Introduction
Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) acts as a powerful bridge between HTTPS and your Oracle Database. It enables secure access to your data through RESTful APIs and supports features like SQL Developer Web, PL/SQL Gateway, SODA for REST, and the Database Management REST API.
With the release of ORDS 23.3, support for JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) was introduced. This allows ORDS to delegate authentication and authorization to any OAuth 2.0-compliant identity provider (IdP). ORDS validates the JWT access token and grants access to protected resources accordingly.
ORDS supports two mechanisms for JWT-based authentication and authorization:
Scope-Based Access Control (introduced in 23.3) – With scope based access control, the scope (or scp) claims of a valid JWT that is considered as the list of ORDS privileges consented to be used by the application on behalf of a user. The ORDS privilege protecting the resource must match with one of the JWT scopes.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) (introduced in 25.1) – With role based access control, a claim of a valid JWT can provide an array of roles granted to the user, considered as the list of ORDS user roles. The ORDS privilege protecting the resource must be granted to an ORDS role that matches with one of the JWT roles.
Note: An ORDS JWT profile can support either scope-based or role-based access control—not both.
If you haven’t yet explored scope-based access control, check out my earlier tutorial: Securing ORDS with OCI IAM – Scope Based Access Control
In this blog, we’ll focus on RBAC, and how you can protect your ORDS endpoints behind OCI API Gateway using this mechanism.
Note: This blog refers to the preconfigured and fully managed ORDS that comes with Autonomous Database (ADB) Serverless.If you haven’t already set up the environment—enabled ORDS for your database schema, defined RESTful APIs, and created Confidential Applications of type “Resource Server” and “Client” in your IAM domain—refer to this tutorial.It covers everything you need to get started, from setting the right audience and scopes to securing your APIs end-to-end—a necessary foundation regardless of whether you implement scope-based access control or RBAC, as shown in this blog.
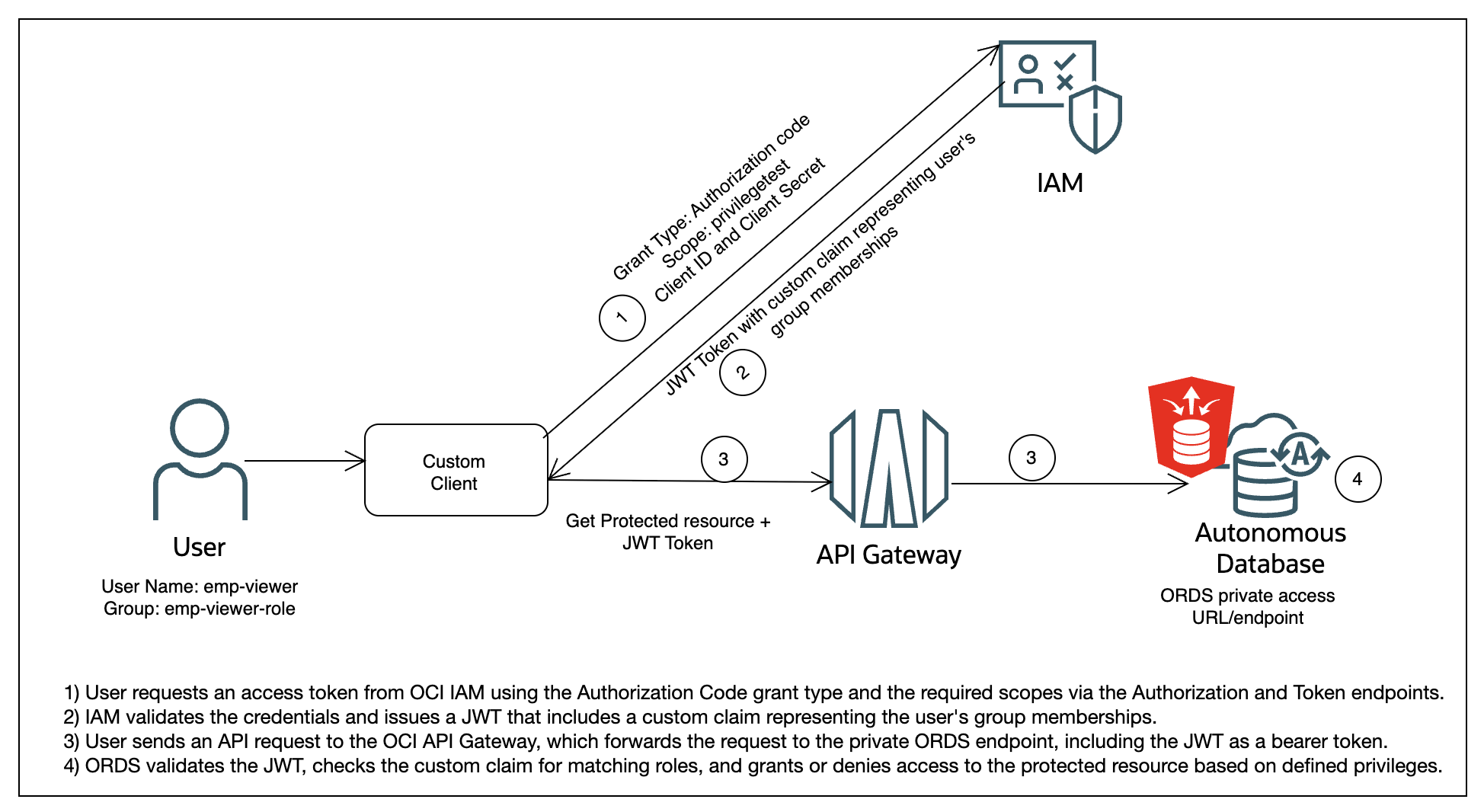
The following image shows the high-level representation of the solution architecture.
What is Role-Based Access Control in ORDS?
With RBAC, a JWT issued by the identity provider includes a custom claim that lists the user’s roles (usually mapped to groups). ORDS evaluates this claim to determine whether the user should be granted access to a resource.
To implement RBAC in ORDS using OCI IAM:
1. Create a custom claim in OCI IAM that represents the user’s group membership.
2. Configure the JWT profile in ORDS to reference this claim.
3. Match the roles defined in ORDS with the IAM group names.
4. Protect your ORDS module using the appropriate privileges and roles.
Step-by-Step: Implementing RBAC with ORDS and OCI IAM
1. Create a Custom Claim in OCI IAM
In your OCI IAM domain, define a custom claim (e.g., /iam_group) that maps to the groups assigned to the user. This claim will appear in the JWT issued to the user.
For example, if a user belongs to the IAM group emp-viewer-role, this group name will be added as a value in the custom claim in the JWT.
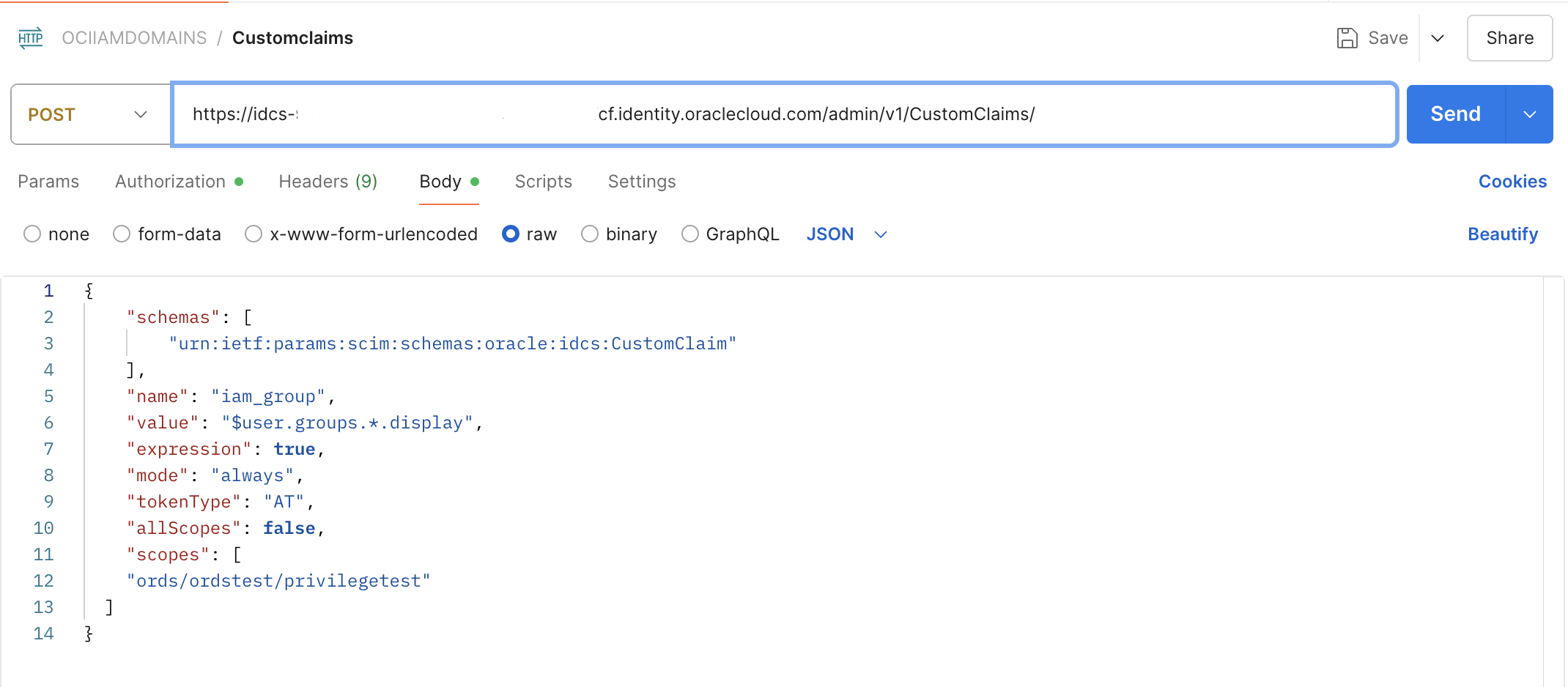
Generate an Access Token by following this Tutorial and use it to send a Post request to the IAM domain custom claim endpoint to create custom claim.
{
"schemas": [
"urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:oracle:idcs:CustomClaim"
],
"name": "iam_group",
"value": "$user.groups.*.display",
"expression": true,
"mode": "always",
"tokenType": "AT",
"allScopes": false,
"scopes": [
"ords/ordstest/privilegetest"
]
}
2. Configure the JWT Profile in ORDS
Use the following PL/SQL block to create a JWT profile in ORDS that points to the IAM issuer and identifies the custom role claim.
BEGIN
OAUTH_ADMIN.DELETE_JWT_PROFILE(p_schema => 'ordstest');
OAUTH_ADMIN.CREATE_JWT_PROFILE(
p_schema => 'ordstest',
p_issuer => 'https://idcs-123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvw.identity.oraclecloud.com',
p_audience => 'ords/ordstest/',
p_jwk_url => 'https://idcs-123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvw.identity.oraclecloud.com:443/admin/v1/SigningCert/jwk',
p_role_claim_name => '/iam_group'
);
COMMIT;
END;
/
3. Create a Matching Role in ORDS
If your user is in a group named emp-viewer-role, create an ORDS role with the same name.
BEGIN
ORDS_ADMIN.CREATE_ROLE(
P_Schema => 'ordstest',
P_ROLE_NAME => 'emp-viewer-role'
);
COMMIT;
END;
4. Assign the Role to an ORDS Privilege
Use the following code to associate your ORDS role with a privilege protecting the resource.
DECLARE
L_PRIV_ROLES owa.vc_arr;
L_PRIV_PATTERNS owa.vc_arr;
L_PRIV_MODULES owa.vc_arr;
BEGIN
L_PRIV_ROLES(1) := 'emp-viewer-role';
ORDS.DEFINE_PRIVILEGE(
P_PRIVILEGE_NAME => 'privilegetest',
P_ROLES => L_PRIV_ROLES,
P_PATTERNS => L_PRIV_PATTERNS,
P_MODULES => L_PRIV_MODULES,
P_LABEL => 'privilegetest',
P_DESCRIPTION => 'privilegetest',
P_COMMENTS => 'privilegetest'
);
COMMIT;
END;
5. Generate and Test access using JWT
Create a user (e.g., emp-viewer) and assign them to the IAM group emp-viewer-role. Then, configure the Client Confidential Application in IAM domain to use the Authorization Code grant type.
Note: This blog uses the Authorization Code Flow grant type. You may choose a different grant type based on your application’s requirements and security model.
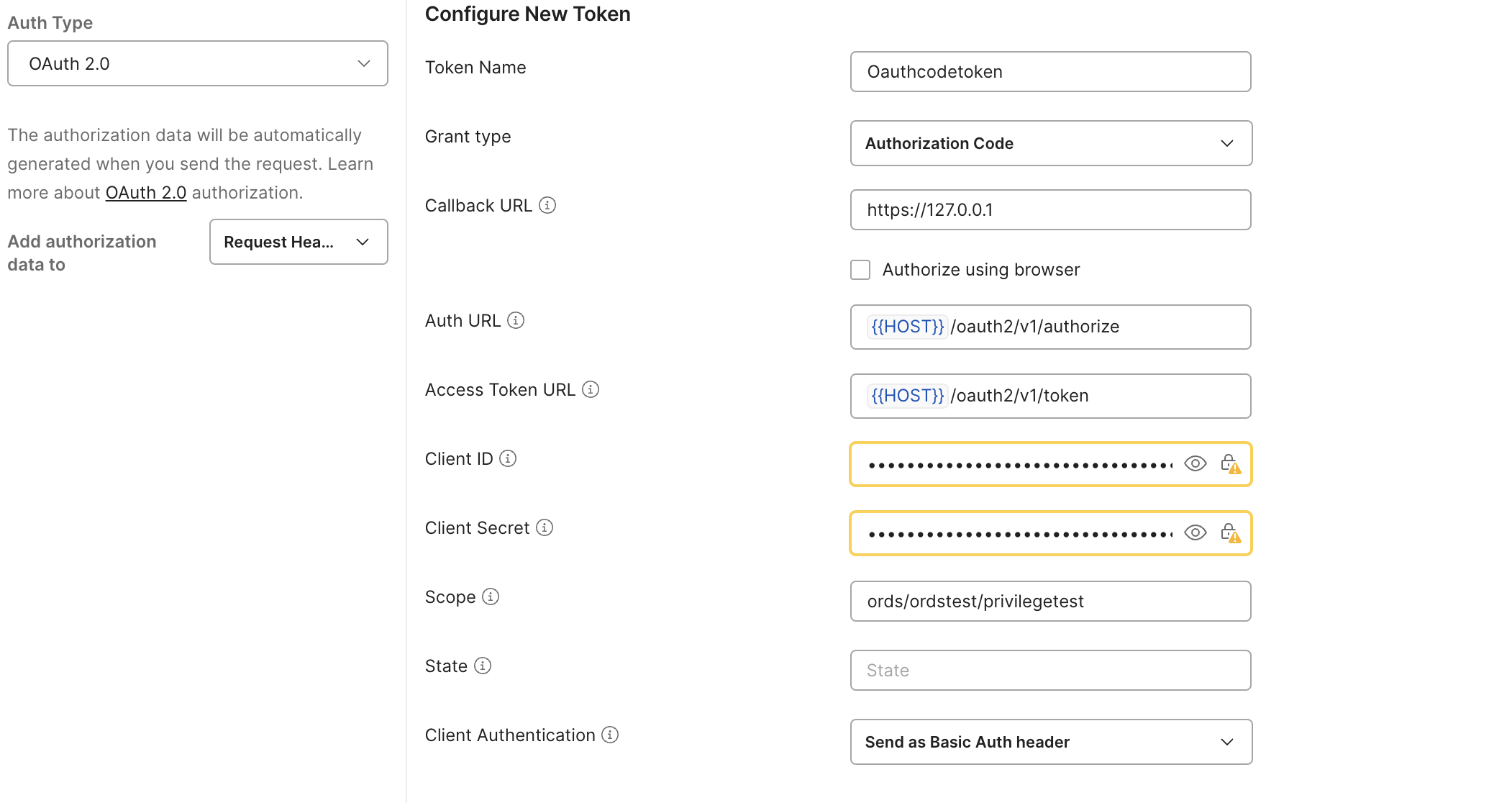
The user can obtain an access token by sending requests to the IAM domain’s authorization and token endpoints using Postman with the Authorization Code grant type, as shown below.
Inspect the token to confirm the presence of the custom claim (e.g., /iam_group: [“emp-viewer-role”]).
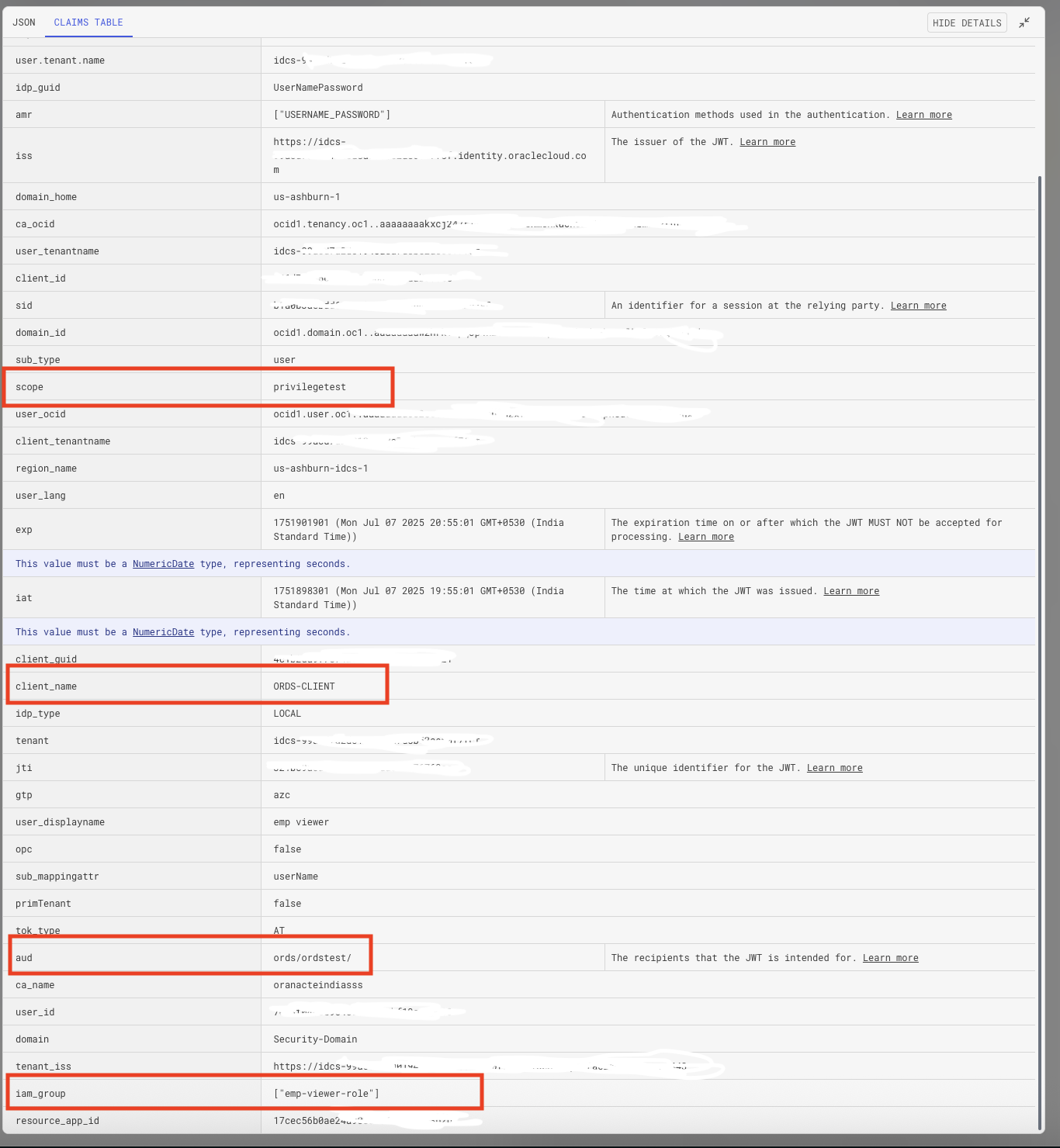
Now, when the user makes a request to the protected ORDS module using the JWT bearer token, ORDS will validate the token and grant access if the role matches.
Exposing ORDS Securely via API Gateway
Autonomous Database (ADB) Serverless can be configured with either public or private access during provisioning. When configured with public access, tools like APEX and ORDS are exposed via public URLs, accessible over the internet.
For enhanced security, you can choose to configure ADB with a private endpoint, which ensures that APEX and ORDS are accessible only through private access URLs. You can set up a private endpoint for ADB/ORDS by following this Oracle ADB’s Network Considerations blog.
To enable secure external access for ORDS in this setup, you can expose the private ORDS access URL through OCI API Gateway. This allows you to maintain private backend connectivity while providing controlled, authenticated access from outside your network.
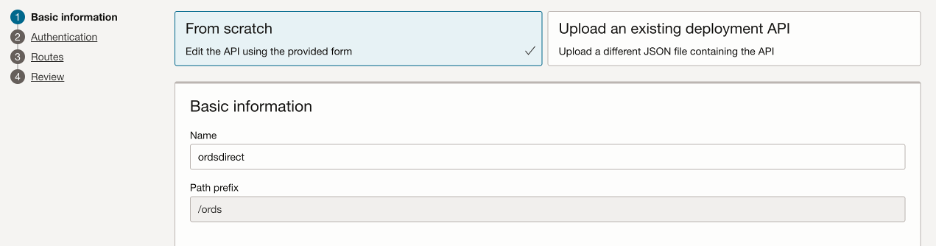
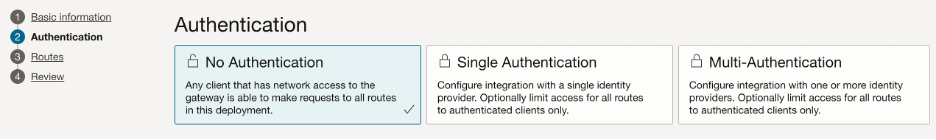
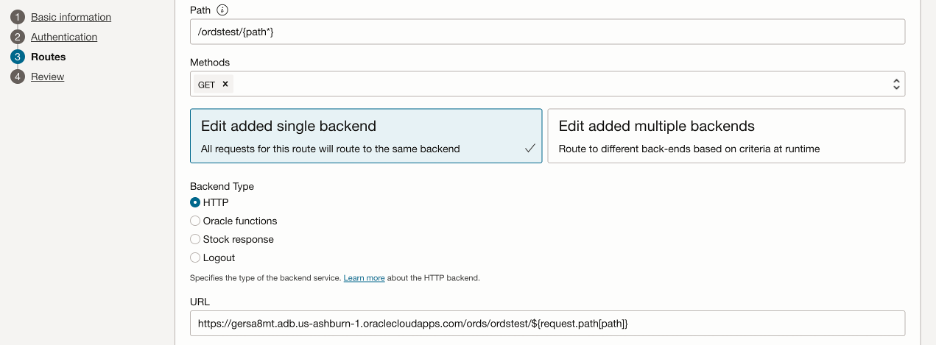
To proceed, create an API Gateway and then create and configure an API deployment to securely route requests to the ORDS private access URL or endpoint, as shown below.
Once configured, you can send requests directly to the API Gateway URL.
Final Thoughts
By leveraging RBAC in ORDS with OCI IAM, you simplify access control by aligning it with organizational roles and groups. Combining this with a secure API Gateway setup ensures robust, token-based protection for your Oracle RESTful services.