Background
In the first blog in this series, we explored how to use OCI native services and capabilities to protect your OCI tenancy against ransomware threats. We also referenced our CIS Secure Landing Zone that can assist you in deploying a tenancy that meets the CIS Foundations Benchmark for OCI and includes Oracle best practices around many of its services and introduced our Cyber Resilience Architecture.
The reality is that, despite our best efforts to protect our environments from compromise, determined attackers will eventually find their way in so we need to backstop protection with detection and implement capabilities to help us identify signs of malicious activity and signs that your environment has been compromised.
To recap, attacks unfold in three stages: Recon, Weaponize, & Deliver; Exploit & Control; and Execute & Maintain. As a defender, you have opportunities to thwart attacks at each stage. OCI provides several services and capabilities that can be leveraged to help Protect, Detect and Recover from ransomware attacks. These are included in the reference architecture shown below and are each discussed in more detail throughout the series.
In this blog we will discuss the OCI services and capabilities that fall under the Detect stage and that can be used to uncover these signs within your OCI tenancy.
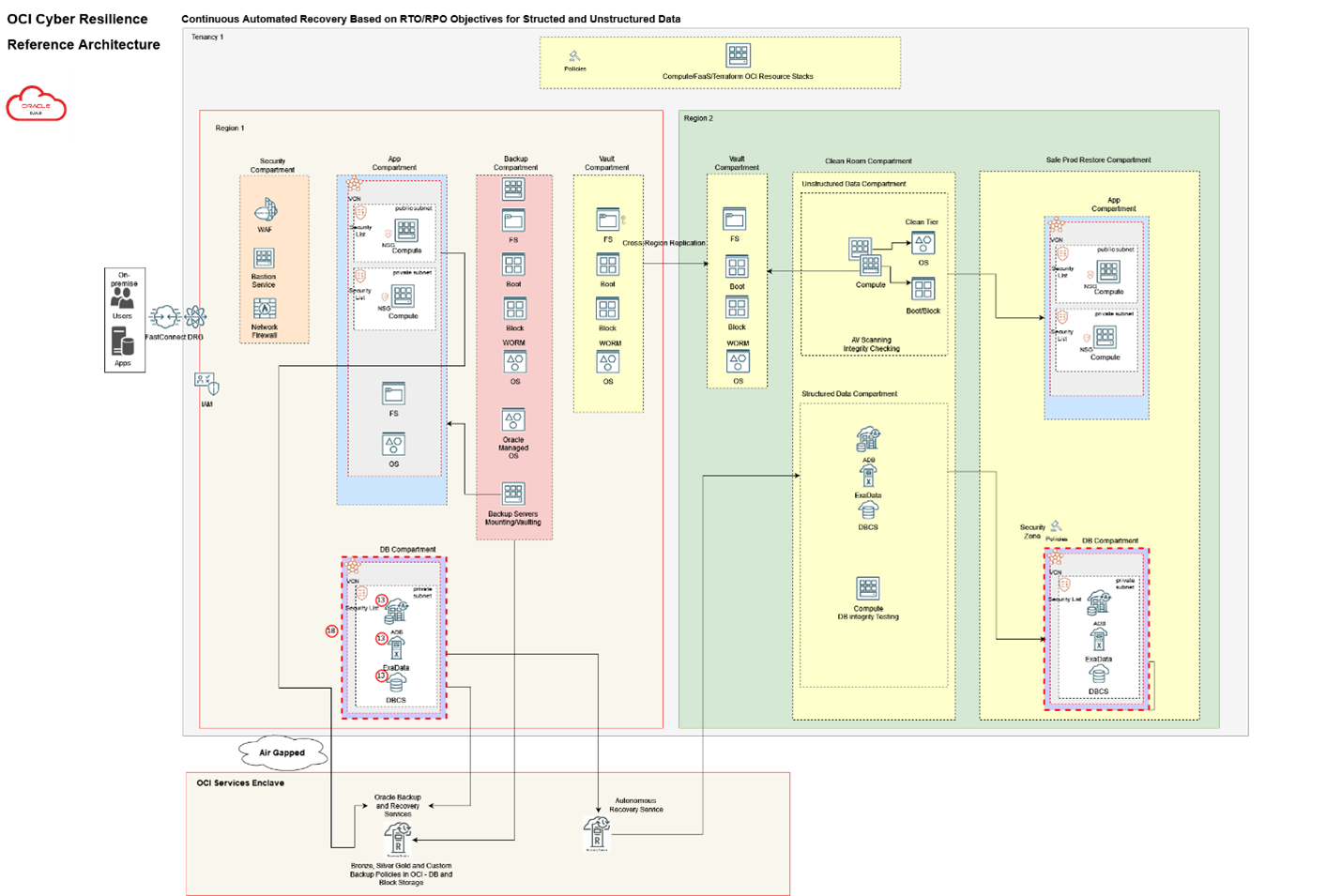
Your cloud environment is likely accessed via multiple methods; the most common of which is via APIs through automation. It is critical to have an immutable record of every action taken within your cloud environment to enable the forensic analysis of attacks including ransomware. In addition to this record, it is also critical to collect other logs from the tenancy including OCI service logs, VCN flow logs, OS logs, database access and activity logs, application logs and others depending on what is deployed within the tenancy. Finally, it is important to be able to collect, store and export these logs to your security analytics tooling for correlation and analysis like you perform for your other environments. This analysis helps you understand how attacks took place and provide you with valuable insight into how to make the changes necessary to help prevent future attacks. OCI provides several services and capabilities to facilitate this process that we will explore through the remainder of this post.
Loggings and Analytics
The foundation for log collection in OCI is the Logging service. The Logging service is a highly scalable and fully managed single pane of glass for all the logs in your tenancy. Logging provides access to logs from Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources. These logs include critical diagnostic information that describes how resources are performing and being accessed. There are three kinds of logs:
Audit logs: Logs related to events emitted by the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Audit service. These logs are available from the Logging Audit page or are searchable on the Search page alongside the rest of your logs. The Audit service logs all actions taken within your tenancy whether via the console, command line or API. The contents of the Audit log are not directly available and cannot be altered or deleted. The audit log can be searched from the console and entries can be turned into Events that can then be sent via the Notifications service to your security teams.
Service logs: Emitted by OCI native services, such as API Gateway, Events, Functions, Load Balancer, Object Storage, and VCN Flow Logs. Each of these supported services has pre-defined logging categories that you can enable or disable on your respective resources.
Custom logs: Logs that contain diagnostic information from custom applications, other cloud providers, or an on-premises environment. Custom logs can be ingested through the API, or by configuring the Unified Monitoring Agent. You can configure an OCI compute instance/resource to directly upload Custom Logs through the Unified Monitoring Agent. Custom logs are supported in both a virtual machine and bare metal scenario.
Logs are indexed in the system, and searchable through the Console, API, and CLI. You can view and search logs on the Logging Search page. When searching logs, you can correlate across many logs simultaneously. For example, you can view results from multiple logs, multiple log groups, or even an entire compartment with one query. You can filter, aggregate, and visualize your logs.
All logs are encrypted in-flight and at rest and are also when they are archived or transferred to storage such as object storage. Logging integrates with the Service Connector Hub which can be used to forward logs to object storage for longer/archive storage, or to the Streaming service for ingestion by your SIEM and other security analytics tooling.
If you don’t have a SIEM and want to be able to perform analytics on your logs, you should consider using the OCI Logging Analytics service. Oracle Logging Analytics is an OCI native solution that lets you index, enrich, aggregate, explore, search, analyze, correlate, visualize and monitor all log data from your applications and system infrastructure on cloud or on-premises. The service provides multiple ways of gaining operational insights from your logs. You can:
- Use the log explorer UI
- Aggregate log information into dashboards
- Utilize the APIs to ingest and analyze data
- Integrate with other Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services
The interactive visualizations provide several possibilities to slice and dice the data. Use the Cluster feature to reduce millions of log entries down to a small set of interesting log signatures, making it easy for you to review. The Link feature enables you to analyze logs in a transaction or identify anomalous patterns using the grouped view.
Security Posture Management
While logging is an important control to understanding what is occurring within your environment, it only provides disparate data points about the activity within it. Having the ability to obtain contextual information about the potential threats you are facing is critical to being able to protect your environment from ransomware and other threats. Traditional SIEM platforms provide the correlation and analysis that many security operations teams rely on for this, but these systems can be difficult and expensive to implement and maintain. OCI has built a cloud native service that addresses many of the capabilities of these solutions.
Cloud Guard is a cloud-native service that helps customers monitor, identify, achieve, and maintain a strong security posture on OCI. Use the service to examine your resources for security weakness related to configuration, and your operators and users for risky activities. Upon detection, Cloud Guard can suggest, assist, or take corrective actions, based on your configuration.
Cloud Guard distills the audit log and configuration information into actionable security related events; reducing the number of raw events that you would normally have to sift through. These events can be actioned within the Cloud Guard console and forwarded to the Streaming service for further forwarding to your SIEM.
Cloud Guard Threat Detector
This detector automatically triages user behaviors using machine learning, data science, and threat intelligence to reduce alert noise. It uses Oracle’s threat intelligence data, monitors targeted behavior models aligned with MITRE ATT&CK techniques, and applies data science to help discover compromised environments quickly. It takes advantage of known attacker behaviors and motivations to identify threat markers and then combines those markers into a scoring algorithm based on attack progression.
Threat Detector also analyzes OCI administrators’ actions using machine learning (ML) and other techniques to help alert security operators of rogue users—someone whose credentials have been stolen or their allegiance compromised.
Log Insight Detector
Cloud Guard Log Insight Detector, using an Insight detector recipe, enables customers to compose custom detection rules using the flexible query language from the OCI Logging service. These custom rules support searching of and correlation across security signals in Logging service data. Search covers multiple log sources, such as Audit logs, Application logs, Fusion Apps logs, and other custom logs. When configured thresholds are met, the Logging service sends alerts to Cloud Guard. Those alerts then appear in Cloud Guard as problems.
Cloud Guard Fusion Applications Detector
Oracle Cloud Guard Fusion Applications Detector helps customers monitor and alert on potential security issues in Oracle Cloud HCM and Oracle Cloud ERP. It provides pre-configured recipes that trigger on changes to sensitive resources in your Fusion Application environment. For example, recipes are triggered by changes to user privileges that may impact access to sensitive data or activities, such as adding, deleting, or modifying sensitive data or functional approval privileges for roles and users. These changes may be particularly sensitive for regulated customers.
Early identification and alerting of sensitive actions that may be related to fraudulent activities is vital to reduce risk to organizations. Oracle Cloud Guard Fusion Applications Detector enables the creation of alerts based on change events to sensitive Fusion objects. For example, you can create alerts notifying administrators when there are changes to an ERP admin and bank account details or when there are modifications to an HCM user’s salary or benefits.
Database Security
Databases are the primary target of most ransomware attacks since they typically contain the information most important to the operation of your organization. Having real time insight into the security posture of your databases is critical to protecting them from ransomware and other attacks.
Data Safe is a unified control center for your Oracle databases which helps you understand the sensitivity of your data, evaluate risks to data, mask sensitive data, implement and monitor security controls, assess user security, monitor user activity, and address data security compliance requirements.
Data Safe provides the following set of features for protecting sensitive and regulated data in Oracle databases, all in a single, easy-to-use management console: Security Assessment; User Assessment; Activity Auditing; Data Discovery; and Data masking.
Events & Notifications
Events enables you to create automation based on the state changes of resources throughout your tenancy. OCI services emit events, which are structured messages that indicate changes in resources.
You work with events by creating rules. Rules include a filter you define to specify events produced by the resources in your tenancy. Rules must also specify an action to trigger when the filter finds a matching event. Actions are responses you define for event matches. When the filter in the rule finds a match, the Events service delivers the matching event to one or more of the destinations you identified in the rule. Destination services for events are Notifications, Streaming and Functions. For purposes of this blog, we will cover the Notifications service.
Notifications let you know when something happens with your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Using alarms, event rules, and service connectors, you can get human-readable messages through supported endpoints, including email and text messages (SMS). You can also automate tasks through custom HTTPS endpoints and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Functions. You can also directly publish messages.
The Audit, Logging, Cloud Guard and Data Safe services are all integrated with both Events and Notifications; allowing you to notify your operations and security teams of security related issues that arise in your tenancy.
Conclusion
The assumption is that determined attackers will eventually find their way into your environment, so you need to be prepared to detect the signs as quickly as possible to hopefully stop any attacks before they cause significant damage. As discussed above, OCI has several services that provide a broad array of abilities to detect potentially malicious behavior and other indicators of compromise. Our robust logging, security posture management and database security tools integrated with the events and notifications services provide you with a strong foundation to detect the signs of compromise early so you can take action to stop the attackers in their tracks.
We’ve now covered both protection against and detection of ransomware and other type attacks. The final blog in the series will detail how OCI can help you prepare for a recover from a successful ransomware attack. This will include discussions of data immutability, secure backups and full cycle testing and recovery, so stay tuned. (See Recovery from ransomware Style Threats).
