Introduction
Generative AI is changing the game in industries like networking and security. It’s making things smarter, more predictive, and better at making decisions. In networking, it’s helping us optimize our networks and keep them safe from new threats. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is the perfect place to build and deploy generative AI solutions at a big scale.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into how generative AI can revolutionize networking and security. We’ll show you some cool examples using Oracle OCI services and share some tips on how to make the most of AI in these important areas.
We’ll use a demo application to illustrate how OCI native services and OCI Generative AI work together. We won’t go into too much detail about the application itself, but we’ll focus on the underlying architecture. Code samples will not be provided.
Pre-requisites
Introduction to Key OCI Services
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) offers a suite of cloud services designed to support a variety of enterprise needs. Here’s a brief overview of some essential OCI services:
OCI Generative AI & Generative AI Agents: These services provide powerful AI capabilities for developing intelligent applications. Generative AI models can be used to create text, images, and code, while Generative AI Agents enhance user interaction by automating responses and actions within applications.
Links:
- https://www.oracle.com/artificial-intelligence/generative-ai/
- https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/generative-ai/home.htm
- https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/generative-ai-agents/home.htm
OCI Resource Manager: This is a managed service that helps automate the deployment and management of your infrastructure resources. By using infrastructure-as-code (IaC) principles, Resource Manager enables you to deploy consistent environments using Terraform configurations.
Links:
OCI APIs: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers a comprehensive set of APIs that allow developers to easily integrate and interact with OCI services. These APIs provide programmatic access to manage resources, automate processes, and build custom applications on OCI.
Links:
Use-cases covered
Using the example application, we will cover the following application modules applied for networking and security:
- Infrastructure Manager
- Create the cloud networking infrastructure using natural human language.
- Update the recently created cloud networking infrastructure using natural human language.
- View the Terraform configuration that was used to build the networking infrastructure.
- Using AI, summarize in an easy-to-understand human-readable format the Terraform configuration.
- Delete the example cloud networking infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Analyzer
- View the Terraform configuration for an existing infrastructure.
- Using AI, evaluate the security risks by analyzing the Terraform configuration for an existing infrastructure and report.
- Networking SME Agent
- Using AI Agents, ask networking-related questions that utilize the power of large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with your own data, letting users query diverse networking knowledge bases. The service provides up-to-date information through a natural language interface and the ability to act directly on it, using citations and providing relevant links.
A little bit about the demo app
The example application is using Vue.js as the front-end, Flask as the back-end acting like a REST API for the front-end app, and Flask which will connect directly to the OCI API or through some custom Python scripts.
Python, Flask, and Vue together form a powerful tech stack for building dynamic web applications, with Python handling back-end logic, Flask serving as a lightweight web framework, and Vue enabling reactive and interactive front-end user interfaces.
Architecture and logic
Based on the description provided in the above use cases, we will break down the logic of the application, describing and exemplifying each OCI service used.
1. INFRASTRUCTURE MANAGER
This application module is divided into four functionalities:
- Create
- Update
- View State
- Destroy
Create
We will start with the create functionality. For easier understanding of the logic used behind it, I’m attaching the following diagram:
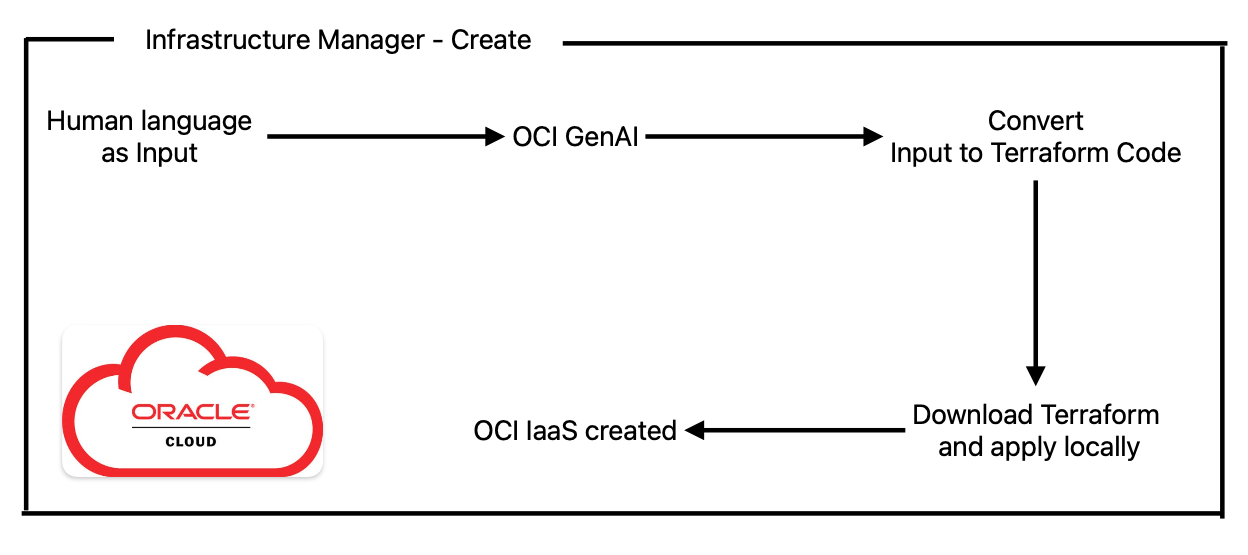
Here we will use human language to describe our networking environment, and use sentences like “Create two VCNs, each one having two private subnets and one public subnet”, or “Create a new VCN using CIDR 192.168.0.0/22 with name My-test-VCN”, etc.
The input will be fed to an OCI GenAI model (there are multiple) that will convert our text into Terraform code. The LLM is being asked to provide just the Terraform code, generated specifically for OCI, with no additional comments. Keep in mind that these LLMs are not perfect and sometimes can make mistakes, which is why a retry logic was implemented in case the Terraform code fails to apply, and for it to learn from errors provided and correct the code to provide working and accurate code. Always check the result.
The code in this case is applied by downloading it from the cloud and applying it locally using Terraform installed on the back-end server.
An example of how it works will be shown in the below video:
Update
Below is the app logic used:
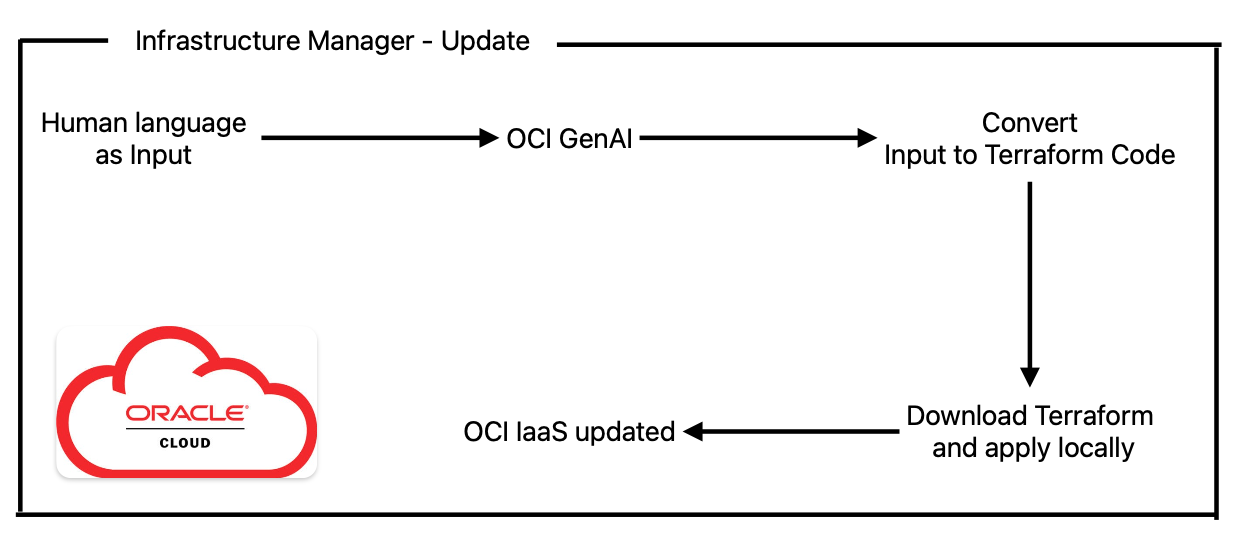
Here we will use human language to describe how we want to change/update our previous infrastructure created, and use sentences like “Add two new public subnets into VCN My-test-VCN, and also create one public load balancer that will use a public IP address from the first public subnet”, etc…
As before, the input will be fed to an OCI GenAI model (there are multiple) together with the existing terraform.tfstate config, that will convert our text into new Terraform code. The LLM is being asked to provide just the Terraform code, generated specifically for OCI, with no additional comments. Keep in mind that these LLMs are not perfect and sometimes can make mistakes, which is why a retry logic was implemented in case the Terraform code fails to apply, and for it to learn from errors provided and correct the code to provide working and accurate code. Always check the result.
The code in this case is applied by downloading it from the cloud and applying it locally using Terraform installed on the backend server.
Example of how it works will be shown in the below video:
View State
Below is the app logic used:
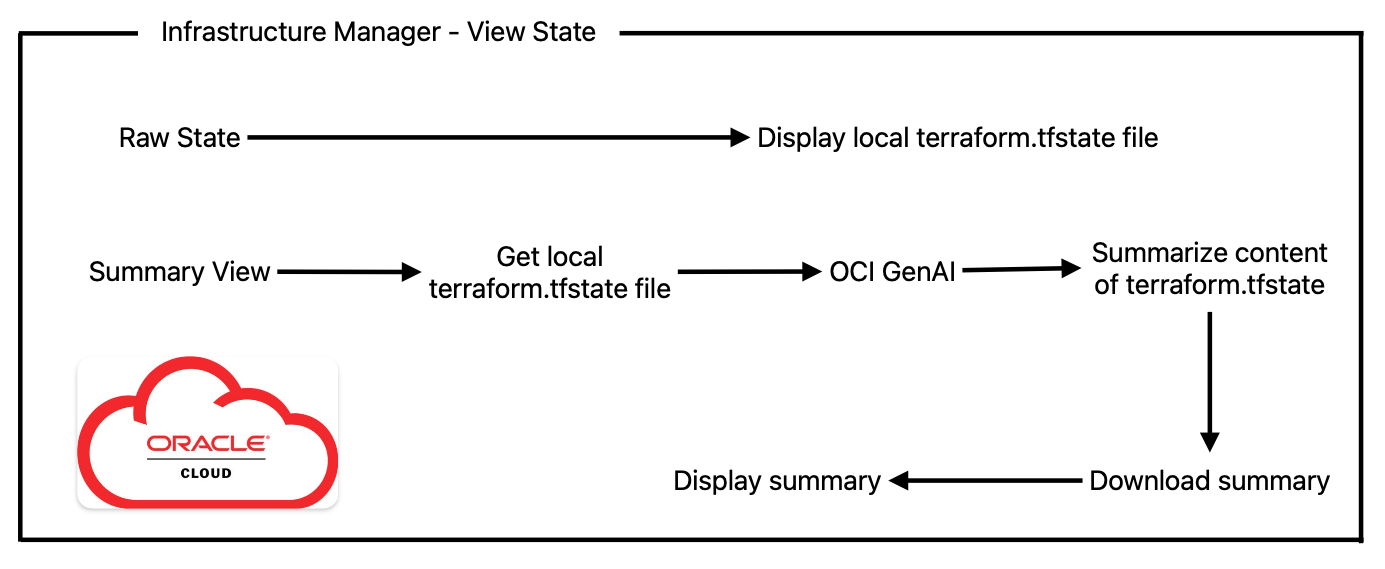
Here we can check the Terraform configuration file that was generated for our networking environment.
In addition, we can send the local terraform.tfstate file to the OCI GenAI model and ask it to summarize for us the code and present it in an easy-to-read and understandable text.
Example of how it works will be shown in the below video:
Destroy
Below is the app logic used:
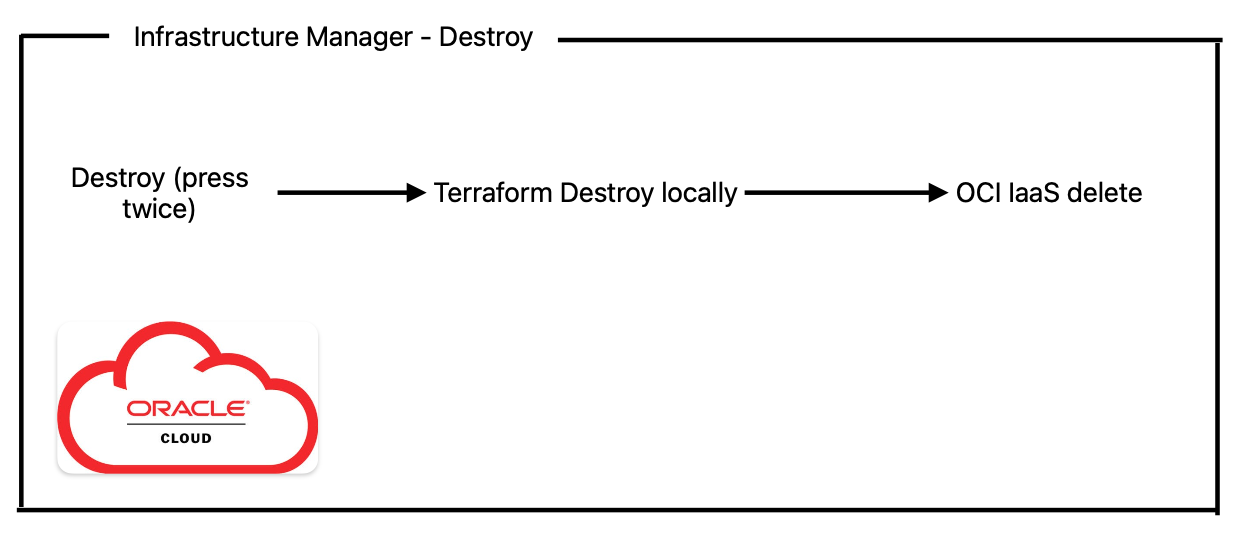
Here we are just using Terraform destroy to delete our recently created environment.
Example of how it works will be shown in the below video:
2. INFRASTRUCTURE ANALYZER
This application module has only one functionality: to translate an existing networking environment into Terraform code and to evaluate the security risks by analyzing that code.
Below is the app logic used:
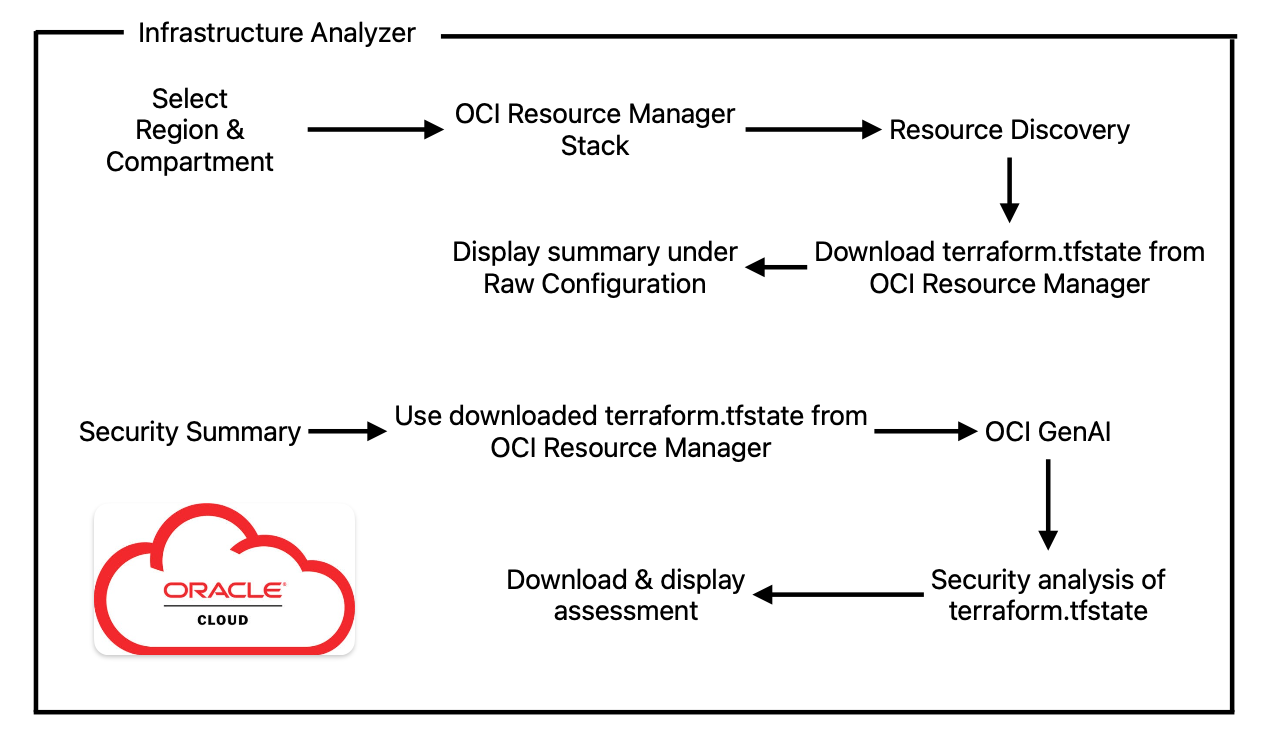
Here we are leveraging another OCI native service called Resource Manager. Basically, we are creating a new stack in Resource Manager which will use the Resource Discovery module to translate existing infrastructure into Terraform code. Afterward, we are downloading the terraform.tfstate file and displaying it.
In addition to this, we can again instruct an OCI GenAI model to evaluate the security risks by analyzing that infrastructure code. The LLM in this case is being asked to provide a security executive summary with what is good/bad, actionable items, etc. Keep in mind that these LLMs are not perfect and sometimes can make mistakes; always check the result.
Example of how it works will be shown in the below video:
3. NETWORKING SME AGENT
This application module focuses on providing recommendations and best practices from a networking and security point of view by leveraging OCI GenAI agents that can connect to a dedicated and customizable knowledge base. This way, the LLM will be able to provide accurate information, use citations, and make reference to links where more details can be reviewed.
Below is the app logic used:
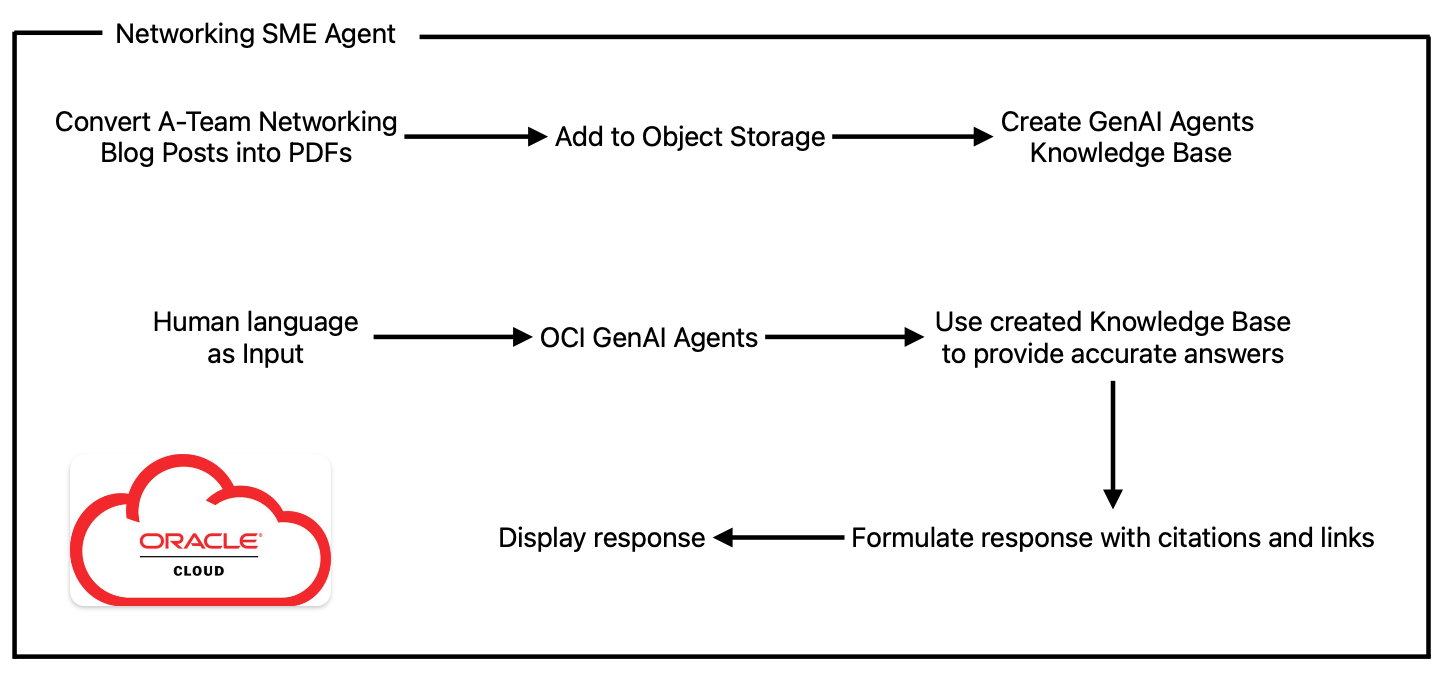
I’m very proud of all the work our networking team is doing when it comes to asset creation, starting from blog posts, to YouTube videos, to LiveLabs, and many more. The time and effort invested is enormous, and this is being reflected in the quality of each asset published.
For this example, I converted the majority of the networking assets into PDFs to be uploaded in a dedicated Knowledge Base that will be used by our OCI GenAI Agent to provide accurate information.
Now we will use human language to ask our Networking SME Agent something about OCI and networking, like “What is the difference between a FastConnect and a VPN”, or “What tools can I use to troubleshoot a VPN issue”, or “ ”. The LLM uses its pre-trained data to provide an answer; it will first check if there is a document in its Knowledge Base that matches the question. If there is one, it will provide a tailored answer using that specific document, together with citations and referenced links.
Example of how it works will be shown in the below video:
Conclusion
Generative AI represents a paradigm shift in how businesses approach networking and security. By automating repetitive tasks, improving threat detection, and enabling proactive responses, AI empowers organizations to stay ahead in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure stands out as a reliable and scalable platform for building AI-driven solutions. With its cutting-edge services and commitment to innovation and security, OCI provides the foundation for enterprises to harness the full potential of generative AI, transforming networking and security operations for the better.
