Multicloud deployments are gaining significant traction in today’s landscape, emphasizing the critical need for a dependable, highly available connection to facilitate seamless connectivity. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) provides two viable options for achieving this remote connectivity.
- FastConnect
- IPSec tunnels
FastConnect offer dedicated connectivity between OCI and Onprem/Co-located infrastructure. It provides private/public dedicated and high bandwidth connectivity. For production workloads OCI always recommends FastConnect.
Another option for remote connectivity is IPSec tunnels. OCI offers this service free of charge but since this service is offered over internet the quality of service is best effort. This type of connectivity is recommended for Dev/Test workloads or management connections.
This blog aims to provide a step-by-step guide on establishing redundant IPSec tunnels between OCI and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).

We will start by configuring Cloud VPN on GCP side. Select the High-availability (HA) VPN option.
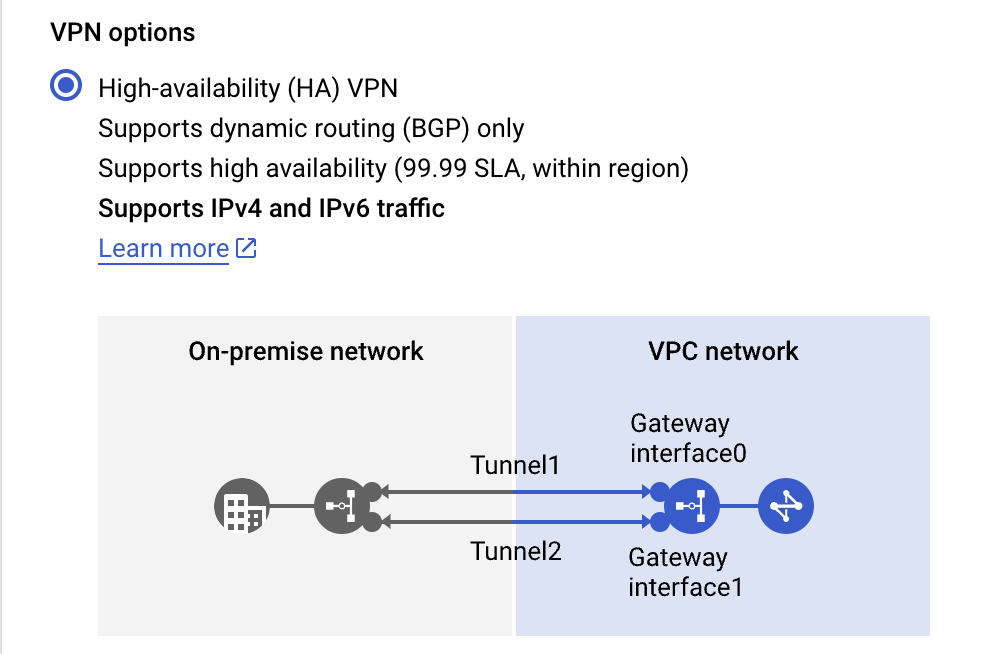
Create the Cloud VPN gateway by filling in the required info (skip the BGP session for now). GCP will allocate two Interface ip addresses for Cloud VPN Gateway which will be used as CPE ip addresses on the OCI side.
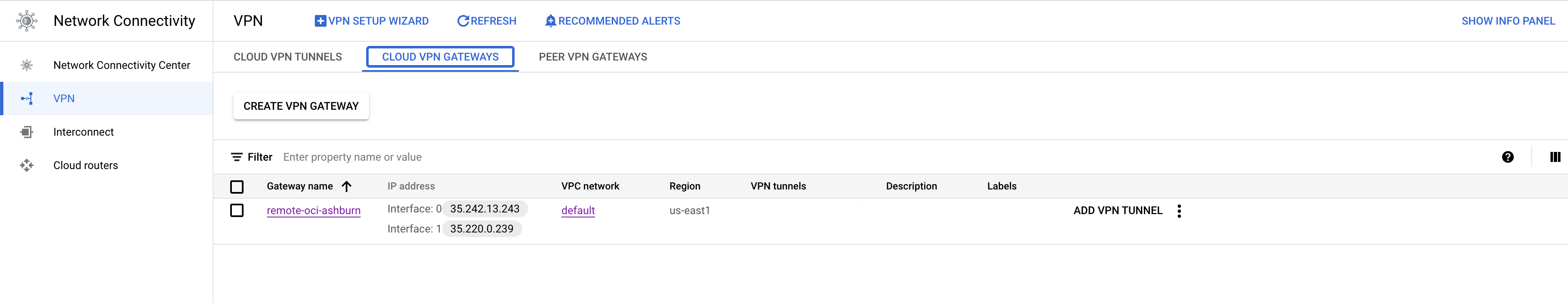
Let’s move on to OCI. Create OCI CPE and IPSec tunnels using GCP Cloud VPN Gateway Interface ip addresses. For more details on creating IPSec tunnels on OCI follow this link.
Note: GCP Cloud Router only allow 169.254.0.0/16 prefix for point to point BGP prefixes, keep that in mind while configuring BGP settings on OCI. Make sure you also enable ECMP on the DRG route table to utilize all active tunnels.
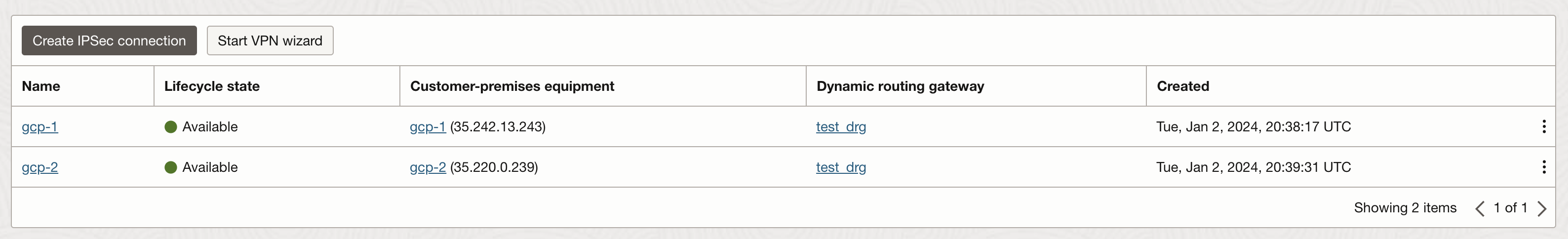
For each IPSec tunnel OCI will allocate two public ip addresses. To bring all IPSec tunnels online we will need to create 4 tunnels on GCP Cloud VPN Gateway. GCP offers multiple ways to accomplish this step. You can create 1 Peer VPN Gateway with 4 interfaces or create 4 individual Peer VPN Gateways (In this example I will create 4 individual Peer VPN Gateways).
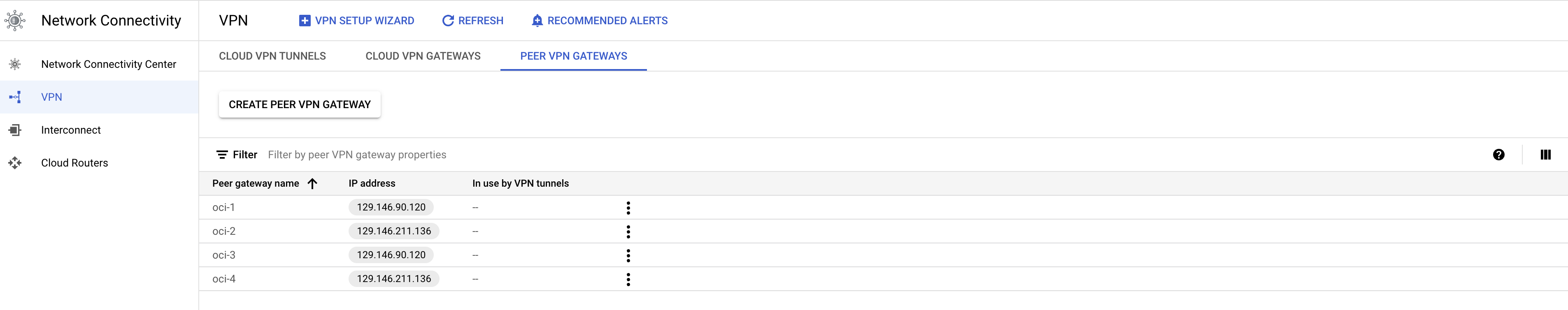
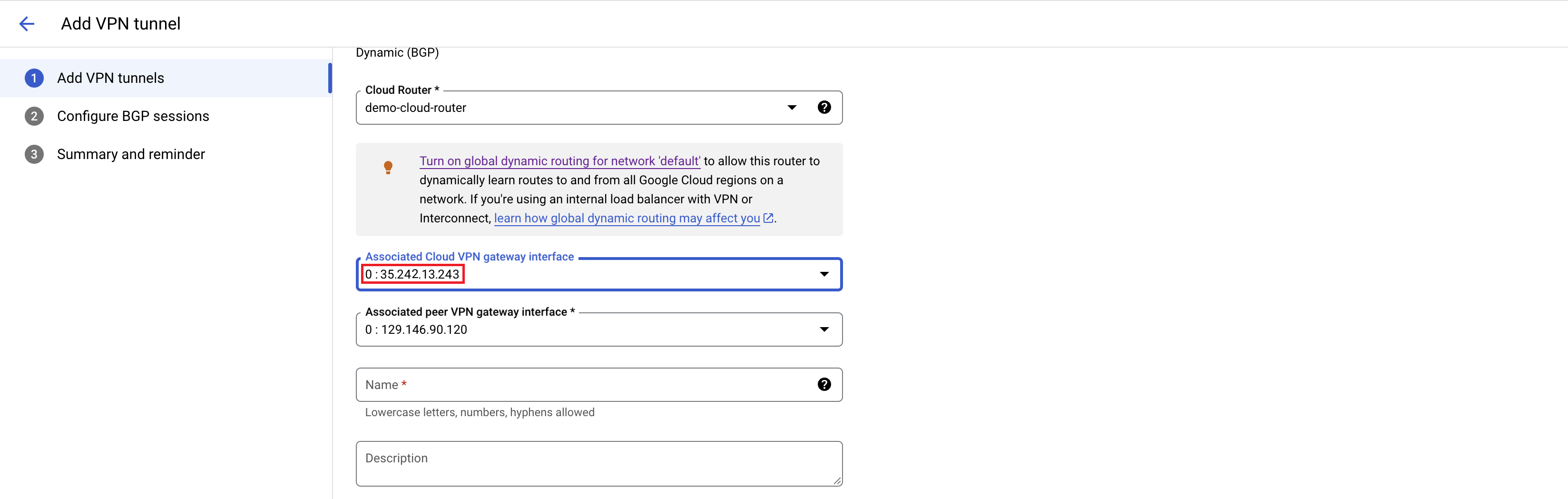
Next add the VPN tunnels to Cloud VPN Gateway and attach it to a Cloud Router.
Make sure to create the correct mapping between the Cloud VPN Gateway and OCI IPSec tunnel endpoints. At this point also add the BGP config on the Cloud Router.
For this example, mapping should look like this:
35.242.13.243 <----> 129.146.211.136 35.242.13.243 <----> 129.146.90.120 35.220.0.239 <----> 129.146.90.120 35.220.0.239 <-----> 129.146.211.136
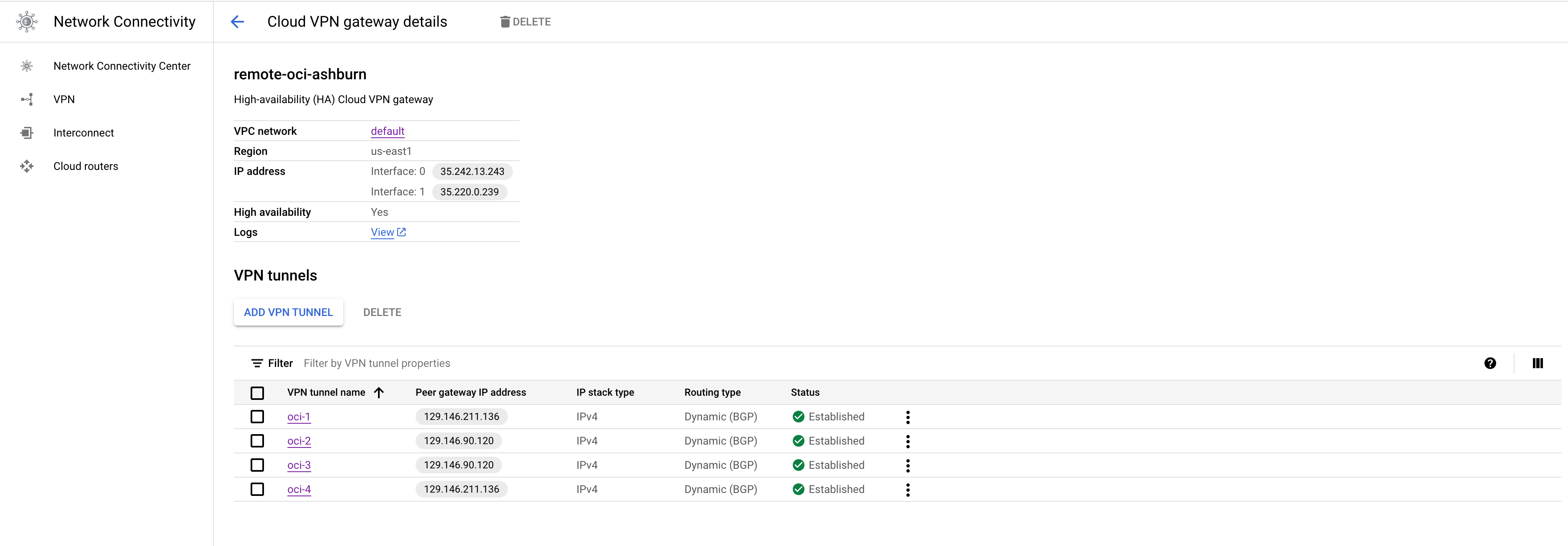
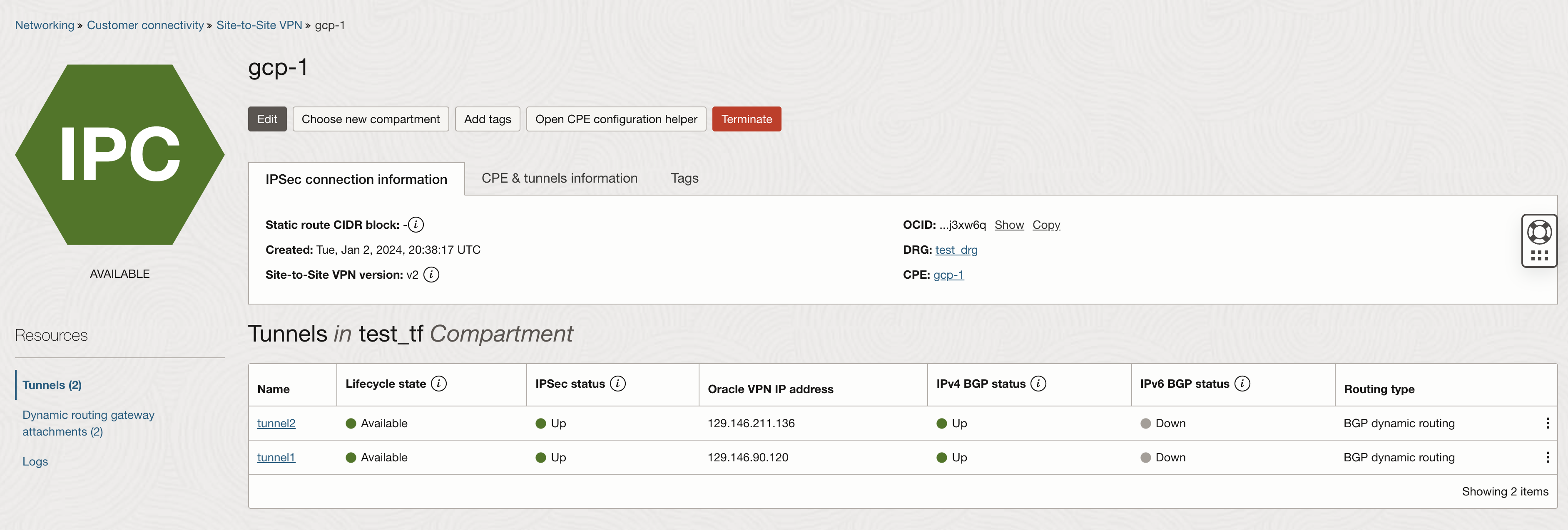
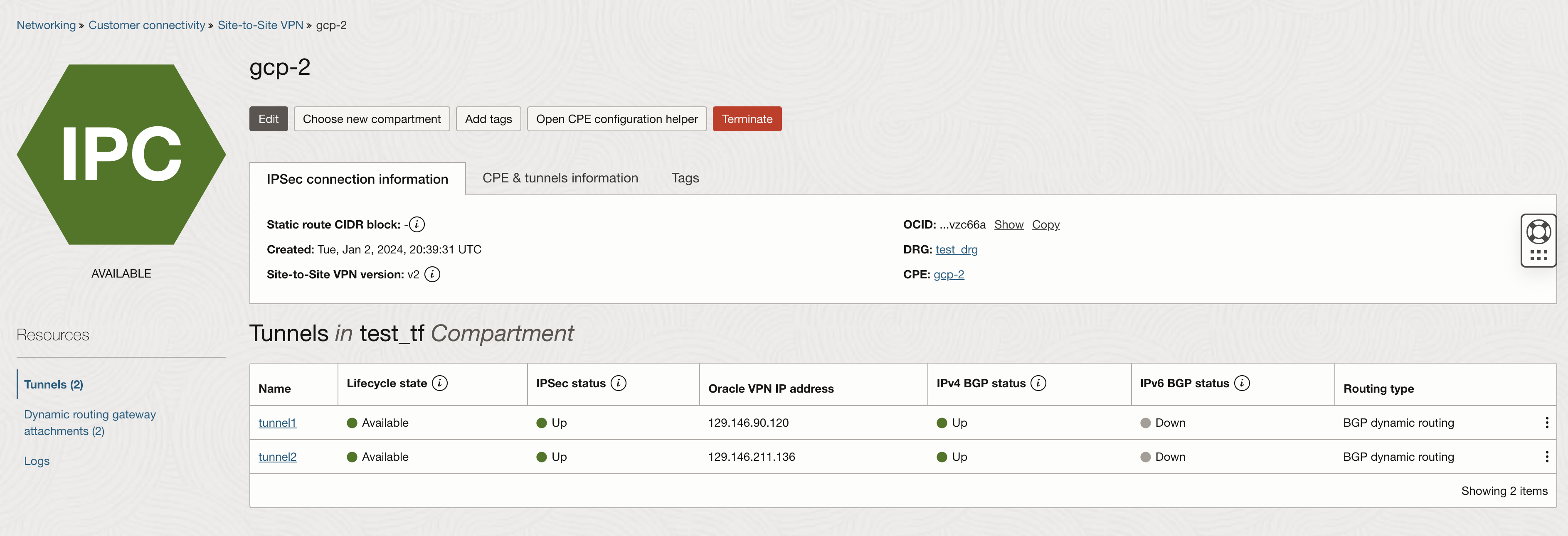
After this step you should start seeing IPSec and BGP sessions to change their status to established. Final Config will look like this.
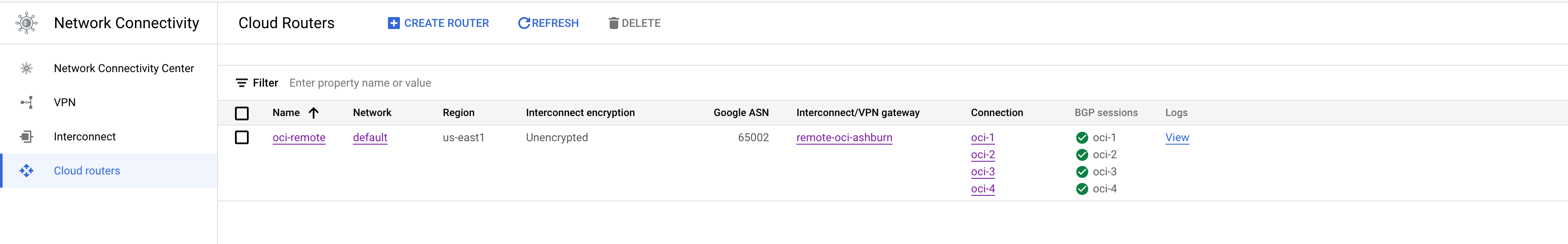
Lets take a look at the Cloud Router and BGP config.
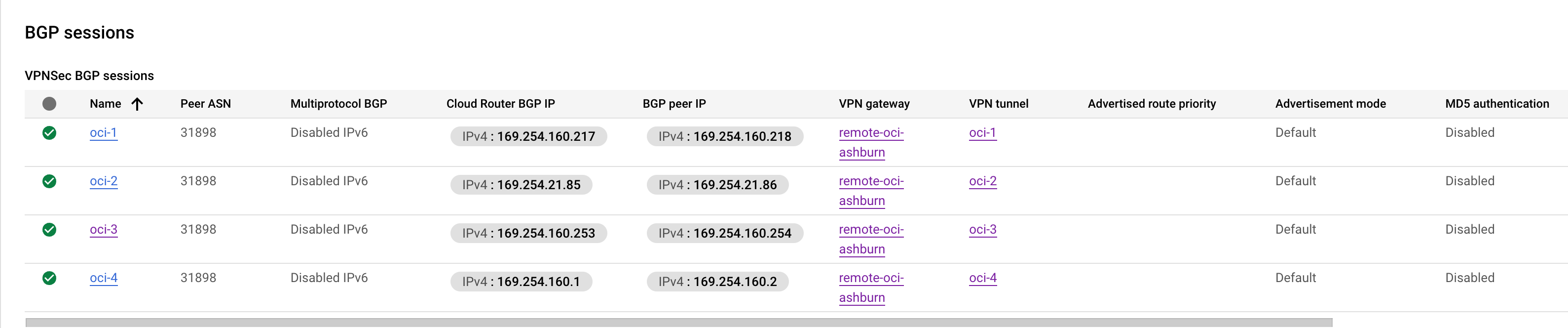
On OCI you will also see the IPSec and BGP in established status.
Conclusion
The intention of this blog is to provide step by step instructions on how to build IPSec tunnels between OCI and GCP while making sure that all tunnels on both side are active and forwarding traffic.
