Introduction
The evolution of cloud computing enables enterprises to embrace multicloud solutions and take advantage of the best capabilities offered by different providers. The Multicloud Oracle Database at AWS (ODBAWS) is a powerful example where businesses can leverage AWS’s robust infrastructure with Oracle’s specialised Database offerings. A vital component of this setup is effective DNS resolution to facilitate smooth cross-cloud operations.
In this blog we will go thought the DNS options when deploying the Oracle Database at AWS service. At the time of writing of this blog, the two products available are the Exadata Cloud Service Dedicated (Exa-D) and Autonomous Database Dedicated (ADB-D).
Before moving forward, I encourage you to read the documentation about the service and the prerequisites for deployment.
When we discuss about networking in the context of ODBAWS, the central piece is the ODB Network that provisions the OCI networking components (VCN, DNS, etc.) from the AWS console.
If you want to learn about the network topologies for the service, please read this reference architecture and also read about the deployment of the ODB network from this step by step document.
DNS options when deploying the ODB Network
During the provisioning of the ODB network there are two choices for DNS:
- Default DNS domain which uses the oraclevcn.com for the service. you can define a domain name prefix (limited to 15 characters).
- Custom Domain Name that will allow the customer to leverage any private domain that they want (limited to 253 characters).
Below you can find a screenshot taken during a provisioning of the ODB Network.
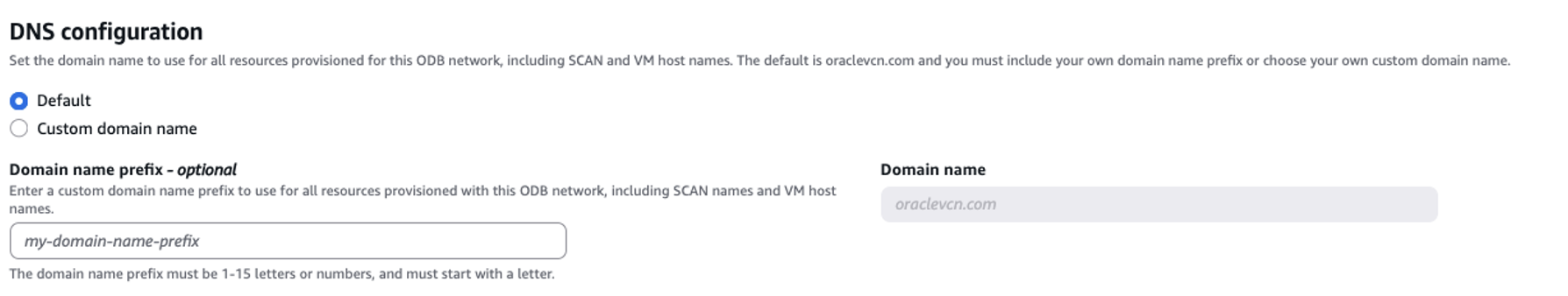
The Default domain can be used by both EXA-D and ADB-D, but the custom domain can be used by only the EXA-D.
When deploying the custom domain name, also the default domain is created. The EXA-D will use the custom domain for the records. If we will deploy the ADB-D in the same odb Network, this service will use the default domain.
DNS resolution architecture
After the ODB Network creation, we will have two OCI DNS endpoints provisioned:
- listener endpoint which is displayed in the AWS console under the ODB network and is used for AWS or on-prem DNS to resolve the DB endpoints.
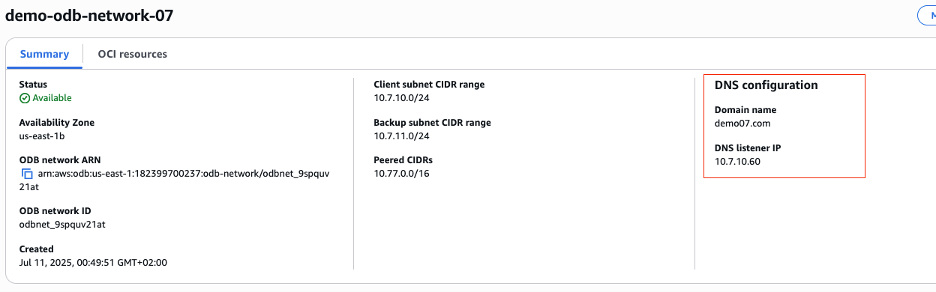
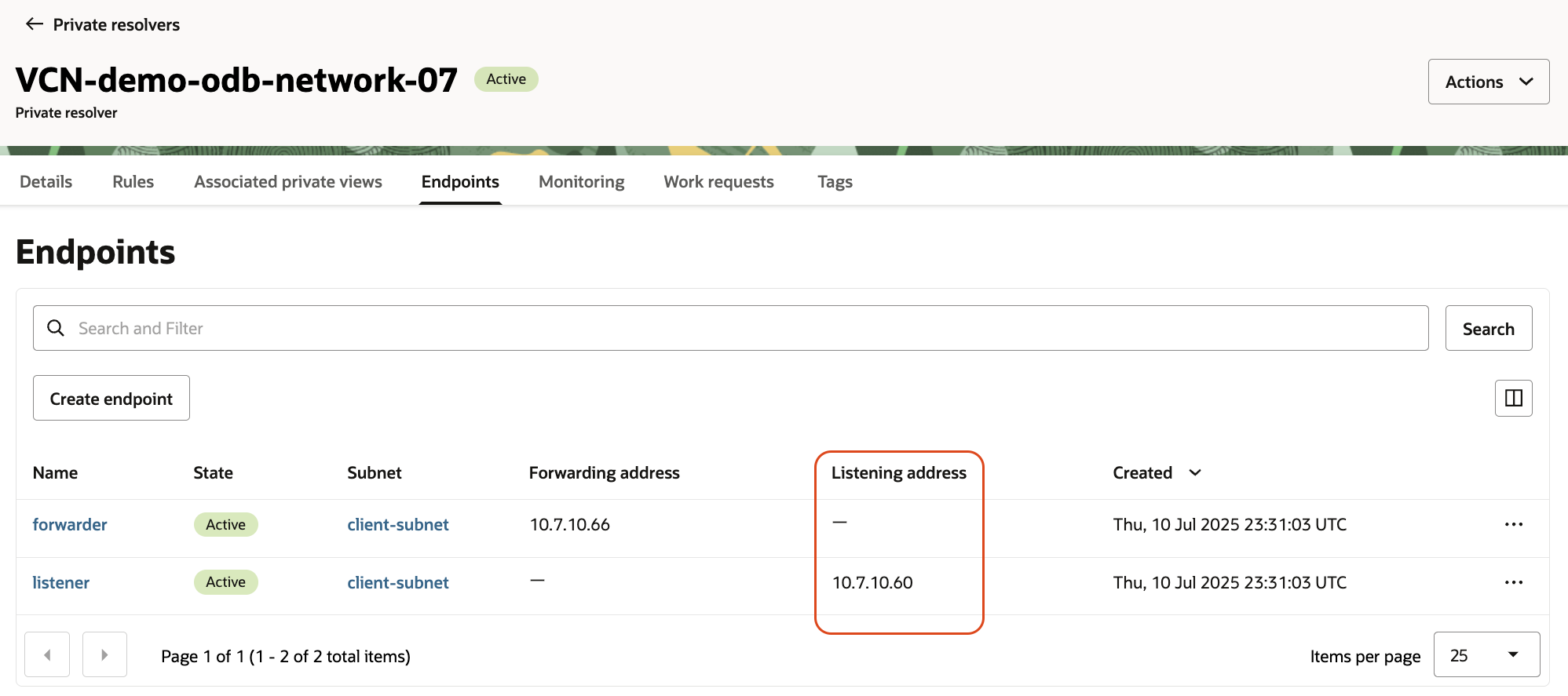
- forwarder endpoint which can be used to enable the DNS resolution from the VCN where the Service is deployed to the DNS resources in AWS or from on-prem. The forwarder can be found in OCI.
Below is the network architecture for the DNS:
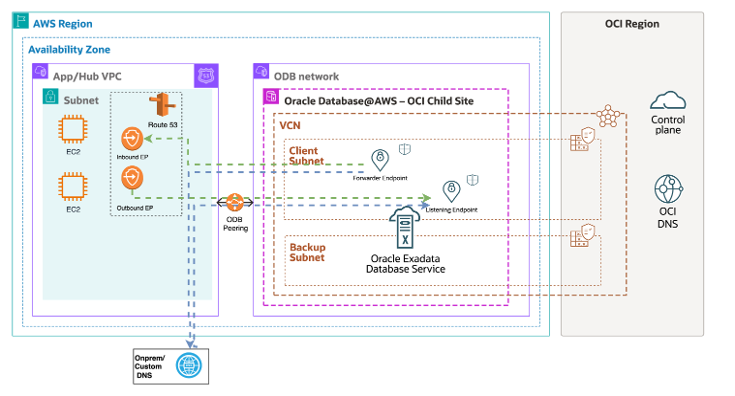
In order to resolve the oraclevcn.com or the custom domain name of the service from an EC2 instance in AWS, we need to configure an outbound DNS endpoint and create a resolver rule to forward the DNS queries to the OCI DNS listener endpoint as described in the AWS documentation. You can read more about the AWS DNS resolution here.
Conclusion
In essence, DNS resolution is a foundational element in ensuring that your application connects to the Oracle Database at AWS without the need of remembering it’s IP address.
