Introduction
Welcome to the second part of our blog series on extending SaaS with AI. In case you missed it, you can catch up on the first part of the series here. In this blog, we will see how we can use the Fusion SaaS data extract generated by Oracle Business Intelligence Cloud Connector (BICC) to prepare AI model training data.
Data preparation is a crucial phase in the field of data science, involving a series of steps to transform raw data into a suitable format for analysis. The process begins with data collection, where relevant data is gathered. Once collected, the next step is data cleaning, which involves identifying and handling missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies. The subsequent step is data transformation, which includes feature scaling, normalization, and encoding categorical variables. Feature selection is then performed to choose the most relevant variables for analysis, enhancing model performance. Lastly, data splitting is done to divide the dataset into training and testing subsets, enabling model evaluation.
Jupyter notebooks provide a powerful and interactive environment for data scientists and AI developers to perform data analysis, manipulation, and model training. By integrating with OCI Data Science, we can leverage the data extracted from Oracle Fusion SaaS using BICC and seamlessly prepare it for training our AI models.
Throughout this blog, we will go through the step-by-step process of setting up Jupyter notebooks in OCI Data Science, connecting to the data extract from BICC, and preparing the data for AI model training.
Architecture
The following diagram shows the reference architecture.
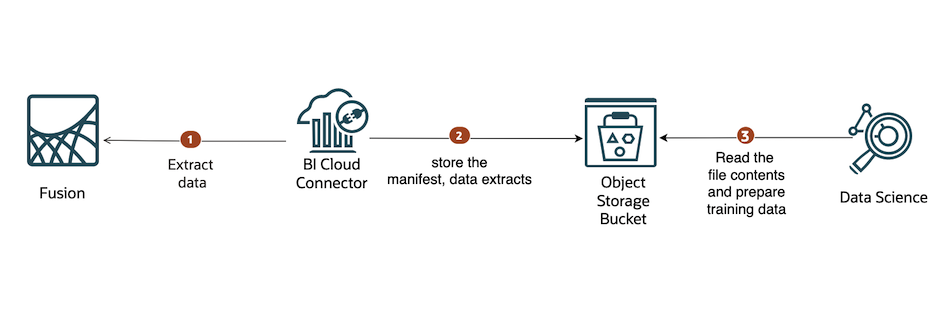
Components
This architecture uses the following components.
OCI Data Science is a fully-managed platform for teams of data scientists to build, train, deploy, and manage machine learning models using Python and open-source tools. It provides a JupyterLab-based environment to experiment and develop models.
Oracle Accelerated Data Science (ADS) is a Python library that’s included as part of the OCI Data Science service. ADS has many functions and objects that automate or simplify the steps in the Data Science workflow.
Object Storage is a highly scalable and secure Object Storage service that can efficiently store large volumes of training data. The data can be easily accessed and shared across different stages of the data science workflow, including data preparation. This ensures that data scientists have the necessary resources to handle big datasets and iterate on their data preparation pipelines effectively.
Business Intelligence Cloud Connector (BICC) can extract business intelligence and other data in bulk and load it into designated external storage areas. In this architecture, we configure External Storage as an Object Storage bucket.
Steps
Before you perform the steps below make sure that you have included required policies for OCI Data Science and Object Storage services.
1. Create an OCI Object Storage bucket.
2. Configure BICC with external data store as the bucket created in Step 1. The configuration to setup OCI Object Storage as the target for extractions is documented in the BICC documentation and various articles in A-Team Chronicles.
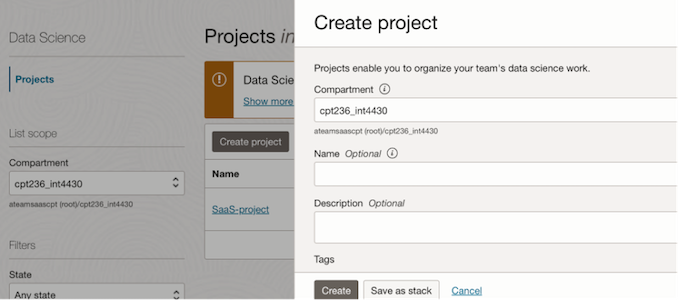
2. Create a new project in OCI Data Science service.
Projects are collaborative workspaces for organizing and documenting Data Science assets, such as notebook sessions and models.
2. Create a notebook session.
Select the project created in Step 1 and create a notebook session.
Choose the right compute shape and block storage based on the use case requirements, while creating a notebook session.
3. Open the notebook session. Notebook sessions come with many preinstalled open source and Oracle-developed machine learning and data science packages called conda environments. The notebook session environment includes the odsc conda CLI tool and the conda Environment Explorer. Using Environment Explorer you can manage and search for conda environments.
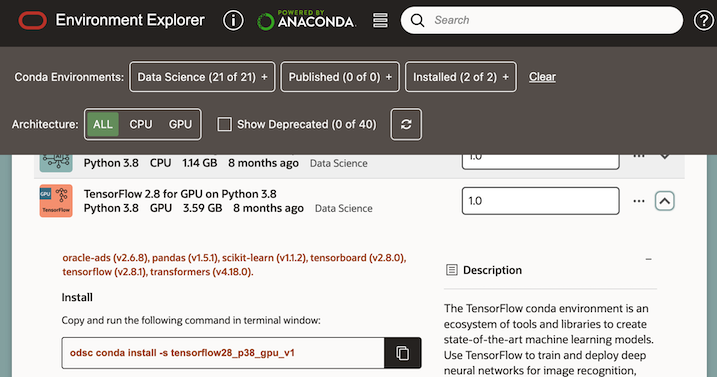
4. Choose the conda environment you want to use and install it, by choosing the Install option from the menu in the Environment Explorer.
5. Create a new Jupyter notebook using File-> New -> Notebook and choose the kernel as the conda environment you installed. You can now add python code for training and building your model.
Let’s consider a use case, to create a Multiclass classification model using an SCM Product Data Hub dataset. The model is to predict the Item Class based on Item Class Description. The BICC extract for this include the Public View Objects (PVO) for Items, Item Classes, and Item Translations .
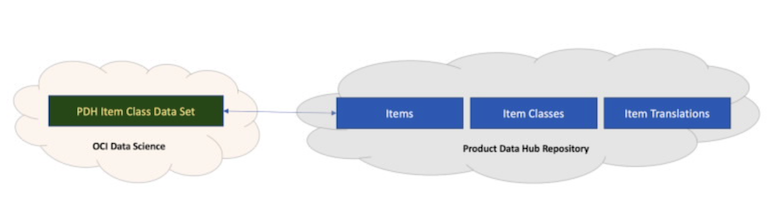 In
In
The dataset should have 2 columns – ITEMTRANSLATIONPEODESCRIPTION and ITEMCLASSBASEPEOITEMCLASSCODE. ITEMTRANSLATIONPEODESCRIPTION is obtained from Item Translations PVO and ITEMCLASSBASEPEOITEMCLASSCODE is obtained from Item Classes PVO.
The joining conditions are –
ITEMTRANSLATIONPEOINVENTORYITEMID column in Item Translations PVO = ITEMBASEPEOINVENTORYITEMID column in Items PVO
and
ITEMBASEPEOITEMCATALOGGROUPID column in Items PVO = ITEMBASEPEOITEMCATALOGGROUPID column in Item Classes PVO
Also, ITEMTRANSLATIONPEODESCRIPTION should be of English language i.e, there is a filter condition on ITEMTRANSLATIONPEOSOURCELANG column in Item Translations PVO; ITEMTRANSLATIONPEOSOURCELANG=’US’ .
Let’s see a few code snippets to generate this data set.
The first step is to read the zip file from the Object Storage bucket. For simplicity let’s asume that the bucket has a single zip file containing the full BICC data extract. The sample code is as below.
from io import BytesIO
from zipfile import ZipFile
import glob
import pandas as pd
import oci
from pathlib import Path
import sys
# Initialize OCI signer and object storage client
signer = oci.auth.signers.get_resource_principals_signer()
object_storage_client = oci.object_storage.ObjectStorageClient(config={}, signer=signer)
bucket_name = "<Enter your Object storage bucket name>"
namespace = "<Enter your Object storage bucket namespace>"
bicc_zip_file_name = "<Enter your BICC extract zip file name>"
bicc_zip_object = object_storage_client.get_object(namespace, bucket_name, bicc_zip_file_name)
current_path = Path(sys.path[0])
if bicc_zip_object.status == 200:
contents = bicc_zip_object.data.content
//unzip the extract and write files to a directory path
with ZipFile(BytesIO(contents)) as archive:
archive.extractall(f'{current_path}')
datazip_found = True
csv_files = glob.glob(f'{current_path}/*.csv')
# Create empty dictionaries to store dataframes
item_translation_dfs = {}
item_extract_dfs = {}
item_class_extract_dfs = {}
# BICC extract will split the PVO into multiple files based on the size
#Loop through CSV files of each type and read them into dictionaries
for file in csv_files:
if 'itemtranslationextractpvo' in file:
item_translation_dfs[file] = pd.read_csv(file)
elif 'itemextractpvo' in file:
item_extract_dfs[file] = pd.read_csv(file)
elif 'itemclassextractpvo' in file:
item_class_extract_dfs[file] = pd.read_csv(file)
# Concatenate dataframes into one dataframe for each type of file
item_translation_df = pd.concat(item_translation_dfs.values(), ignore_index=True)
item_extract_df = pd.concat(item_extract_dfs.values(), ignore_index=True)
item_class_extract_df = pd.concat(item_class_extract_dfs.values(), ignore_index=True)
Pandas provide facilities for easily combining together DataFrame with join / merge-type operations. This is very helpful in joining dataframes and filtering them based on conditions.
# Selecting specific columns from item_translation_df item_translation_df = item_translation_df[ ['ITEMTRANSLATIONPEODESCRIPTION', 'ITEMTRANSLATIONPEOINVENTORYITEMID', 'ITEMTRANSLATIONPEOSOURCELANG'] ] # Selecting specific columns from item_extract_df item_extract_df = item_extract_df[ ['ITEMBASEPEOINVENTORYITEMID', 'ITEMBASEPEOITEMCATALOGGROUPID'] ] # Selecting specific columns from item_class_extract_df item_class_extract_df = item_class_extract_df[ ['ITEMCLASSBASEPEOITEMCLASSID', 'ITEMCLASSBASEPEOITEMCLASSCODE'] ] # Filtering item_translation_extract_df based on ITEMTRANSLATIONPEOSOURCELANG item_translation_df = item_translation_df.loc[ item_translation_df['ITEMTRANSLATIONPEOSOURCELANG'] == 'US' ] # Merging the dataframes merged_df = pd.merge( pd.merge( item_translation_df, item_extract_df, left_on='ITEMTRANSLATIONPEOINVENTORYITEMID', right_on='ITEMBASEPEOINVENTORYITEMID' ), item_class_extract_df, left_on='ITEMBASEPEOITEMCATALOGGROUPID', right_on='ITEMCLASSBASEPEOITEMCLASSID' ).drop_duplicates() # Selecting specific columns from merged_df dataset = merged_df[['ITEMTRANSLATIONPEODESCRIPTION', 'ITEMCLASSBASEPEOITEMCLASSCODE']]
Using Oracle Accelerated Data Science Library SDK
OCI Data Science comes with Oracle Accelerated Data Science Library(ADS) and has various useful capabilities for Data preparartion and Data visualization. A few examples are shown below.
from ads.dataset.dataset import ADSDataset
ds = ADSDataset.from_dataframe(dataset)
ds=ds.set_target('ITEMCLASSBASEPEOITEMCLASSCODE')
To see the issues with the data and recommends changes to apply to the dataset, you can use get_recommendations() API.
ds.get_recommendations()
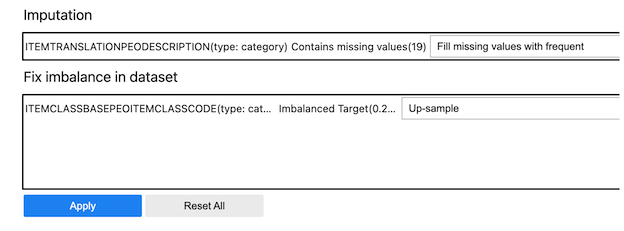
There is also an auto_transform() which can be used to apply all the recommended transformations at once. This returns a transformed dataset with several optimizations applied automatically.
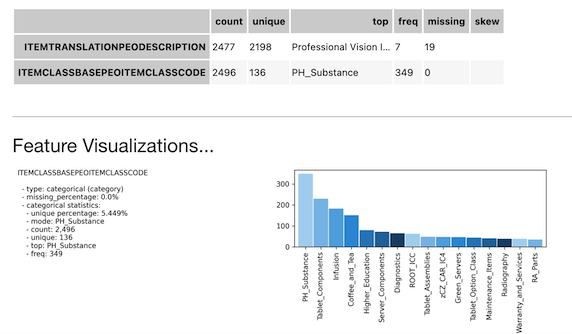
show_in_notebook() is another ADS API that can help to gain an understanding of the data and guides the exploratory data analysis (EDA) . It automatically detects the data type and renders plots that optimally represent the characteristics of the data.
ds.show_in_notebook()
ADS has built-in functions that support categorical encoding, null values, and imputation.
For example, the usage of the built-in categorical encoder,DataFrameLabelEncoder is shown below.
from ads.dataset.label_encoder import DataFrameLabelEncoder
ds_encoded = DataFrameLabelEncoder().fit_transform(ds.to_pandas())
ds_encoded['ITEMCLASSBASEPEOITEMCLASSCODE'].value_counts()
64 349
110 230
31 183
5 151
27 80
...
131 1
67 1
48 1
34 1
19 1
Name: ITEMCLASSBASEPEOITEMCLASSCODE, Length: 136, dtype: int64
The complete list of ADS features is available here.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of Oracle Fusion SaaS data with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Oracle Business Intelligence Cloud Connector (BICC) presents a holistic solution for data scientists in the preparation of model dataset. By combining the capabilities of OCI, BICC, and Oracle Fusion SaaS, data scientists can access a rich source of enterprise data to enhance the data preparation process.
Special thanks to Ulrich Janke, Lyudmil Pelov and Magesh Kesavapillai for their contributions to this blog series.