In this previous blog post, I illustrated the reference architecture and components to use for integrating OCI Document Understanding with other OCI native services to bring AI capabilities to your application. This blog is the second part of it, where we will see the OCI Functions code snippets, which should help you get started with that reference architecture. We are using OCI Python Software Development Kits (SDK ) in the Functions. OCI SDKs are used to build and deploy apps that integrate with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services. Refer to the OCI Document Understanding Python SDKs here
Prerequisites
Refer to the earlier blog, for the setup instructions.
Assumptions
For simplicity, I am assuming there are 2 types of documents.
Function Application
To start with you need a Function Application with configuration parameters as shown below.
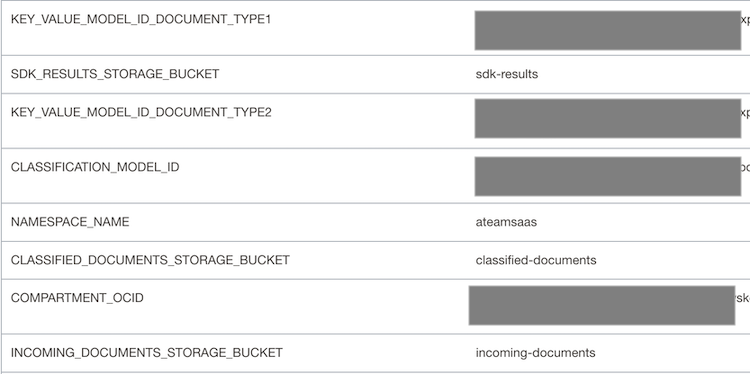
- CLASSIFICATION_MODEL_ID – OCID of the custom document classification model.
- KEY_VALUE_MODEL_ID_DOCUMENT_TYPE1- OCID of the custom key-value extraction model for the documents of type1.
- KEY_VALUE_MODEL_ID_DOCUMENT_TYPE2- OCID of the custom key-value extraction model for the documents of type2.
- COMPARTMENT_OCID – OCID of the compartment where the OCI Document Understanding service is running.
- NAMESPACE_NAME – Namespace of the OCI Object Storage buckets
Python Function Code
There are 2 OCI Functions used, classify-document and extract-key-values.
- classify-document is to classify the documents added to the incoming-documents bucket. These documents are then copied to the classified-documents bucket under subfolders based on the document type.
- extract-key-values is to extract key-values from the documents added to the classified-documents bucket.
Let’s start with the classify-document Function.
classify-document
func.yaml of the Function is defined as below.
name: classify-document
version: 0.0.220
runtime: python
build_image: fnproject/python:3.8-dev
run_image: fnproject/python:3.8
entrypoint: /python/bin/fdk /function/func.py handler
memory: 1024
Following are the code snippets from func.py, which is the entrypoint of the Function.
In the initialization section, grab config variables defined at the Application level. There is also a call to get_resource_principals_signer(). The resource principal provider uses a resource provider session token (RPST) that enables the function to authenticate itself with other Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services. Here, use resource principal to authenticate to OCI Object Storage and OCI Document Understanding services.
The input and output locations for document processors are also defined here. The input location is the location from where the document processor reads the document. Here it is pointing to an Object Storage bucket, incoming-documents. The output location is where the processing results are stored. It is pointed to another bucket, sdk-results.
import io
import json
import logging
import os
import uuid
import oci.ai_document
import oci.object_storage
from fdk import response
try:
signer = oci.auth.signers.get_resource_principals_signer()
object_storage_client = oci.object_storage.ObjectStorageClient(config={}, signer=signer)
ai_document_client = oci.ai_document.AIServiceDocumentClientCompositeOperations(oci.ai_document.AIServiceDocumentClient({}, signer=signer))
if os.getenv("COMPARTMENT_OCID") is not None:
compartment_ocid = os.getenv('COMPARTMENT_OCID')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key COMPARTMENT_OCID ")
if os.getenv("NAMESPACE_NAME") is not None:
namespace = os.getenv('NAMESPACE_NAME')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key NAMESPACE_NAME ")
if os.getenv("SDK_RESULTS_STORAGE_BUCKET") is not None:
sdk_results_storage_bucket = os.getenv('SDK_RESULTS_STORAGE_BUCKET')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key OUTPUT_STORAGE_BUCKET ")
if os.getenv("INCOMING_DOCUMENTS_STORAGE_BUCKET") is not None:
incoming_documents_storage_bucket = os.getenv('INCOMING_DOCUMENTS_STORAGE_BUCKET')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key INCOMING_DOCUMENTS_STORAGE_BUCKET ")
if os.getenv("CLASSIFIED_DOCUMENTS_STORAGE_BUCKET") is not None:
classified_documents_storage_bucket = os.getenv('CLASSIFIED_DOCUMENTS_STORAGE_BUCKET')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key CLASSIFIED_DOCUMENTS_STORAGE_BUCKET ")
if os.getenv("CLASSIFICATION_MODEL_ID") is not None:
classification_model_id = os.getenv('CLASSIFICATION_MODEL_ID')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key CLASSIFICATION_MODEL_ID ")
# Setup the input location from where processor reads the documents
input_location = oci.ai_document.models.ObjectLocation()
input_location.namespace_name = namespace
input_location.bucket_name = incoming_documents_storage_bucket
# Setup the output location where processor job results will be created
output_location = oci.ai_document.models.OutputLocation()
output_location.namespace_name = namespace
output_location.bucket_name = sdk_results_storage_bucket
output_location.prefix = "classify"
except Exception as e:
logging.getLogger().error(e)
raise
Let’s now use OCI Document Understanding SDKs to do classification by making use of the custom model.
CreateProcessorJobDetails is used to create a new document processor job. The feature used by the job is the DocumentClassificationFeature and it set to use the custom model OCID. Once the processor is run, we wait till we get the response. The response is written to the output location.
The response object contains the inference results returned by the API. This JSON is parsed to obtain documentType node, which contains the type of the document detected.
def classify(document_name):
logging.getLogger().info("Inside classify")
# Set the object_name to classify
input_location.object_name = document_name
# Feature to invoke is the classification feature
document_classification_feature = oci.ai_document.models.DocumentClassificationFeature()
# Set the custom model OCID
document_classification_feature.model_id = classification_model_id
# Call the processor job
create_processor_job_details = oci.ai_document.models.CreateProcessorJobDetails(
display_name=str(uuid.uuid4()),
input_location=oci.ai_document.models.ObjectStorageLocations(object_locations=[input_location]),
output_location=output_location,
compartment_id=compartment_ocid,
processor_config=oci.ai_document.models.GeneralProcessorConfig(
features=[document_classification_feature],
is_zip_output_enabled=False
)
)
# Wait for the processor job response
create_processor_response = ai_document_client.create_processor_job_and_wait_for_state(
create_processor_job_details=create_processor_job_details,
wait_for_states=[oci.ai_document.models.ProcessorJob.LIFECYCLE_STATE_SUCCEEDED],
waiter_kwargs={"wait_callback": create_processor_job_callback})
# Get the output json from the bucket
create_processor_job_response = create_processor_response.data
process_job_id = create_processor_job_response.id
get_object_response = object_storage_client.get_object(namespace_name=output_location.namespace_name,
bucket_name=output_location.bucket_name,
object_name="{}/{}/{}_{}/results/{}.json".format(
output_location.prefix, process_job_id,
input_location.namespace_name,
input_location.bucket_name,
input_location.object_name))
# Get the inference json
data = json.loads(get_object_response.data.content)
# parse the response json to get the classified document type
document_type = data['pages'][0]['detectedDocumentTypes'][0]['documentType']
return document_type
def create_processor_job_callback(times_called, response):
logging.getLogger().info("Waiting for processor lifecycle state to go into succeeded state:", response.data)
Move the documents to different subfolders under OCI Object Storage bucket for further processing. The subfolders are chosen based on document type.
def move_classified_documents_to_bucket(document_name, document_type):
logging.getLogger().info("inside move_classified_documents_to_bucket")
# Get the document from source bucket
response_object = object_storage_client.get_object(namespace, incoming_documents_storage_bucket, document_name)
# decide the sub folder names in object storage bucket based on document type
if document_type == 'document_type1':
folder_name = 'document_type1'
if document_type == 'document_type2':
folder_name = 'document_type2'
# Write to classified documents bucket
with io.BytesIO() as buf:
for chunk in response_object.data.raw.stream(1024 * 1024, decode_content=False):
buf.write(chunk)
buf.seek(0)
object_storage_client.put_object(namespace, classified_documents_storage_bucket,
folder_name + '/' + document_name, buf.read())
This Function is called by the OCI Event service when documents get added to the incoming-documents bucket. The object creation event in the OCI Event service generates a JSON that looks like below.
{
“cloudEventsVersion”: “0.1”,
“eventID”: “unique_ID”,
“eventType”: “com.oraclecloud.objectstorage.createobject”,
“source”: “objectstorage”,
“eventTypeVersion”: “2.0”,
“eventTime”: “2019-01-10T21:19:24.000Z”,
“contentType”: “application/json”,
“extensions”: {
“compartmentId”: “ocid1.compartment.oc1..unique_ID”
},
“data”: {
“compartmentId”: “ocid1.compartment.oc1..unique_ID”,
“compartmentName”: “example_name”,
“resourceName”: “my_object”,
“resourceId”: “/n/example_namespace/b/my_bucket/o/my_object”,
“availabilityDomain”: “all”,
“additionalDetails”: {
“eTag”: “f8ffb6e9-f602-460f-a6c0-00b5abfa24c7”,
“namespace”: “example_namespace”,
“bucketName”: “my_bucket”,
“bucketId”: “ocid1.bucket.oc1.phx.unique_id”,
“archivalState”: “Available”
}
}
}
The handler() method of the Function will get this JSON as an input value. Therefore, we can use this to get the document name uploaded to Object Storage bucket and pass it as a parameter to classify() method. Once the document type is determined by the classify() method, the move_classified_documents_to_bucket() method will copy the document to a subfolder in the classified-documents bucket.
# Handler method
def handler(ctx, data: io.BytesIO = None):
try:
body = json.loads(data.getvalue())
document_name = body["data"]["resourceName"]
document_type = classify(document_name)
# Move the documents to a classified_documents bucket
move_classified_documents_to_bucket(document_name, document_type)
except Exception as handler_error:
logging.getLogger().error(handler_error)
return response.Response(
ctx,
status_code=500,
response_data="Processing failed due to " + str(handler_error)
)
return response.Response(
ctx,
response_data="success"
)
Now let’s have a look at the extract-key-values Function.
extract-key-values
Here also get the Application configuration parameters in the initialization section. Also, set the document processing input and output locations. The input location is the classified-documents bucket and the output location is the sdk-results bucket.
import io
import json
import logging
import os
import uuid
import oci.ai_document
import oci.object_storage
from fdk import response
try:
signer = oci.auth.signers.get_resource_principals_signer()
object_storage_client = oci.object_storage.ObjectStorageClient(config={}, signer=signer)
ai_document_client = oci.ai_document.AIServiceDocumentClientCompositeOperations(
oci.ai_document.AIServiceDocumentClient({}, signer=signer))
if os.getenv("COMPARTMENT_OCID") is not None:
compartment_ocid = os.getenv('COMPARTMENT_OCID')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key COMPARTMENT_OCID ")
if os.getenv("NAMESPACE_NAME") is not None:
namespace = os.getenv('NAMESPACE_NAME')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key NAMESPACE_NAME ")
if os.getenv("SDK_RESULTS_STORAGE_BUCKET") is not None:
sdk_results_storage_bucket = os.getenv('SDK_RESULTS_STORAGE_BUCKET')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key OUTPUT_STORAGE_BUCKET ")
if os.getenv("CLASSIFIED_DOCUMENTS_STORAGE_BUCKET") is not None:
classified_documents_storage_bucket = os.getenv('CLASSIFIED_DOCUMENTS_STORAGE_BUCKET')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key CLASSIFIED_DOCUMENTS_STORAGE_BUCKET ")
if os.getenv("KEY_VALUE_MODEL_ID_DOCUMENT_TYPE1") is not None:
key_value_model_id_document_type1 = os.getenv('KEY_VALUE_MODEL_ID_DOCUMENT_TYPE1')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key KEY_VALUE_MODEL_ID_DOCUMENT_TYPE1 ")
if os.getenv("KEY_VALUE_MODEL_ID_DOCUMENT_TYPE2") is not None:
key_value_model_id_document_type2 = os.getenv('KEY_VALUE_MODEL_ID_DOCUMENT_TYPE2')
else:
raise ValueError("ERROR: Missing configuration key KEY_VALUE_MODEL_ID_DOCUMENT_TYPE2 ")
# Setup the output location where processor job results will be created
output_location = oci.ai_document.models.OutputLocation()
output_location.namespace_name = namespace
output_location.bucket_name = sdk_results_storage_bucket
output_location.prefix = "keyvalue"
input_location = oci.ai_document.models.ObjectLocation()
input_location.namespace_name = namespace
input_location.bucket_name = classified_documents_storage_bucket
except Exception as e:
logging.getLogger().error(e)
raise
CreateProcessorJobDetails is used to create a new document processor job. The feature used by the job is the KeyValueExtractionFeature and it uses the custom model OCID. Once the processor is run, we wait till we get the response. The response is written to the output location, which is the sdk-results bucket.
The response object contains the inference results returned by the API. You can parse this JSON result and extract key values from it. Use these key values in your target application REST API call.
def extract_key_value(document_name, input_location):
input_location.object_name = document_name
key_value_detection_feature = oci.ai_document.models.DocumentKeyValueExtractionFeature()
# Get the custom key-value extraction model ids based on document_name.
if "document_type1/" in document_name:
key_value_detection_feature.model_id = key_value_model_id_document_type1
if "document_type2/" in document_name:
key_value_detection_feature.model_id = key_value_model_id_document_type2
# Set up the Key-Value extraction processor job
create_processor_job_details = oci.ai_document.models.CreateProcessorJobDetails(
display_name=str(uuid.uuid4()),
input_location=oci.ai_document.models.ObjectStorageLocations(object_locations=[input_location]),
output_location=output_location,
compartment_id=compartment_ocid,
processor_config=oci.ai_document.models.GeneralProcessorConfig(
features=[key_value_detection_feature],
is_zip_output_enabled=False,
)
)
# Wait for the processor job response
create_processor_response = ai_document_client.create_processor_job_and_wait_for_state(
create_processor_job_details=create_processor_job_details,
wait_for_states=[oci.ai_document.models.ProcessorJob.LIFECYCLE_STATE_SUCCEEDED],
waiter_kwargs={"wait_callback": create_processor_job_callback})
# Get the output json from the bucket
create_processor_job_response = create_processor_response.data
process_job_id = create_processor_job_response.id
get_object_response = object_storage_client.get_object(namespace_name=output_location.namespace_name,
bucket_name=output_location.bucket_name,
object_name="{}/{}/{}_{}/results/{}.json".format(
output_location.prefix, process_job_id,
input_location.namespace_name,
input_location.bucket_name,
input_location.object_name))
# TODO-You can parse the response JSON and get the values of keys you defined.
data = json.loads(get_object_response.data.content)
# TODO-Call your target application APIs by passing the extracted key values
def create_processor_job_callback(times_called, response):
logging.getLogger().info("Waiting for processor lifecycle state to go into succeeded state:", response.data)
handler() method gets the document name from the Event payload and calls the extract_key_value() method.
def handler(ctx, data: io.BytesIO = None):
try:
body = json.loads(data.getvalue())
document_name = body["data"]["resourceName"]
extract_key_value(document_name, input_location)
except Exception as handler_error:
logging.getLogger().error(handler_error)
return response.Response(
ctx,
status_code=500,
response_data="Processing failed due to " + str(handler_error)
)
return response.Response(
ctx,
response_data="success"
)
Conclusion
Combining OCI AI services and other OCI native services is an efficient way to integrate AI capabilities into your Fusion SaaS or other applications. Now that you are familiar with using OCI Document Understanding SDKs in your Function you can leverage this to build solutions that enhance your applications with AI.
