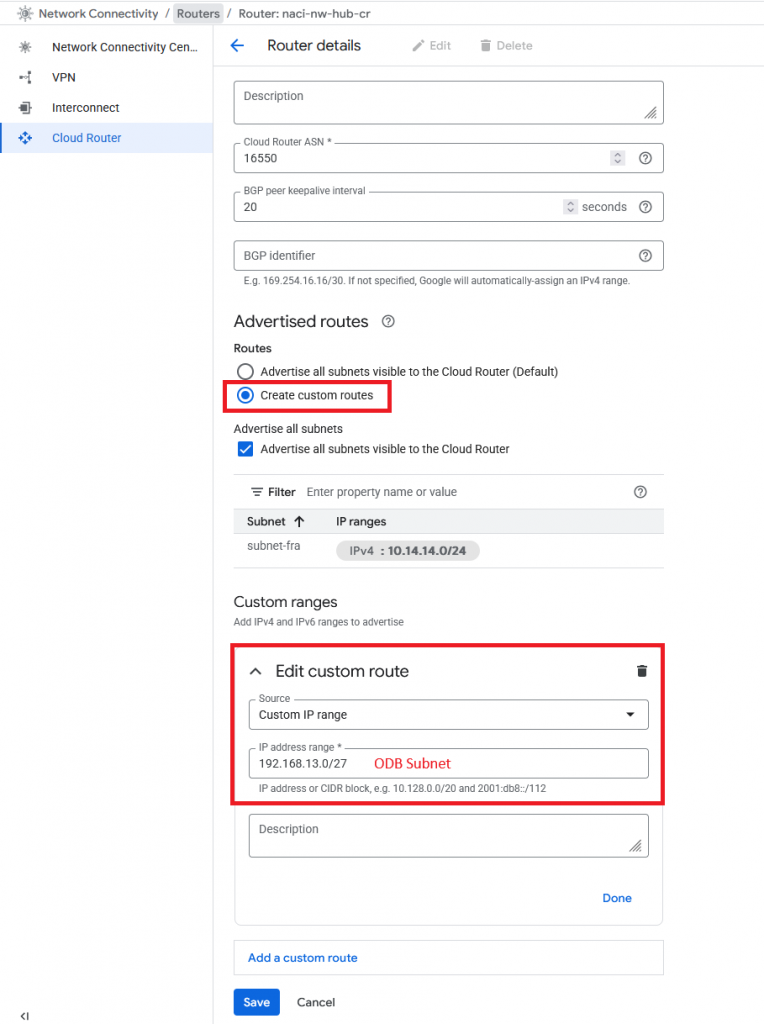
After you press Save you will see the route being received on the other side:
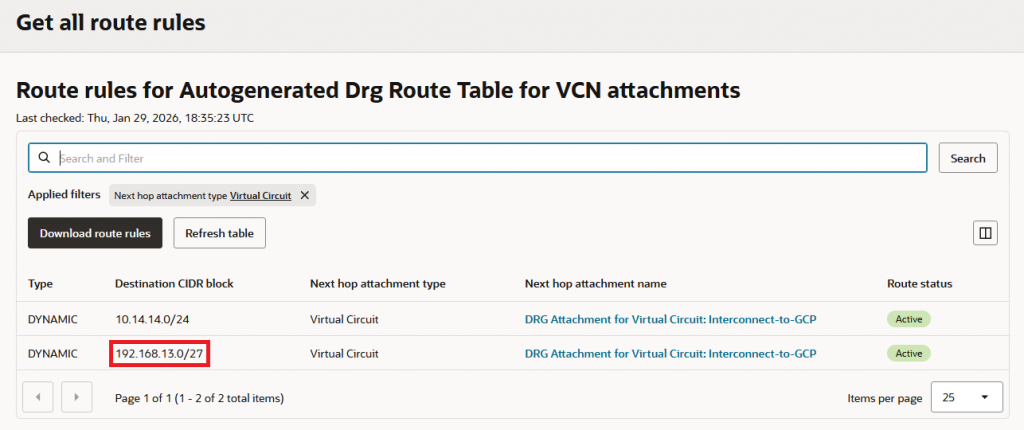
G. Connectivity test
Let’s test connectivity from a Compute instance I have in the OCI VCN. In the client subnet of the GCP ODB Network there is an IP that answers to DNS requests on TCP and port 53. Let’s see if I can reach it:
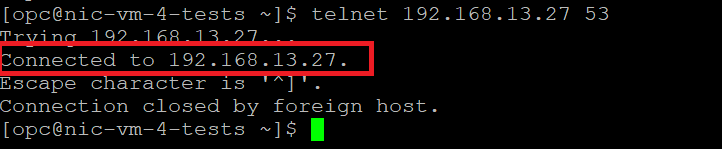
Success, I can reach into the ODB Network from a remote location, via GCP Interconnect.
And that’s it! I hope this helps you.

