The OCI-Classic or for short OCI-C was the very first Oracle Public Cloud. Relevant to that, the initial name was OPC (Oracle Public Cloud) and latter was changed to OCI-Classic.
OCI-C offered a broader range of IaaS, PaaS and SaaS and some of our customers are still running the workloads on OCI-C. The process of migrating all our customers from OCI-C to OCI is still in progress. During the workload migration process, we need to make sure the IP connectivity between OCI-C and OCI is in place and in good condition.
In the following sections we will explore how we can connect the OCI-C to OCI and the configuration that needs to be done on OCI-C. The connectivity part is one of the most asked subject when it comes to workload migration from OCI-C to OCI, so, let’s explore the options we have.
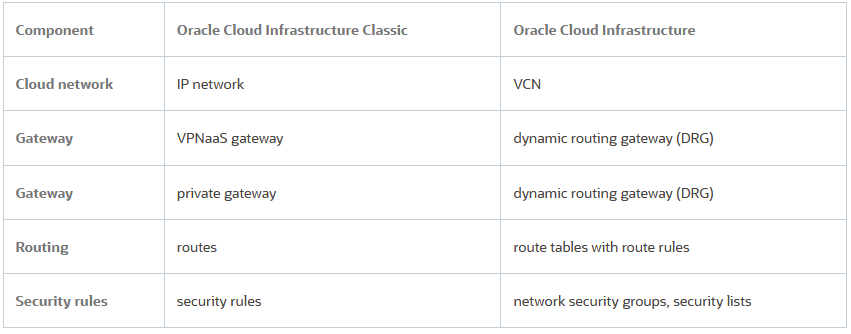
First, we need to analyze some corresponding terms that we will use between OCI-C and OCI , summarized in the below table:
And the networking diagram to place the gateways:
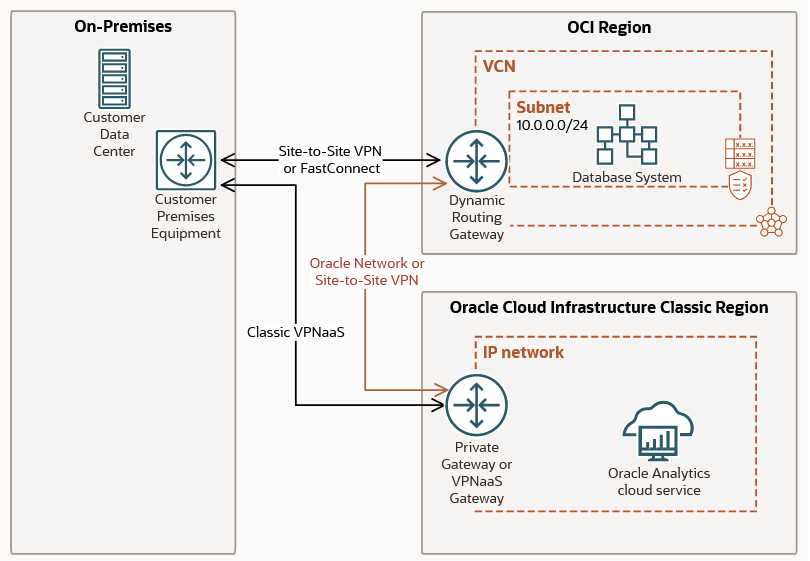
Note 1: The above diagram reflects the private connectivity between the two clouds.
Note 2: If IP connectivity using the public IP addresses is needed, then, the gateways depicted above are not necessary at all. The OCI and OCI-C datacenters are connected through the OCI Backbone network and any public to public IP address connectivity between OCI-C and OCI is using the OCI Backbone Network.
Note 3: Mostly, the focus will be on the OCI-C configuration.
Method 1 – Using the OCI-C VPNaaS to create IPSec tunnels to OCI VPNaaS and connect IPNetwork(s) to VCN(s)
– OCI-C VPNaaS supports only Policy Based IPSec tunnels so, OCI VPNaaS should be configured for Policy Based IPSec tunnels;
– OCI-C VPNaaS is behind a NAT, that being said, the NAT-T on OCI should be set to Auto;
If you want more than one IPNetwork to be reachable over the IPSec tunnel, you should have an IPNetwork Exchange and attach to the IPX all the IPNetworks that needs to be reachable over the IPSec tunnel. An IPNetwork Exchange enables access between IPNetworks that have non-overlapping addresses, so that instances on these networks can exchange packets with each other without NAT and in case the VPN is used, all the IPNetworks in the same IPX will be added to the encryption domain.
You’ve created a vNICset for the vNICs that you want to access using this VPN connection, if required. Alternatively, you can use the default vNICset.
A Virtual NIC Set, or vNICset, is a collection of one or more vNICs. vNICSets are useful when you want to use multiple vNICs for the same action. For example, you use vNICSets to specify multiple vNICs as a source or a destination in a security rule. You can also use vNICsets in routes to specify multiple vNICs as the next hop destination for that route or provide IP reachability to vNICs in a vNICSet over an IPSec tunnel (our case).
For a complete OCI-C resource guide, please use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute Classic.
The key element for Method 1 relates to the fact that OCI-C VPNaaS permits the change of the IPSec peer public IP address after the VPN tunnel is created.
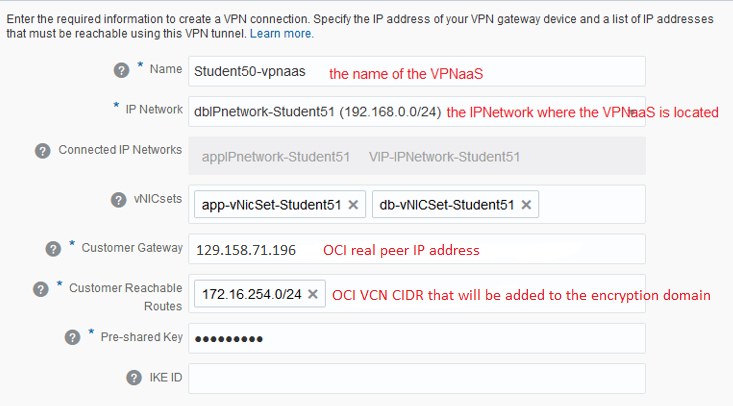
As we know, in order to define the CPE on the OCI side (and by the way, the OCI-C VPNaaS public IP address will act as a CPE on OCI and vice-versa) we will define a dummy peer on the OCI-C VPNaaS in order to complete the configuration and obtain the public IP address of the OCI-C VPNaaS. With the OCI-C VPNaaS public IP address, we will define the CPE and create the VPN connection on the OCI. At the end of the process the real public IP addresses (there are two but we will use only one) of the OCI VPN will be obtained. We pick one IP address and update the OCI-C VPNaaS with the correct peer IP address.
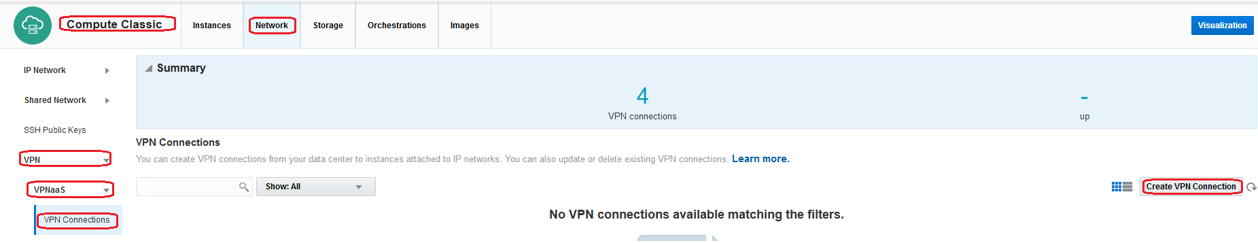
1. Navigate to: Compute Classic -> Network -> VPN (bottom left side) -> VPNaaS -> VPN Connections -> Create VPN Connection
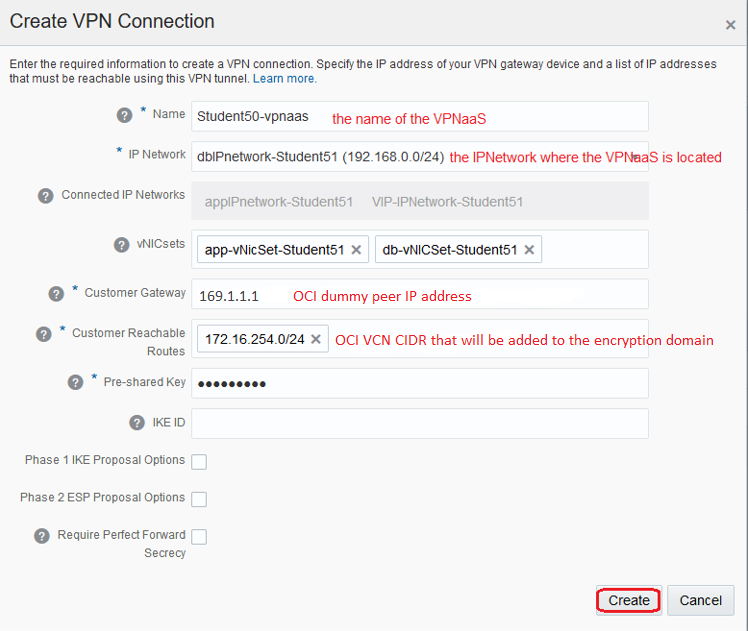
OCI-C VPNaaS supports Phase 1 and 2 specific parameters.
The public IP address of the VPNaaS will be assigned only after the VPNaaS connection is created using the above step.
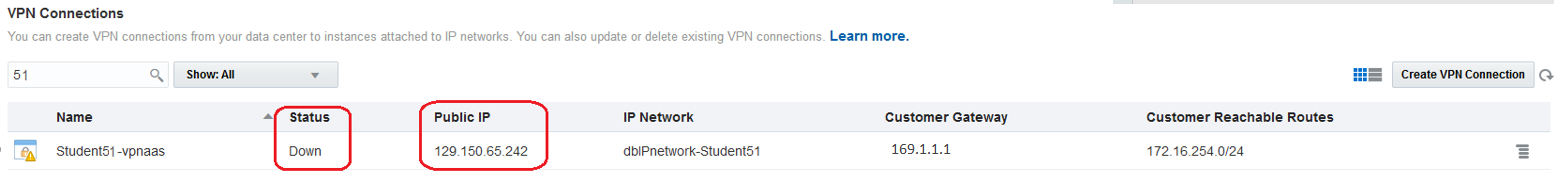
The OCI-C VPNaaS public IP address will be used to define the CPE and complete the VPN connection on the OCI side. One public IP address from OCI VPN connection will be used to configure the real peer on OCI-C VPNaaS:
After changing the dummy peer IP address to the correct one obtained from OCI, the IPSec status will change to Up.
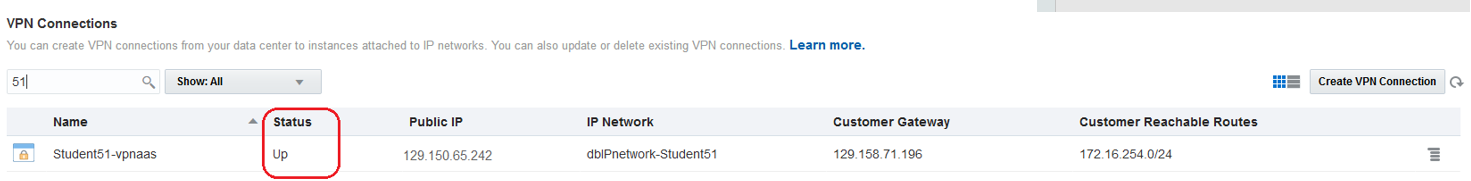
Now, a working IPSec tunnel is in place and ready to encrypt/decrypt the traffic using the policy based between the two clouds. Make sure the proper security is in place to allow the desired traffic.
Method 2 – Create a dedicated connection between OCI-C IPNetwork(s) and OCI VCN(s)
You can run a hybrid workload between your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Classic and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure environments.
Oracle connects the IPNetwork’s Private Gateway to the VCN’s attached dynamic routing gateway (DRG). The connection runs over the OCI Backbone Network. You configure routing and security in the environments to enable traffic. The two environments must belong to the same company and not have overlapping CIDRs. The cloud resources can communicate over the connection only with private IP addresses.
The two environments must both be in the Ashburn area, the London area, or the Sydney area. Connectivity to other regions is not supported.
The connection is free of charge.
The connection is supported only between these regions:
– Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Australia East (Sydney) region and the Sydney Classic region;
– Oracle Cloud Infrastructure US East (Ashburn) region and the Ashburn Classic region;
– Oracle Cloud Infrastructure UK South (London) region and the Slough Classic region;
The configuration will start by creating the OCI-C Private Gateway. While creating a Private Gateway, specify the IPNetworks that you want to associate with the Private Gateway.
The IPNetworks associated with the Private Gateway will be announced via BGP to the peer (OCI in our case).
To create the Private Gateway using the Web UI navigate to: Compute Classic -> Network -> VPN -> FastConnect -> Private Gateways -> Create Private Gateway
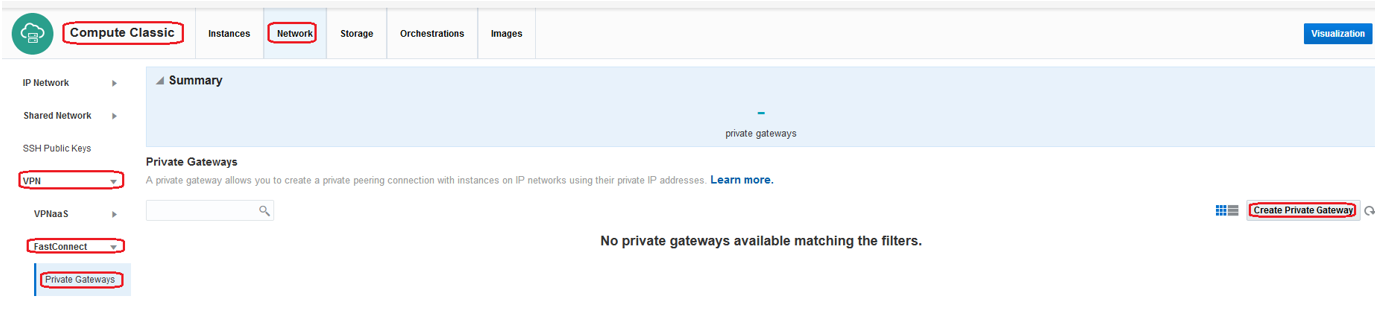
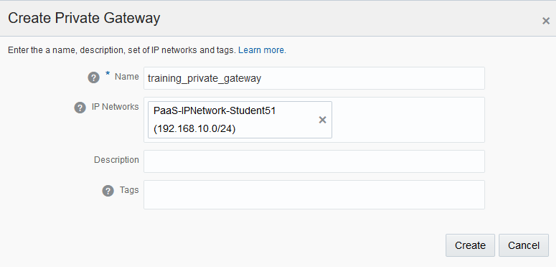
You can add/remove IPNetworks at any moment after the connection is provisioned.
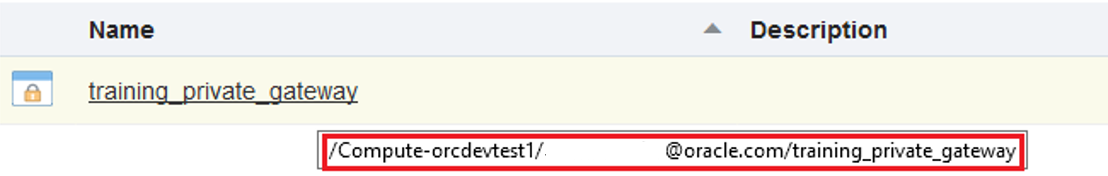
Note down the three-part name (/Compute-identity_domain/user/object) of your Private Gateway. You’ll need to provide this name in the SR that needs to be opened for provisioning the dedicated connection between OCI-C and OCI.
For the connection to be ready for provisioning, an OCI tenancy and DRG needs to be in place.
Login to My Oracle Support and open an SR with the following information:
- Ticket name: Create IP Network – VCN Connection – <your_company_name> – Ashburn
- OCI-C identity domain
- OCI-C private gateway name
- Region
- OCI tenancy OCID
- OCI DRG OCID
It can take three to four business days before your My Oracle Support ticket is complete and the connection is ready to test. After the connection provision confirmation is received, the connection is ready for testing.
