Introduction
In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, the fusion of natural language processing (NLP) with data manipulation transforms how we interact with databases. This blog delves into the intriguing synergy between LangChain, an innovative open source language interface, and a robust language model to query the Oracle Database effortlessly. I will demonstrate to you how to harness the potential of these tools for streamlined database querying.
Prerequisites
Install Oracle Database on Docker
The Oracle Database setup on Docker ensures a self-contained and isolated environment for experimentation. The procedure is as follows:
- Install Docker: Set up Docker on your machine.
- Pull the Oracle Database Docker image: Fetch the Oracle Database image using this command:
docker pull container-registry.oracle.com/database/express:latest
- Create a Docker container: This command creates a Docker container named “oracle-db” from the pulled image, mapping required ports:
docker container create -it --name oracle-test -p 1521:1521 -e ORACLE_PWD=<Enter Your Password> container-registry.oracle.com/database/express:latest
- Connect to the database: To interact with the Oracle Database, download and install JDeveloper or other SQL editors and use the following database info:
host: localhost port: 1521 username: system password: <Your Password> sid: xe
- Create a user and some tables. For example,
CREATE USER smith IDENTIFIED BY password;
GRANT CREATE TABLE TO smith;
### Connect to the database using this user and create a table.
CREATE TABLE "AUTHOR"
( "NAME" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"COUNTRY" VARCHAR2(100 BYTE),
"JOB_ROLE_ID" VARCHAR2(20 BYTE),
"ID" VARCHAR2(20 BYTE) NOT NULL ENABLE,
CONSTRAINT "AUTHOR_PK" PRIMARY KEY ("ID"));
- Download and install Python database client: SQLAlchemy supports cx_Oracle and python-oracledb. To interact with the Oracle database, I am using cx_Oracle in this blog; hence, you need to follow the instructions in this doc to install cx_Oracle: https://cx-oracle.readthedocs.io/en/latest/user_guide/installation.html.
Download and Install LangChain from GitHub
LangChain acts as a crucial bridge between human language and database queries. Follow these steps for a successful installation:
- Visit LangChain GitHub repository: Access the GitHub repository at: https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain.
- Clone the repository:** Use the following command to clone the repository to your local machine: git clone https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain.git
- Follow the LangChain documentation instructions to install it from the source: https://python.langchain.com/docs/get_started/installation#from-source.
Install SQLAlchemy (If required)
The SQLAlchemy library streamlines database access and manipulation tasks in Python. LangChain is using this library to interact with the database. If it is not installed, you can install SQLAlchemy using pip: pip install sqlalchemy
Query the Database by Asking a Question
The amalgamation of LangChain and the language model facilitates the effortless translation of natural language queries into database operations. A basic example illustrates this process:
Before using LangChain to query the database, you must modify the LangChain source code to handle the issue when the language model generated SQL statement contains additional double quotes and semi-colon that the Oracle database driver cannot execute. Locate the following Python script: …/LangChain/langchain/langchain/sql_database.py. Then, go to line 390, above the cursor variable, and add the following lines:
command = command.replace(";","").replace('"','')
cursor = connection.execute(text(command))
This workaround uses the replace function to remove the “;” and double quotes in the SQL statements before execution.
Create a query script: Develop a Python script (e.g., `query_database.py`) that seamlessly integrates LangChain and the database connection:
from langchain import OpenAI, Cohere, SQLDatabase, SQLDatabaseChain
import cx_Oracle
import os
import cohere
from langchain.chains import load_chain
import os
COHERE_API_KEY="Your Cohere API Key"
os.environ["COHERE_API_KEY"] = COHERE_API_KEY
lib_dir = os.path.join(os.environ.get("HOME"), "Development", "instantclient_19_8")
cx_Oracle.init_oracle_client(lib_dir=lib_dir)
hostname='localhost'
port='1521'
service_name='xe'
username='<Your DB User>'
password='<Your Password>'
# cx_Oracle.init_oracle_client(lib_dir=lib_dir)
oracle_connection_string_fmt = (
'oracle+cx_oracle://{username}:{password}@' +
cx_Oracle.makedsn('{hostname}', '{port}', service_name='{service_name}')
)
url = oracle_connection_string_fmt.format(
username=username, password=password,
hostname=hostname, port=port,
service_name=service_name,
)
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
engine=create_engine(url, echo=True)
db = SQLDatabase(engine)
llm = Cohere(temperature=1, verbose=True)
db_chain = SQLDatabaseChain.from_llm(llm, db, verbose=True)
db_chain.run("Is Casey Brown in the database?")
This code snippet demonstrates how to use the LangChain library, specifically the `Cohere` module and the `cx_Oracle` library, to interact with an Oracle Database using natural language queries. It leverages LangChain’s capabilities to convert human language into SQL queries for execution on the Oracle Database. See sample output below:
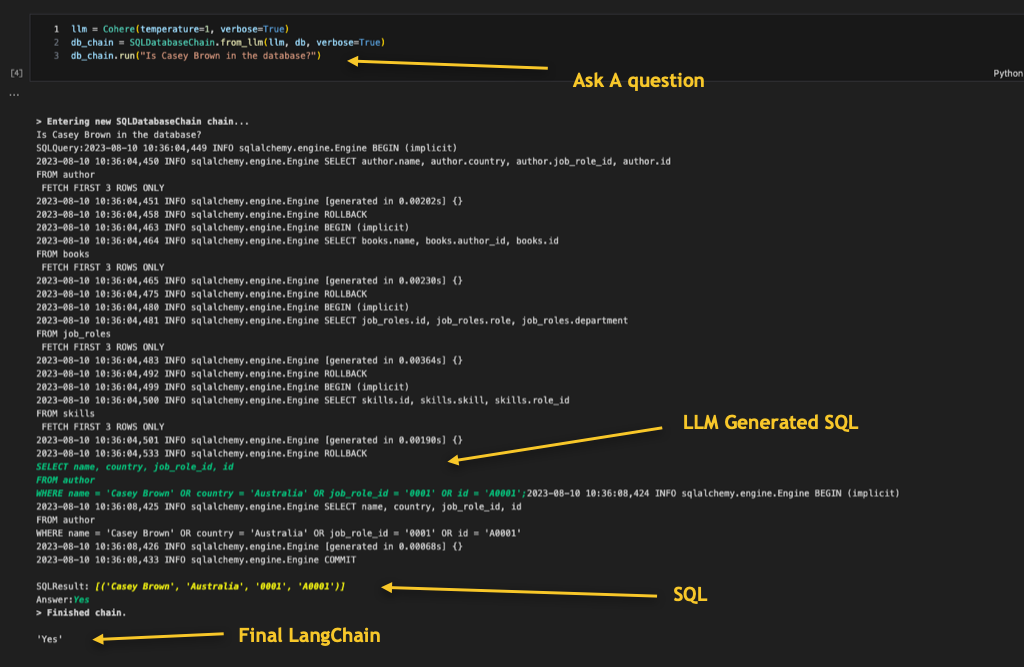
What are the things to watch out for?
You should be aware of certain considerations and potential challenges when using LangChain and integrating it with an Oracle Database to perform natural language queries. Here are some important things to watch out for:
- Query Complexity and Ambiguity: Be cautious when dealing with complex or ambiguous queries. Natural language can sometimes be open to interpretation, and LangChain may not always generate the exact SQL query you intended. Review the generated SQL queries carefully to ensure accuracy.
- Data Security and Privacy: While LangChain enhances accessibility, ensure that sensitive data is not exposed or mishandled. Protect sensitive information using appropriate security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and validation.
- Performance Impact: Introducing natural language queries can impact database performance, especially for complex queries. Regularly monitor and optimize query execution to maintain acceptable performance levels.
- Language Model Limitations: Language models, including those used by LangChain, may have limitations in understanding specialized or domain-specific terminology. Ensure your queries are clear and concise, avoiding jargon that the language model might not comprehend.
- False Positives and Negatives: Language models might generate SQL queries that are technically correct but not relevant to your query’s intent. Be prepared to deal with false positives (incorrectly executed queries) or false negatives (relevant SQL queries not recognized).
- Maintenance and Updates: Stay informed about updates, bug fixes, and improvements to LangChain and the underlying language model. Regularly update your tools to benefit from the latest features and enhancements.
- Validation and Testing: Thoroughly test different types of queries to ensure LangChain accurately translates natural language into SQL queries. Establish a validation process to catch discrepancies before executing queries on the database.
- Unintended Consequences: Natural language queries might lead to unintentional actions on the database. Always verify generated SQL queries and consider implementing safeguards, such as transaction rollbacks, when necessary.
- Resource Consumption: Generating SQL queries from natural language can be resource-intensive, especially when dealing with large datasets or complex SQL queries. Monitor resource consumption and scale your infrastructure accordingly.
- User Expectations: Users might have high expectations for natural language querying capabilities. Manage expectations and provide clear guidance on what SQL queries can be effectively processed through LangChain.
- Vendor or Library Dependencies: Keep an eye on dependencies like LangChain, language models, and database libraries. Changes or discontinuations in these dependencies could impact your application’s functionality.
- Learning Curve: Integrating LangChain and working with natural language querying may have a learning curve for developers and end-users. Provide adequate documentation and support resources.
- Legal and Compliance Considerations: Depending on your use case and industry, ensure that using natural language queries and LangChain complies with relevant legal, regulatory, and compliance requirements.
By being aware of these potential challenges and watching out for them, you can proactively address issues and successfully integrate LangChain with your Oracle Database for natural language queries.
Some Tips
Here are some tips to enhance your experience when using LangChain and integrating it with an Oracle Database:
- Understand Natural Language Query Complexity: When formulating natural language queries, consider the complexity of the question. LangChain’s ability to accurately convert language into SQL queries may vary based on the complexity of the query. For more intricate queries, provide clear and detailed instructions to increase accuracy.
- Provide Context and Keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords and context in your natural language queries. Including table names, column names, and key identifiers can help LangChain accurately interpret your query and generate appropriate SQL commands.
- Review Generated SQL Queries: Always review the SQL queries generated by LangChain before executing them on the database. This task allows you to verify that the generated query aligns with your intended action and prevents unintentional data manipulation.
- Database Structure Familiarity: A solid understanding of your Oracle Database’s schema and structure is crucial. Familiarize yourself with table names, column names, relationships, and data types. This knowledge helps you formulate more precise natural language queries.
- Data Security and Validation: While using LangChain for database queries, ensure that you have appropriate security measures. Validate user inputs and sanitize data to prevent SQL injection attacks and unauthorized access.
- Use Parameterized Queries: When executing SQL queries generated by LangChain, consider using parameterized queries for enhanced security and performance. Parameterized queries prevent SQL injection and optimize query execution.
- Optimize for Performance: Efficiently utilize indexing, caching, and query optimization techniques on the database side to enhance performance when processing LangChain-generated SQL queries.
- Regularly Update Language Models: Stay updated with the latest advancements in LangChain and the underlying language model. Update the language model regularly ensures you benefit from improved accuracy and expanded capabilities.
- Experiment and Refine: Experiment with different query phrasings and variations to see how LangChain interprets and converts them into SQL queries. Refine your approach based on the results to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Error Handling and Logging: Implement robust error handling and logging mechanisms when integrating LangChain with your database. It helps track issues, troubleshoot errors, and maintain a reliable system.
- Collaborate and Seek Help: Engage with the LangChain and developer communities for support, insights, and best practices. Collaborating with others can provide valuable tips and solutions to challenges you may encounter.
With these tips, you can make the most of LangChain’s capabilities and seamlessly integrate them with your Oracle Database for efficient and intuitive querying using natural language.
Conclusion
Using LangChain and a large language model for natural language querying of an Oracle Database offers a user-friendly and accessible way to interact with data. It simplifies data access, enhances productivity, and empowers users without SQL expertise. This innovative approach not only amplifies productivity but also simplifies intricate database interactions. As you continue exploring the boundless potential of natural language processing in database management, you are poised to unlock novel dimensions of data-driven decision-making. However, challenges like accuracy, security, performance, and maintaining external dependencies should be addressed carefully.
