Introduction
Oracle Cloud Applications Suite is the complete cloud applications suite that brings consistent processes and a single source of truth across the business functions—from enterprise resource planning, supply chain management, and human capital management to advertising and customer experience. Oracle Fusion Applications Suite uses a unified data model across all application modules (ERP, SCM, HCM, CX (Sales, Service)).
Several A-Team blogs that provide architectural guidelines, sample code, best practices, and architectural guidelines are available. The purpose of this blog is to provide a consolidated view of key A-Team blogs related to the Fusion Cloud Applications implementation process.
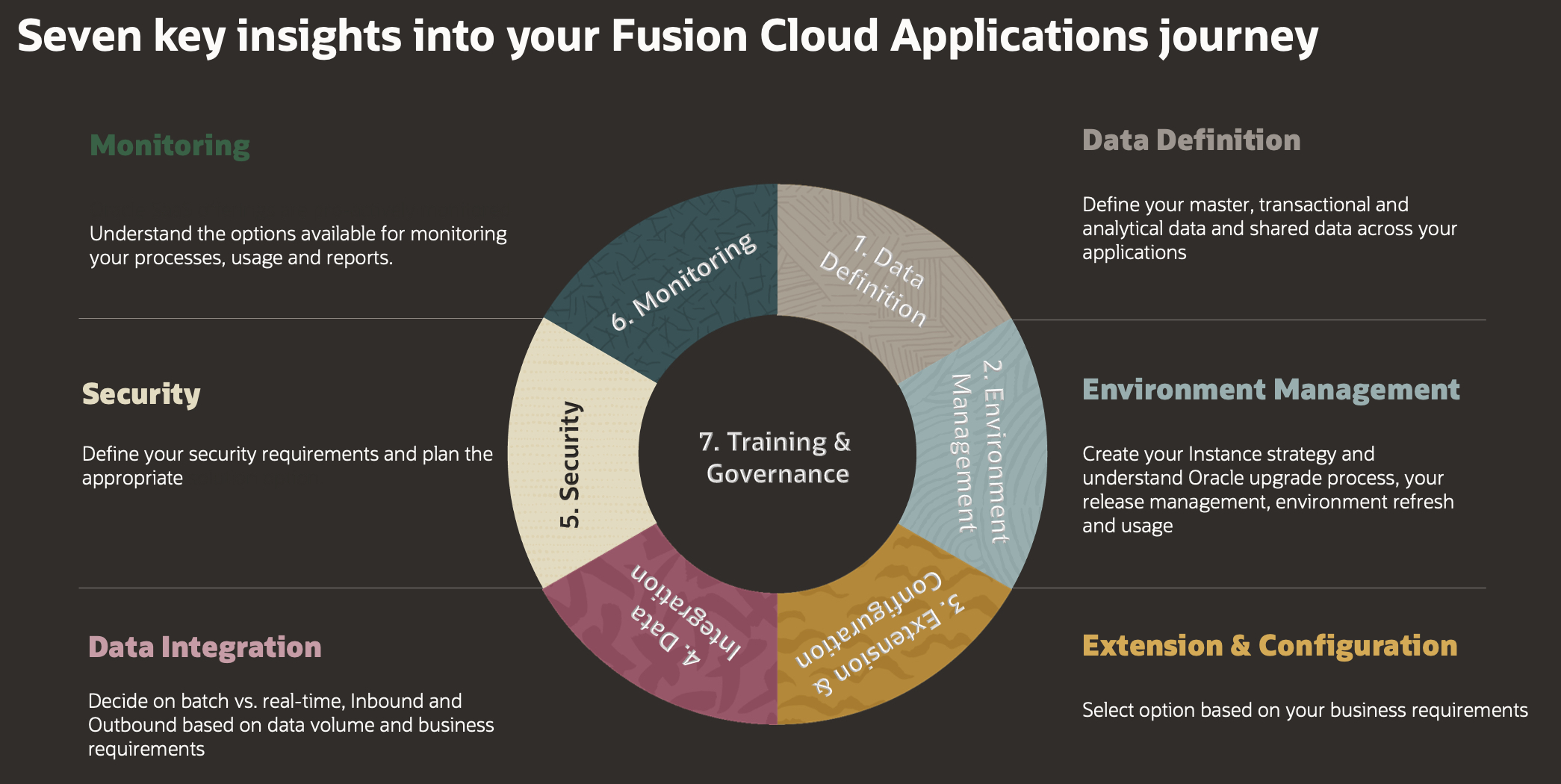
Seven key insights into your Fusion Cloud Applications implementation journey:
- Data Definition
- Environment Management
- Extension & Configuration
- Data Integration
- Security
- Monitoring
- Training & Governance
It is recommended that your architects and team become familiar with the terminology and solution sets during the early stages of the project. While blog will provide you with a strong understanding of the seven focus areas, I recommend referring to the standard documentation for details.
1. Data Definition
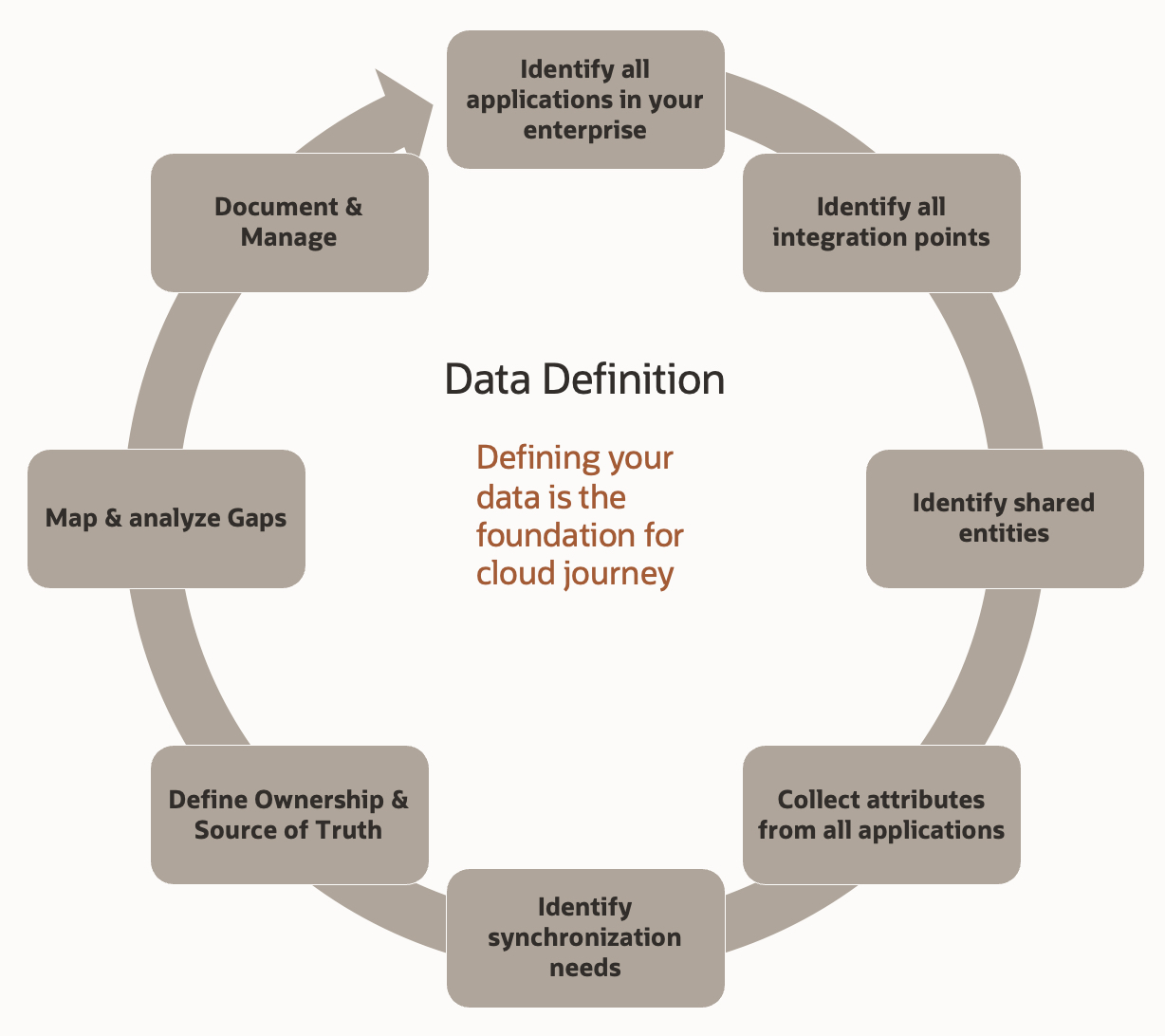
Data definition and mapping are the foundation for your successful cloud journey. Designing your enterprise structures and objects plays a vital role that helps in defining your entities and attributes to support your business processes. Identifying and defining ownership at the initial stage is the most critical success factor in your cloud journey. Plan your integrations, conversions, operations, reporting, and compliance requirements during data definition. Along with your data definition and mapping from your legacy applications, you should also understand the terminologies within Fusion Cloud Applications across modules. Your time and effort in defining your data and mapping will enable a smooth cloud transformation journey.
Suggested approach for data definition:
- Define & map your objects and attributes to standard objects & attributes in Fusion Cloud Applications across all your line of businesses and avoid creating from scratch.
- Start with standard core objects & attributes required for your business processes and expand to module-specific transactional, analytical, and operational objects. For example, customer, product, supplier, employees, and financial master data, such as charts of accounts, and cost centers are the core objects for any business operations.
- Analyze & arrive at core objects and attributes from your legacy systems. During your gap analysis, you may find attributes from your legacy applications to be created in Fusion Cloud Applications. Do not simply create extensions because you had them in your legacy applications; instead, conduct a thorough data analysis and define how you are going to use that extension in your business processes. Adding more custom fields could increase your cost of implementation significantly.
Key Reference Blogs:
- Best Practices to Model Prospects, Customers, Suppliers, Partners in an Oracle Fusion Cloud Implementation
- Best Practices to Model Customer, Supplier, and Partner Hierarchies in Oracle Fusion Cloud.
- Learn How to Be the Best at Fusion Cloud Applications multi-pillar implementation
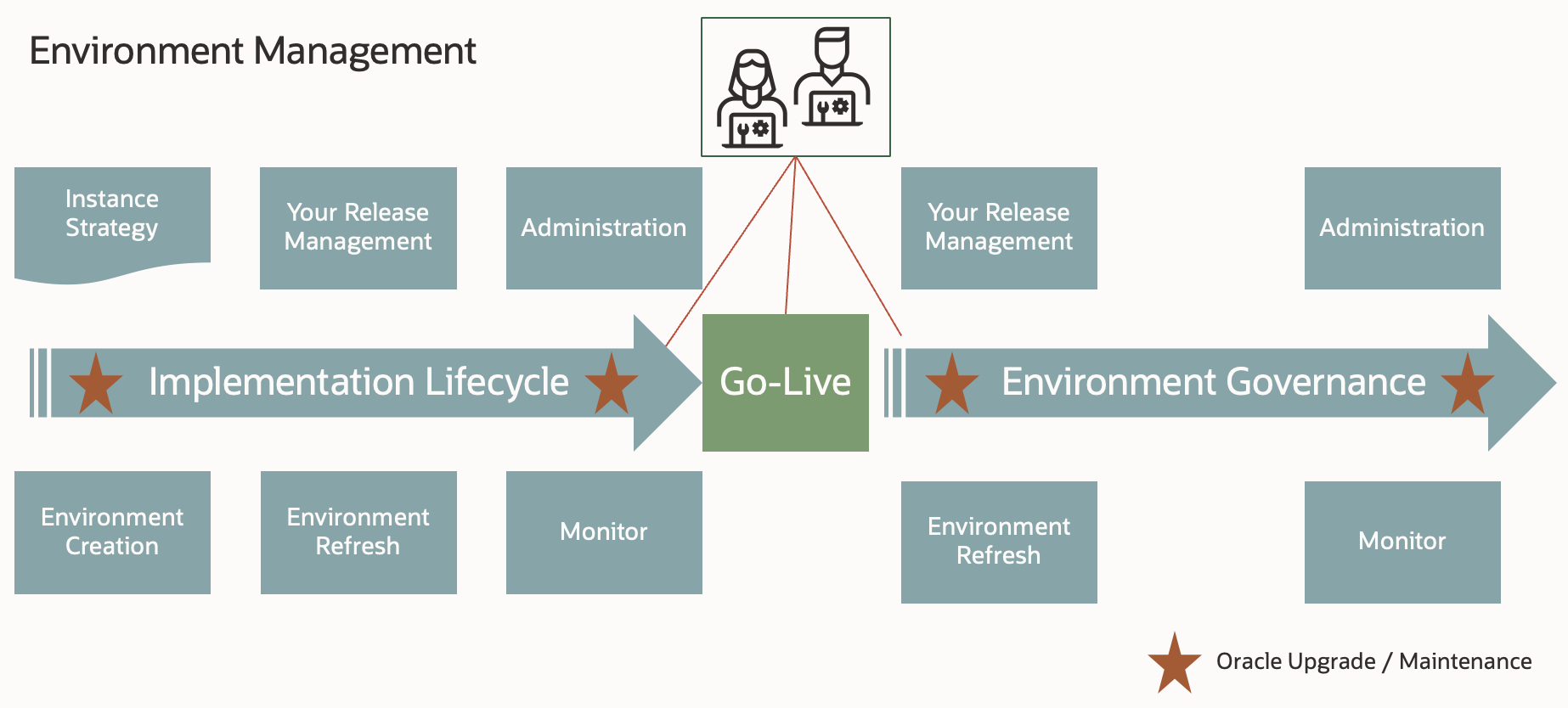
2. Environment Management
Environment lifecycle and management planning tasks are crucial for the success of your project. The Oracle Cloud Console provides self-service management of the environments where you provision, run, and maintain your Fusion Applications. When you subscribe to Fusion Applications, you are allotted one production environment and one test environment. You also have the option of purchasing development environments.
Define your environment strategy and instance management tasks early in your implementation planning. When you are planning to implement multiple pillars and applications, plan your environment lifecycle management including quarterly updates, cross-project teams’ coordination, and maintenance schedules.
The number of environments could significantly increase the complexity of the project tasks including code environment refreshes, migration, automation, testing, and governance.
There are two aspects of environment management.
- Environment management during implementation.
- Governance after going live.
Key Reference Blogs:
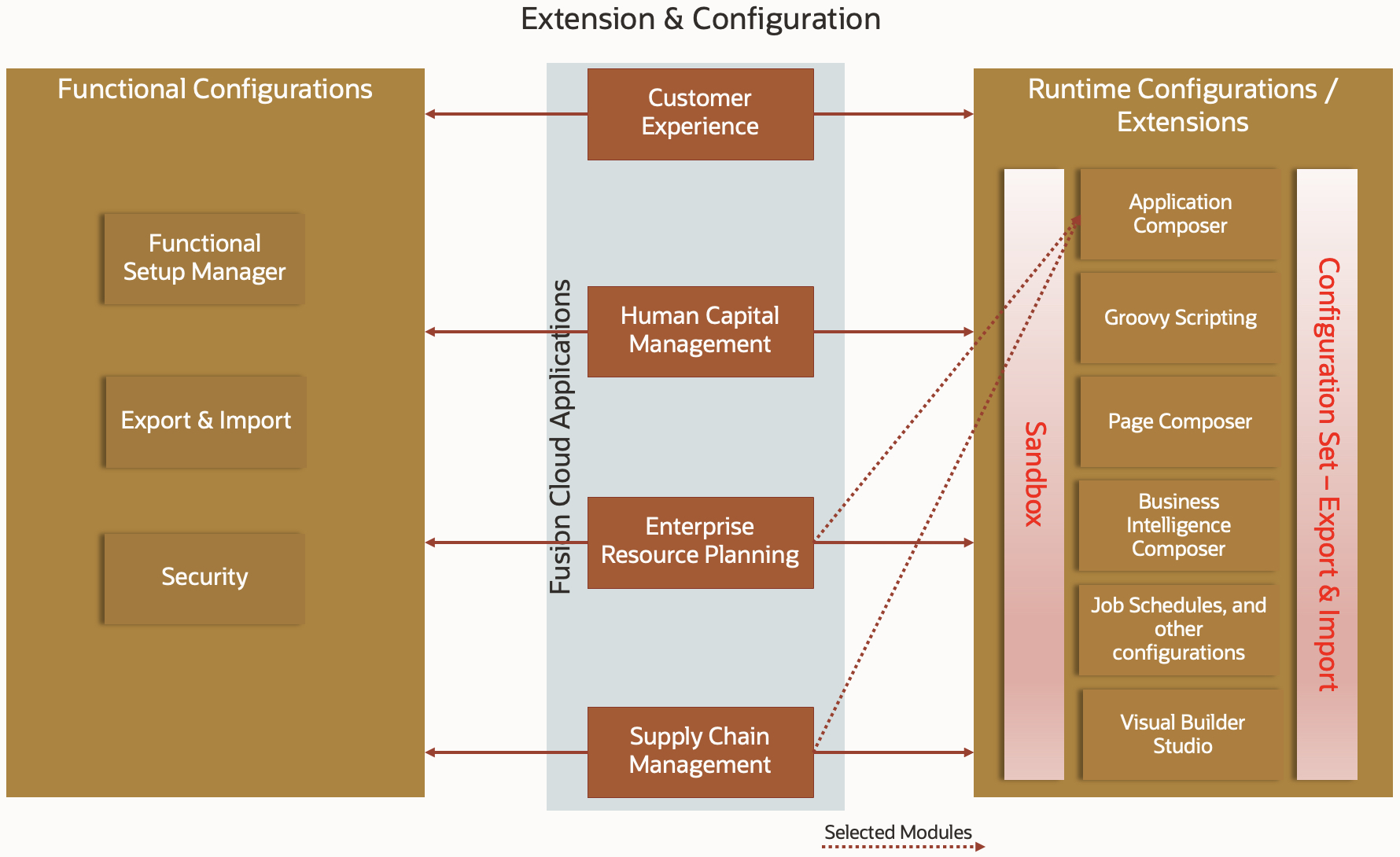
3. Extension & Configuration
Fusion cloud applications provide robust functionality by default that supports most of the business needs an organization may have. Nevertheless, you can still make changes to your application to suit your individual business needs.
You can configure and extend the application using browser-based composers and other tools.
Key Reference Blogs:
- Best Practices for configuring & extending Fusion Cloud Applications
- Extend Fusion Cloud Applications cross-pillar data using VB Studio
- Extending Oracle Fusion SaaS – Best Practices
- Introducing the Scheduler REST API and guidelines for monitoring scheduled processes in Fusion Cloud Applications
4. Data Integration
Fusion cloud applications provide purpose-built utilities and services to integrate between your source and target applications. Both batch and near real-time integrations are supported. You can import data into or export data out of the applications. Depending on your business requirements you can explore and choose between synchronization vs. federation, batch vs. real-time and appropriate solution/tool options. Plan your project with tasks to support data validation and data conflict resolution. The iterative approach is recommended for all your data integration development. Consider your historical data migration and options thoroughly, as it might significantly increase the data integration complexity.
You can leverage Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) services to orchestrate and automate your integrations.
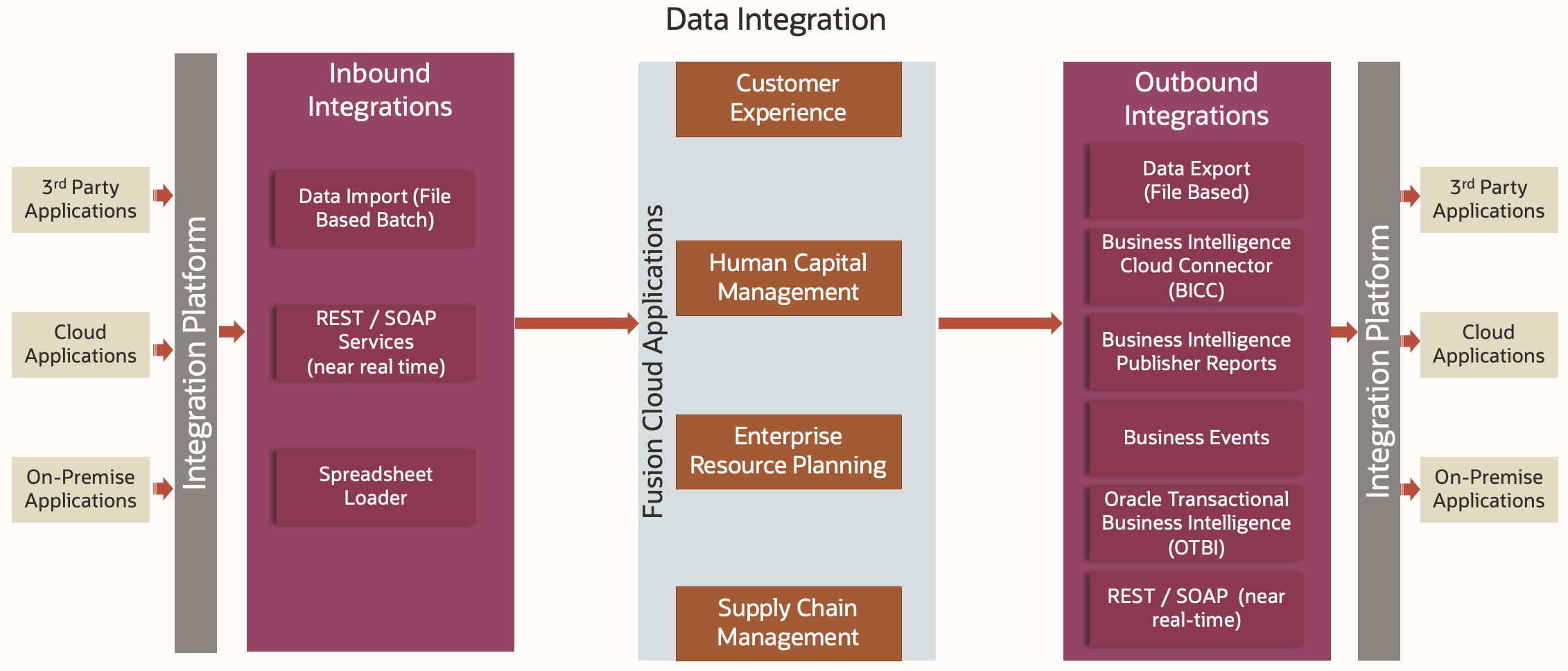
Key Reference Blogs:
- Migrating clean data options
- Data Extraction Options
- Data Import Options and Guidelines for Fusion Cloud Applications
- Using Synchronous BIP for Extracting Data? Don’t
- Performance implications of Synchronous and Asynchronous patterns in large enterprise Oracle Integration Cloud implementations with SaaS Applications
- Asynchronous Webservices in Fusion ERP and SCM
- Oracle Cloud HCM Integration Using Oracle PaaS – Patterns & Use Cases
- A Simple Guide to ERP Cloud Customer Creation through integration
- Using OCI DI and Functions for Fusion SaaS data load
- Efficient File Handler Pattern with OIC Scheduler for SaaS Integration
5. Security
Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications suite was developed with a primary focus on security. Use the Security Console to manage application security in your Oracle Applications Cloud service for role management, role analysis, user-account management, and certificate management.
The key security focus areas to be considered is given below.

Key Reference Blogs:
- Securing Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Cloud Security: User Provisioning to Fusion Applications Cloud
- How to add multiple Identity Cloud Service (IDCS) instances as OAuth Authentication Providers to Oracle (Fusion) Cloud Applications
- Securing Oracle Fusion Cloud Supplier Portal with IAM Domains and MFA
- Securing Oracle Fusion Bill Management with IAM Domains
- Extending Oracle Fusion SaaS with OCI – Security
6. Monitoring
Application monitoring is a critical area every SaaS cloud customer should plan during the implementation. Application monitoring is a process of collecting relevant data to help your organization track/audit long-running jobs, application usage, and proactively identify potential jobs for tuning. Understanding the functionalities implemented within your Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications and defining monitoring governance will help your organization improve the user adoption of your deployed SaaS applications.

Key Reference Blogs:
- Five key Fusion Cloud Applications monitoring features for better user adoption
- Introducing the Scheduler REST API and guidelines for monitoring scheduled processes in Fusion Cloud Applications
7. Training & Governance
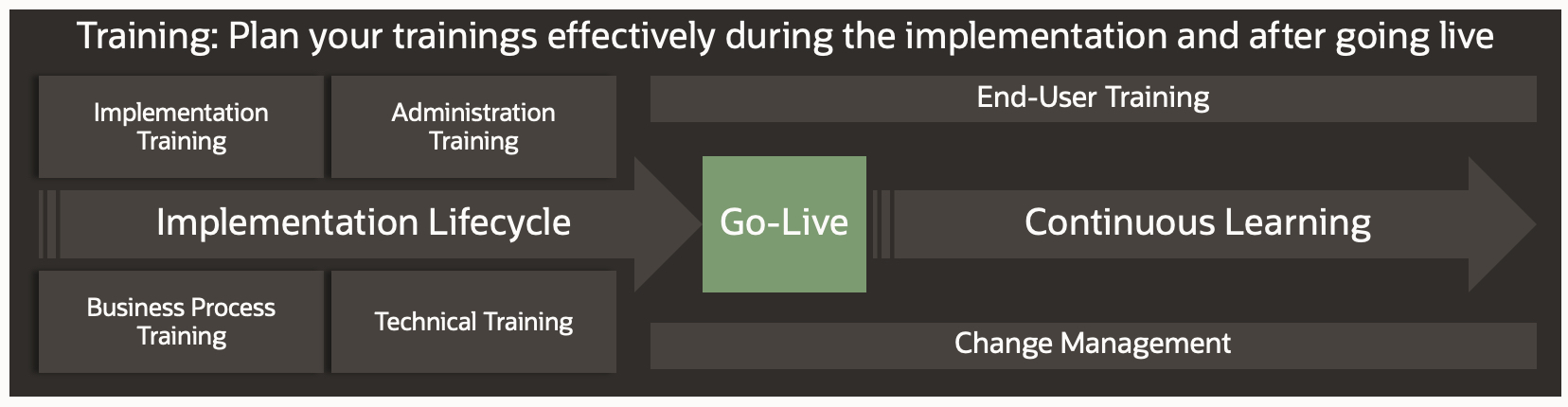
Training
One of the main activities in cloud transformation projects is training and governance. From my experience, this activity is often given a low priority, resulting in challenges and poor user adoption.
Oracle Guided Learning is included with every Fusion Cloud Application. Leverage the power of in-application guidance to support your implementation, end-user adoption, training, and use of Fusion Cloud Applications.
Governance
Cloud governance is a set of rules and processes that you create, monitor, and change so that you can control costs, improve efficiency, and eliminate security risks. Migrating to the cloud means you need to plan your policies around user adoption, monitoring, cross-pillar/teams collaboration, audit & compliance, and support processes. The governance model provides a structure to design and improve cloud user adoption.

In my opinion, ensuring tight coordination and communication between cross-project teams, and establishing guidelines for cross-team collaboration during Oracle upgrades & maintenance, and your project releases, are the two key success factors in establishing on-going governance model.
Conclusion
The purpose of this blog is to assist you in gaining a better understanding of the seven key insights into Oracle Fusion Cloud Application implementation and navigate to the detailed blogs related to each.
It is my sincere hope that this blog will help you get started quickly with Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications implementation.
