CISO Perspectives
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Security Executive Overview
As companies transition to the cloud for greater speed and agility, they’re also starting to see security as a cloud benefit rather than a risk. But with today’s larger and more diversified threat landscape, businesses need to be sure of the depth of their security before they trust the cloud with such important workloads.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is the first public cloud built from the ground up to be a better cloud for every application. By rethinking core engineering and systems design for cloud computing, we created innovations that solve problems that customers have with existing public clouds including architecture and security. In most public clouds, apps are built, then as they become larger and more functional, security is bolted on to the application and the services that run it. Every application you want to secure requires a host of different services, often with different pricing per service. At OCI, we’ve designed security into the core experience from the start of your application build or migration, and we’ve made most of our security tooling free as part of your environment.
OCI security stands out due to its security-first design, built-in security services, and focus on customer control and transparency. It incorporates a zero-trust architecture, always-on encryption, and Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies to minimize risk and ensure secure access. Furthermore, OCI emphasizes a shared responsibility model, with Oracle managing the security of the infrastructure and customers securing their applications and data.
Shared responsibility
Security in the cloud is shared, and it is essential that subscribers of cloud services 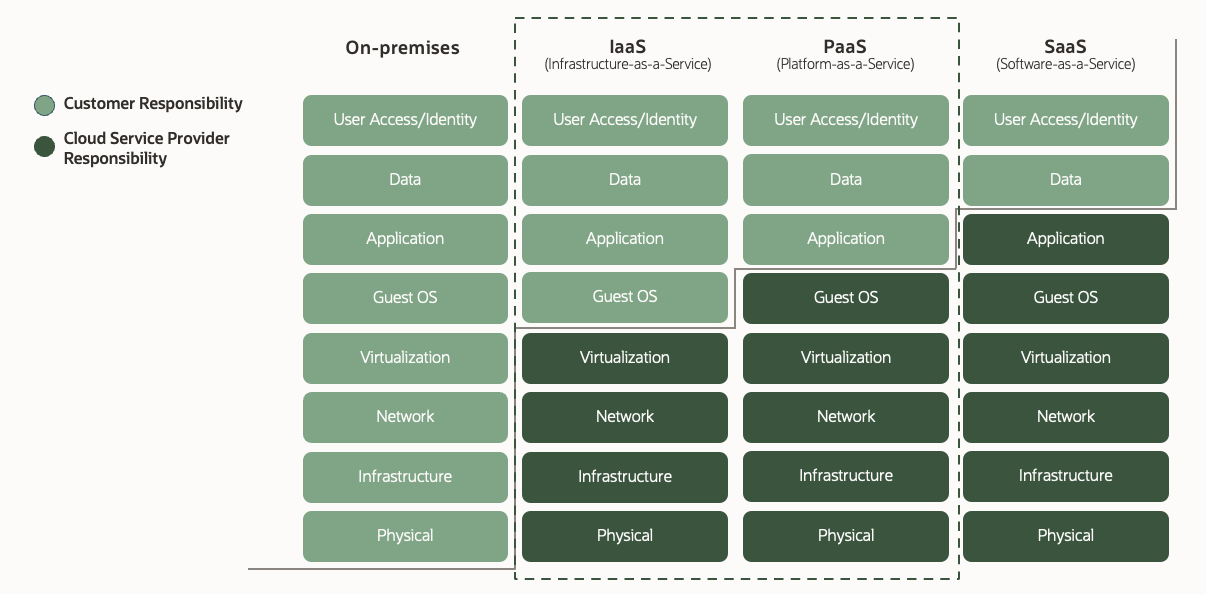 be fluent in, and up to date on how they and their service providers share the responsibility for securing their cloud footprint. In a cloud security context, the shared responsibility model conveys how a cloud service provider is responsible for managing the security of public-cloud while the subscriber of the service is responsible for securing what is in the cloud. Simply put at Oracle we manage the cloud, and you manage what you put in the cloud, and OCI’s security differentiators are present on both sides of this shared responsibility model.
be fluent in, and up to date on how they and their service providers share the responsibility for securing their cloud footprint. In a cloud security context, the shared responsibility model conveys how a cloud service provider is responsible for managing the security of public-cloud while the subscriber of the service is responsible for securing what is in the cloud. Simply put at Oracle we manage the cloud, and you manage what you put in the cloud, and OCI’s security differentiators are present on both sides of this shared responsibility model.
The responsibility may shift depending on what type of engagement model you are using, Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), or software as a service (SaaS), but how Orace secures the underlying cloud and how we enable you to secure your side of the cloud model remains the same.
How Oracle delivers a more secure foundation
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is an infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) offering that is different from other clouds as it is architected on security-first design principles. These principles include isolated network virtualization and reproducible known-good-state physical host deployment, which significantly reduce risk from advanced persistent threats.
Hardware root of trust
As the threat landscape evolves so does the risk of firmware-based attacks. To reduce the risk of firmware-level attacks against cloud tenants. Oracle establishes each new tenancy with a root of trust technology designed to wipe and reinstall the firmware every time a new server is provisioned, or a new customer tenancy is established.
A hardware root of trust (RoT) in the cloud is a secure, hardware-based fouindation that provides a trusted starting pint for security operations. It ensures the integrity of the system by verifying the authenticity and trustworthiness of software and firmware components during the boot process and beyond. This foundation is crucial for building a secure cloud environment, protecting against various attacks, and establishing a basis for trust between different components
Oracle cleans and power cycles new servers, each time, every time to reduces the risk from a permanent denial of service (PDoS) attack or attempts to embed backdoors in the firmware. By power cycling the hardware host, installing the firmware, and confirming the process has been performed as expected for every new server, Oracle helps you maintain a more secure foundation in your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Benefits of the hardware Root of Trust include:
- Enhanced Security: By providing a trusted foundation, HRTs significantly enhance the security of cloud infrastructure and workloads.
- Reduced Risk of Attacks: HRTs help mitigate the risk of firmware-based attacks and other threats that target the system’s core components.
- Improved Trust and Compliance: HRTs enable stronger security guarantees, which can help cloud providers demonstrate compliance with various security standards and regulations.
- Enabling Zero Trust Security: A HRT can be a foundational element in a zero-trust security architecture, ensuring that every component is verified and trusted before being granted access.
Isolated Network Virtualization
The hypervisor is the software that manages virtual devices in a cloud environment, handling server and network virtualization. In traditional virtualization environments, the hypervisor manages network traffic, enabling traffic to flow between VM instances and physical hosts. This traffic flow adds considerable complexity and computational overhead to the hypervisor. Proof-of-concept computer security attacks that demonstrate escaping hypervisor isolation have highlighted the substantial risk that can come with this design. These attacks exploit hypervisor complexity by enabling an attacker to “break out” of a VM instance, access the underlying operating system, and gain control of the hypervisor and embedded network virtualization. The attacker can then potentially alter the network configuration to access other hosts.
OCI reduces threat proliferation between hosts by implementing network virtualization outside the hypervisor referred to as off-box virtualization. Even if a bad actor escapes a VM and compromises the hypervisor, they will not be able to reconfigure the network virtualization, limiting lateral movement to other hosts and increasing the overall security of the tenancy.
Tenant Isolation via off box virtualization
A foundational element of OCI’s security-first architecture is its isolated network virtualization that prevents attacks on customer tenancies. Customer isolation that allows you to deploy your application and data assets in an environment that commits full isolation from other tenants and Oracle’s staff, as well as between the same tenant’s workloads. Let’s look a little more closely about why it matters.
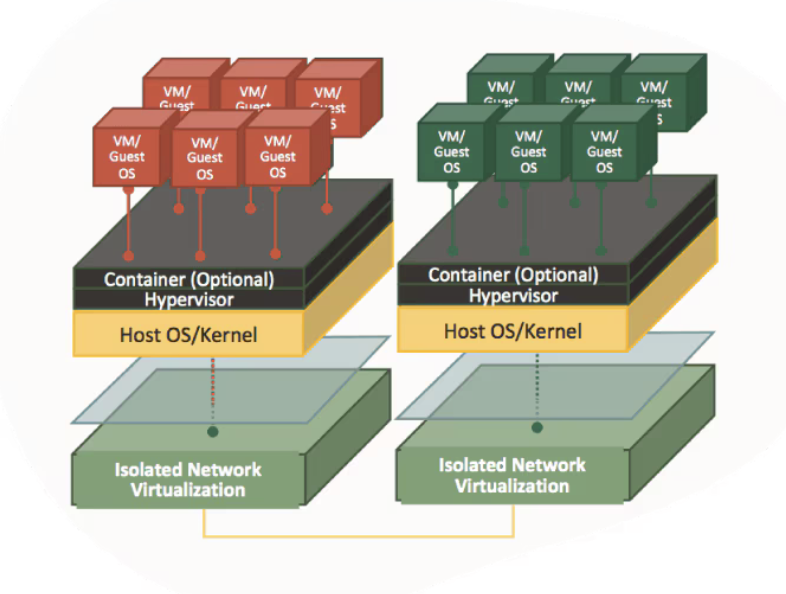 In first-generation cloud offerings, offerings that are still in place in many clouds, if a successful attack compromises a virtual machine instance and subsequently a hypervisor, there are no barriers to prevent an attacker’s attempts to modify the network. The networking function is managed by the same hypervisor that has been compromised: a virtual machine escape that gains access to the hypervisor also has access to the network. This can lead to several threats to hosts on the network and could expose private tenant data.
In first-generation cloud offerings, offerings that are still in place in many clouds, if a successful attack compromises a virtual machine instance and subsequently a hypervisor, there are no barriers to prevent an attacker’s attempts to modify the network. The networking function is managed by the same hypervisor that has been compromised: a virtual machine escape that gains access to the hypervisor also has access to the network. This can lead to several threats to hosts on the network and could expose private tenant data.
OCI is different from first-generation clouds because of its use of a custom-designed SmartNIC that isolates and virtualizes the network. The SmartNIC is isolated by hardware and software from the host, preventing a compromised instance from compromising the network. OCI maintains greater external control of host network functionality and can prevent network traversal attacks. Customer isolation allows you to deploy your application and data assets in an environment that commits full isolation from other tenants and Oracle’s staff, as well as between the same tenant’s workloads.
Off-box virtualization, as implemented in OCI, involves running the cloud control plane (privileged code) on dedicated hardware, separate from the servers hosting customer workloads.
The benefits of off-box virtualization include:
- Reduced Attack Surface: Separating the control plane from customer workloads reduces the potential attack surface for malicious software.
- Enhanced Isolation: If a hypervisor security issue arises, it’s less likely to impact the cloud control plane or other customer instances, as they are isolated on separate hardware.
- Simplified Hypervisor: The hypervisor on the compute instances can be stripped down to basic functionality, like launching VMs and allocating memory, reducing its complexity and attack surface.
Fault-tolerate high availability data centers
Additionally, OCI is built on fault-independent data centers that enable high availability scale-out architectures and are resilient against network attacks, ensuring constant uptime in the face of disaster and security attack. We over 200 secure regions available for you, and we continue to grow.
Security-first advantages to enable best practices in your tenancy
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) utilizes a “defense in depth” security strategy, employing multiple layers of security controls to protect data and systems. This approach combines various security mechanisms to create a robust defense against cyber threats, aiming to reduce the likelihood of successful attacks and minimize their impact.
In addition to the capabilities above, OCI offers a multitude of capabilities enable your defense in depth strategy:
- Zero Trust Model: OCI operates under a zero-trust model, meaning that no user or device is inherently trusted. Access to resources is granted based on verified identities and strict adherence to least-privilege policies and is always controlled by the customer.
- IAM and Security Zones: OCI offers robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) capabilities, including fine-grained access control, multi-factor authentication, integration with your IDPs, and Security Zone policies that allow you to be confident that your resources comply with security principles and best practices related to encryption, network access, and so on.
- Always-on Encryption: Data stored in OCI is encrypted at rest by default, using technologies like Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), providing an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. Always-on encryption protects customer data at-rest and HTTPS-only public APIs.
- Security Posture Management with Cloud Guard: OCI Cloud Guard helps monitor the security posture of your OCI tenancy and provides alerts and optional automated responses to security issues. Detection of security weakness in resource configuration, and detection of risky activities performed by operators and end users.
- Maximum Security Zones (MSZ) enforce a highly secure and restrictive security policy around sensitive resources.
- Customer Control and Transparency: OCI provides customers with a high degree of control and visibility into their cloud environment, including the ability to isolate their applications and data, monitor activity, and audit actions. Oracle includes complete transparency to your tenancy and has teams of security experts on staff to help you on your journey.
- Comprehensive log data that can be integrated with your third party SIEM or analyzed directly in the OCI tenancy, allows you to audit and monitor actions on your resources, helping you to meet your audit requirements while reducing security and operational risk.
- Data Safe: Oracle Data Safe is a fully integrated Cloud service focused on the security of your data. It provides a complete and integrated set of features for protecting sensitive and regulated data in Oracle Cloud databases. Features include Security Assessment, User Assessment, Data Discovery, Data Masking, Activity Auditing, Alerts, and SQL Firewall.
- Integrated Security Services: OCI offers a range of integrated security services, many of which are included at no additional cost, to help customers manage their security posture, detect threats, and respond to incidents.
- Defensive Security Team: OCI has a dedicated team of security experts who monitor and respond to threats within the OCI service enclaves.
- Oracle Assurance Practices provide rigorous internal processes and use of effective security controls in all phases of cloud service development and operation.
OCI benefits from tiered defenses and highly secure operations that span all layers in the infrastructure stack, from physical hardware to the web layer, in addition to the protections and controls available in our cloud.
Many of these protections also work with third-party clouds and on-premises solutions to help secure modern enterprise workloads and data where they reside. Meeting customers where they are at on their journey is important to us, managing your cloud should be a simple task that you can integrate into your current environment.
Oracle is a leader in cloud
Oracle practices strict adherence to over 81 security standards through third-party audits, certifications, and attestations, and can help customers demonstrate compliance readiness to internal security and compliance teams, and to their customers, auditors, and regulators. Additionally, we meet you where you are on your journey through support of third-party software solutions for protecting customer data and resources in the cloud, while enabling your security teams to maintain their single pane of glass.
What’s more Oracle has been identified as a leader in cloud by several independent assessments including IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Public Cloud Infrastructure as a Service 2025 Vendor Assessment, and 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Strategic Cloud Platform Services, who said Oracle is the only Hyperscaler capable of delivering more than 150 AI and cloud services across public, dedicated, and hybrid cloud environments, anywhere in the world.
Conclusion
All Oracle Cloud Infrastructure security capabilities have been designed with one goal in mind: allowing you to run your mission-critical workloads in the cloud with complete control and confidence, without sacrificing security. Oracle continues to invest in these areas and more to offer unmatched security and assurance to enterprise customers.
References
To learn more visit us at the following links
- For a general overview of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure security concepts, see Security Overview.
- For an overview of the security services in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, see Security Services.
- For an overview of the security capabilities in core services like Compute, Networking, and Block Volume, see Security for Core Services.
- For general recommendations on getting started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure security, see Securing Your Tenancy.
- For service-specific best practices and policy examples, see Security Best Practices.
Connect with us
Call +1.800.ORACLE1 or visit oracle.com. Outside North America, find your local office at: oracle.com/contact.
Copyright © 2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates. This document is provided for information purposes only, and the contents hereof are subject to change without notice. This document is not warranted to be error-free, nor subject to any other warranties or conditions, whether expressed orally or implied in law, including implied warranties and conditions of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. We specifically disclaim any liability with respect to this document, and no contractual obligations are formed either directly or indirectly by this document. This document may not be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without our prior written permission.
Oracle, Java, MySQL, and NetSuite are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.



