Oracle Log Analytics supports various methods for collecting logs, such as using a service connector, management agent, object collection rule, on-demand upload, REST API upload, etc.
In a previous blog, I described the case where we “pull” logs from applications that publish their logs via REST API, using the management agent continuous collection method.
In this blog I describe the case where we want to “push” logs from our application using the Log Analytics REST API upload method.
For this method, you can use one of the following APIs provided by Log Analytics:
The first API is covered in the documentation here: Upload Event Logs Using LogEvents API. In this blog, I cover the second API, which can be easier to use with log files in formats other than plain text, such as JSON, which I am using here. Here’s my sample file:
{
"logRecord": {
"eventTime": "2025-12-01T12:08:00",
"ID": "101",
"appName": "App 1",
"message": "Message 1",
"severity": "Information"
},
"additionalAttributes": {
"compName": "App 1, comp 1",
"emailSent": "N"
}
}
{
"logRecord": {
"eventTime": "2025-12-01T12:09:00",
"ID": "102",
"appName": "App 1",
"message": "Message 2",
"severity": "Warning"
},
"additionalAttributes": {
"compName": "App 1, comp 2",
"emailSent": "Y"
}
}
{
"logRecord": {
"eventTime": "2025-12-01T12:10:00",
"ID": "103",
"appName": "App 2",
"message": "Message 3",
"severity": "Critical"
},
"additionalAttributes": {
"compName": "App 2, comp 1",
"emailSent": "Y"
}
}
Pre-requisites
You need to have enabled Logging Analytics in your tenancy, and to belong to an IAM group with the necessary privileges to use the service, as described in the documentation here: Enable Access to Log Analytics and Its Resources.
You can use Postman to test the configuration described in this blog. Once it’s working for you, you can use it from the application you plan to push its logs to Log Analytics.
- Make a note of your Log Analytics namespace. This is usually your tenancy name, but verify in OCI console in case it’s different: “Observability & Management”->”Log Analytics”->”Administration”->”Service Details”.
- Identify or create a Log Analytics log group to which the log data will be mapped. Reference: Create Log Groups to Store Your Logs. Make a note of your log group OCID.
- The Log Analytics REST APIs require authentication. You can use your OCI user ID or create a dedicated “Service Account” OCI user. In either case, you need to create an API key for the user you intend to use. Reference: Adding an API Signing Key.
- Setup Postman:
- Search for “Oracle Cloud Infrastructure REST APIs” in Postman UI.
- Fork the “OCI Credentials” environment.
- Fork the “Logging Search API” collection (There isn’t one for Log Analytics, but we can use this collection and post to the Log Analytics endpoint).
- Update the “OCI Credentials” environment as per the following screenshot. No need to make updates to the “Logging Search API” collection.
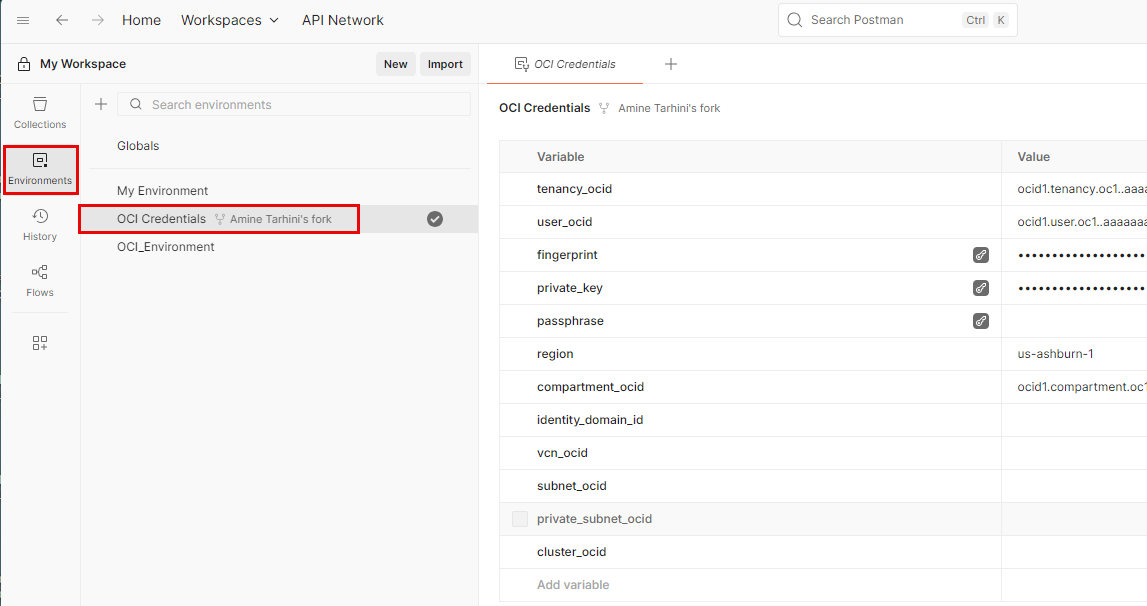
Postman Environment
Tasks
Create a parser
- In OCI console, navigate to: “Log Analytics”->”Administration”->”Parsers”.
- Click “Create Parser”->”JSON Type”.
- Provide a name and a description.
- In the “Example log content” field, paste a sample record or records from your log file.
- On the “Fields” tab, map the fields of your log records to fields in Log Analytics:
- If your log records include a timestamp-type field, map it to the Oracle-defined field “Time”. This will be used as the time field in Log Explorer. If they don’t include a time field, Log Analtyics will use the collection time.
- Leave blank any field you don’t want/need to map.
- You can choose one of the default fields provided by Log Analytics, or create a new field.
- Click the “Parser Test” tab and test to ensure your log records map correctly.
- Click “Create Parser”.
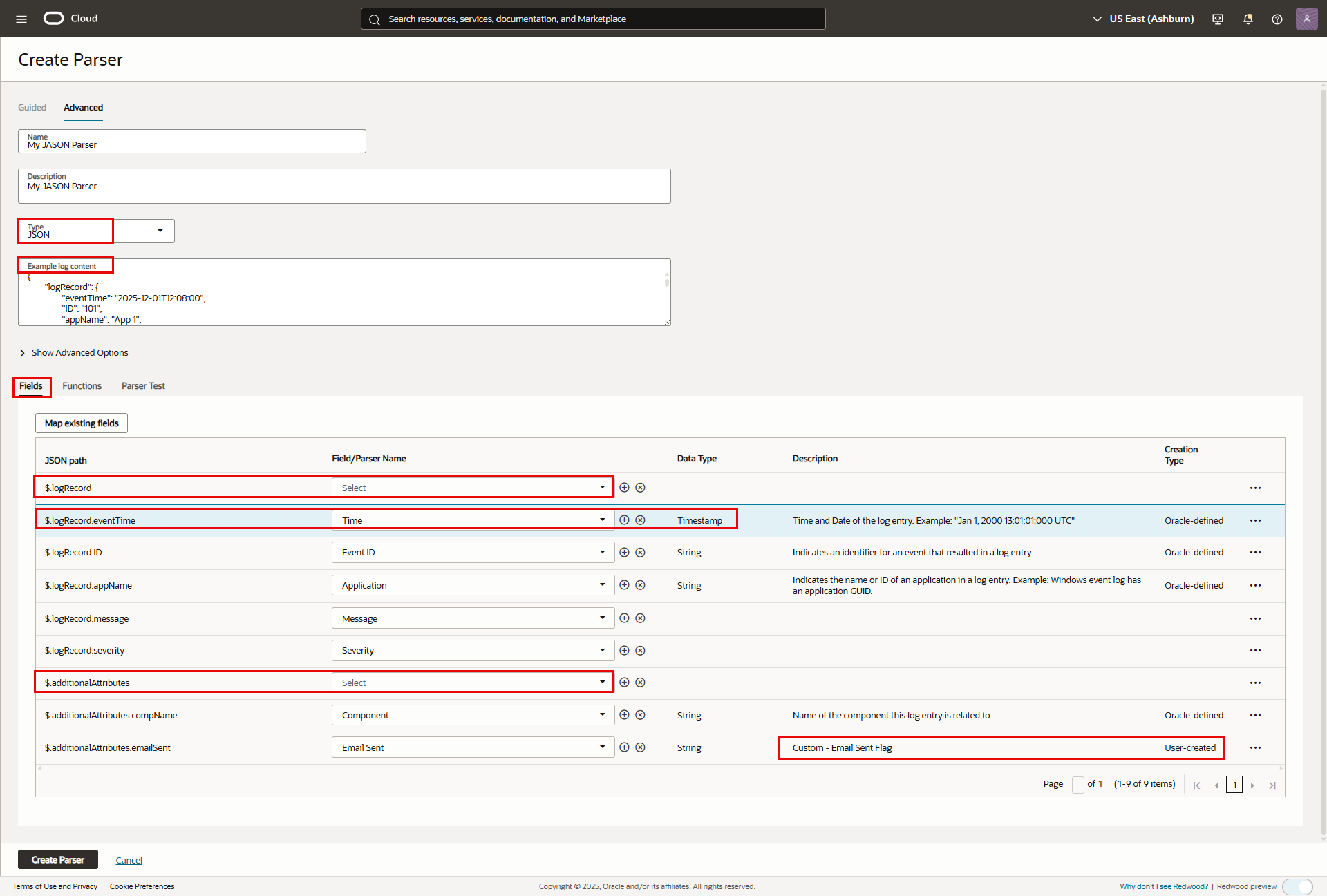
Create Parser 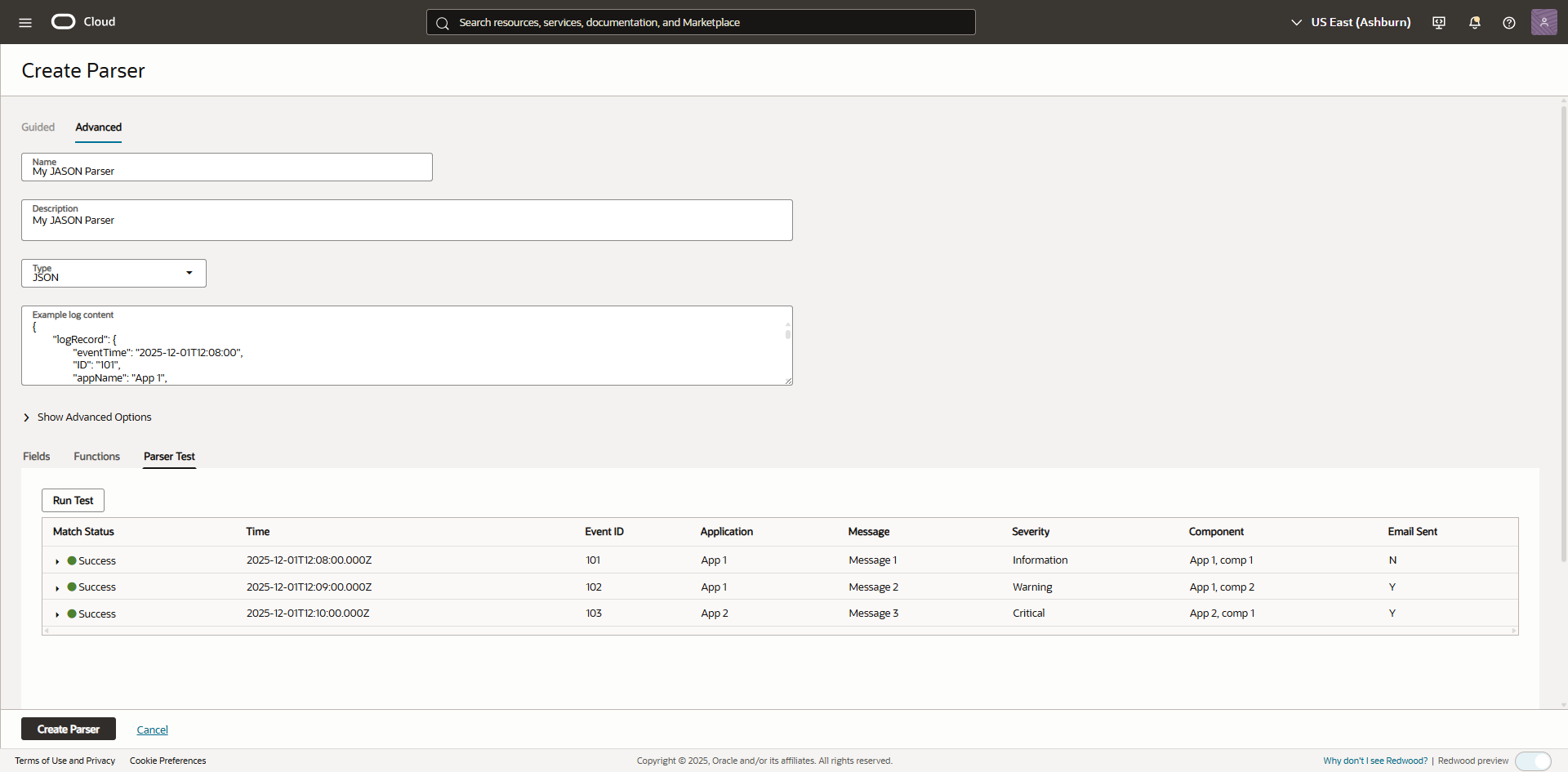
Parser Test
Create a Log Source
- In OCI console, navigate to: “Log Analytics”->”Administration”->”Source”.
- Click “Create Source”.
- Provide a name and a description.
- For “Source Type”, select “File”.
- For “Entity Types”, select “Host (Linux)” (Or another type that better matches your log emitting application).
- For “Parser”, select “Specific Parser(s)”, then select the parser created in the previous step.
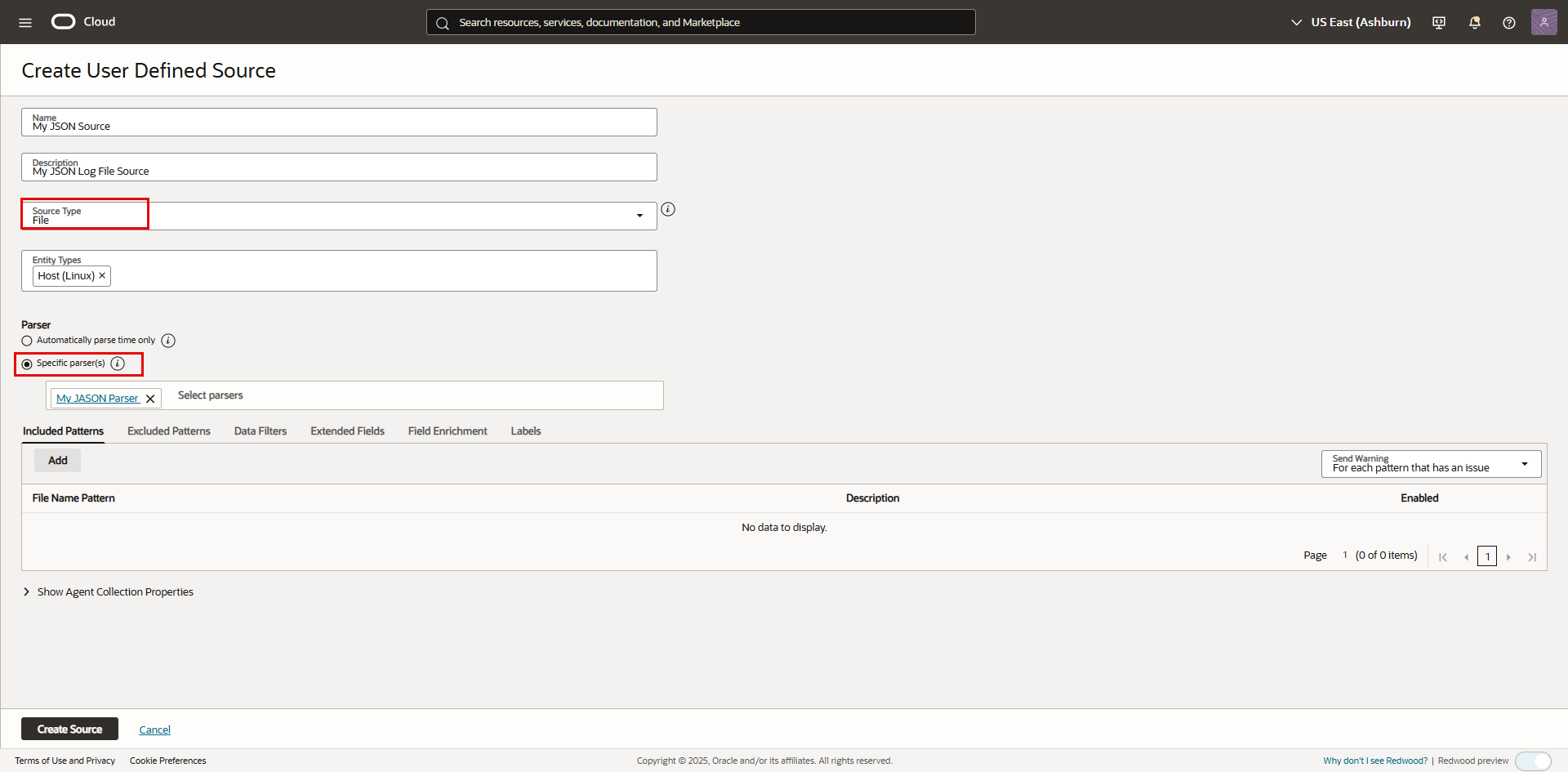
Log Source
Test with Postman
- Create a new request in the “Logging Search API” collection:
- Type: POST
- URI: https://loganalytics.<your OCI region>.oci.oraclecloud.com/20200601/namespaces/<your log analytics namespace>/actions/uploadLogFile?logSourceName=<your log source name>&filename=<your log file name>
- In our scenario, we paste the file content directly in the request body, so the “filename” parameter in the URI is for reference only. We need to supply it since it’s a required parameter, but we can use any text string in this case.
- Authorization: Inherit auth from parent.
- Headers: Add the following headers:
- Content-Type: application/octet-stream
- opc-meta-loggrpid: <OCID of your log group>
- Body:
- You can click “raw” and paste the file content directly,
- or you can click “binary” and specify the file to upload.
- Click Send
- You should get “200 OK” and a message such as:
{
“timeCreated”: “2025-12-01T15:45:20.000Z”
}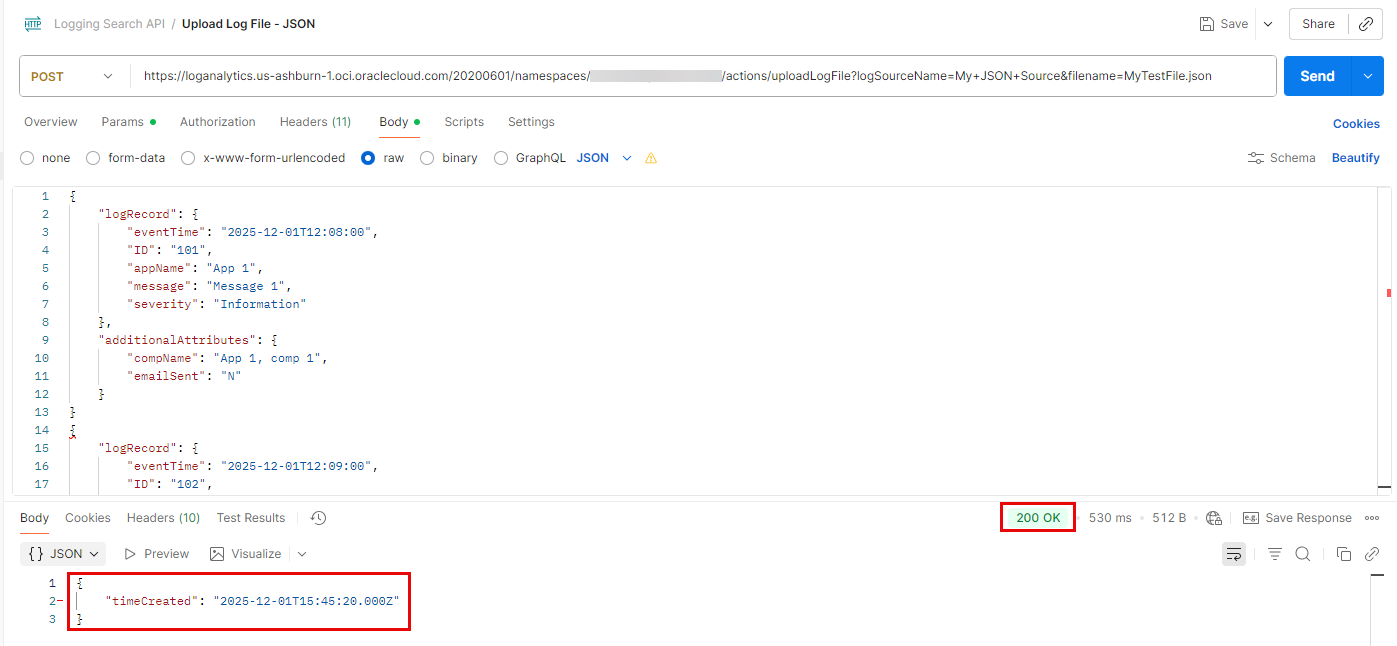
Request Successful
Verify in Log Explorer
- In OCI console, navigate to: “Log Analytics”->”Log Explorer”.
- Enter the following query in the query bar: ‘Log Source’ = <your log source name>.
- Update the time selector to cover the time period in your log records.
- Verify your log records were uploaded successfully.
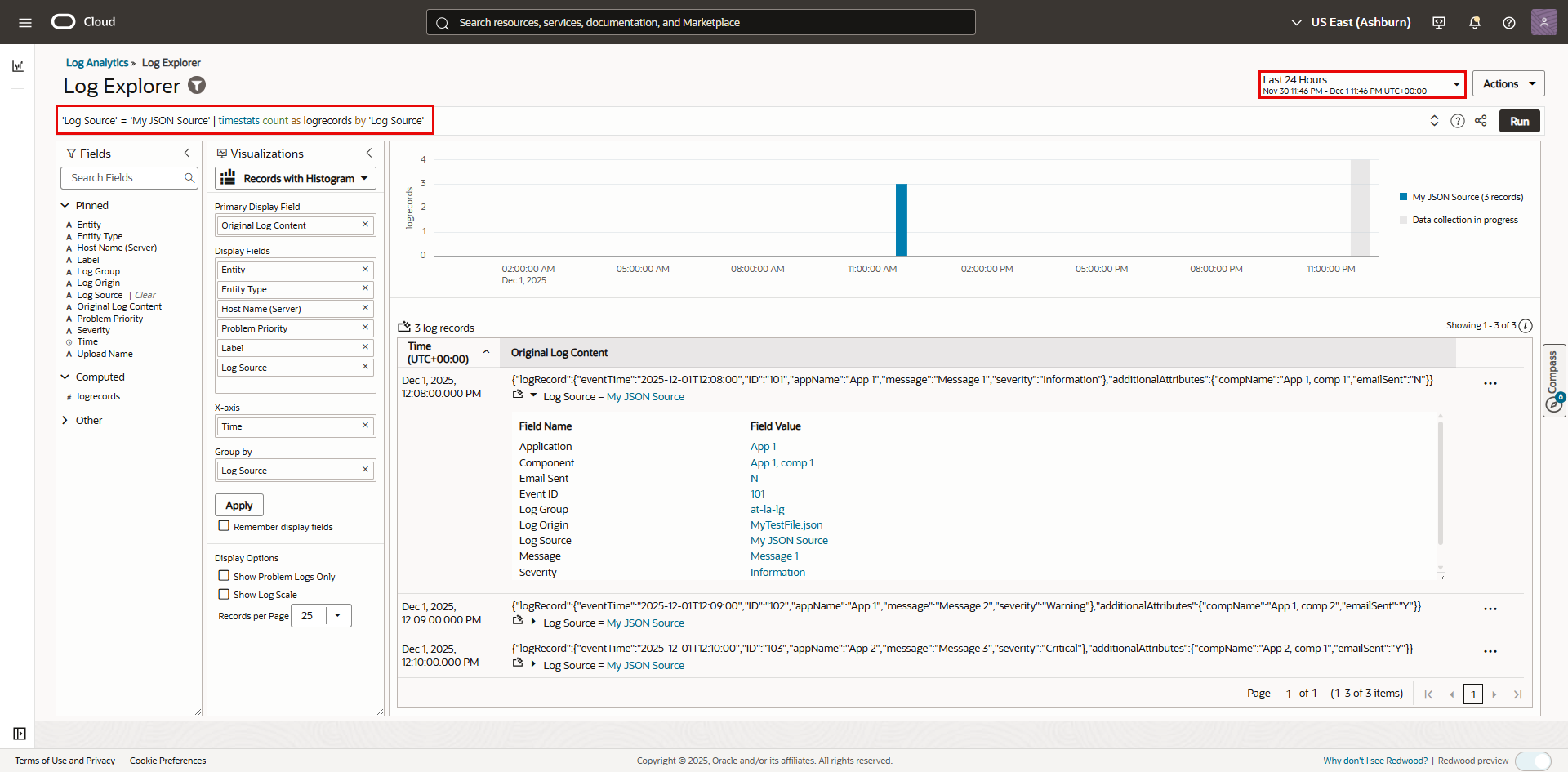
Log Explorer
Reference
- Log Analytics Landing Page on oracle.com: Logging Analytics.
- Logg Analytics Documentation Home page: Logging Analytics.
- Log Analytics API Reference and Endpoints: UploadLogFile.
